Cross reactivity of clinically validated anti
advertisement

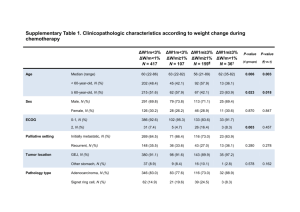
Cross reactivity of clinically validated anti-HER2 antibodies Schrohl A1, Pedersen HC2, Jensen SS2, Nielsen SL1, Brünner N1. 1 University of Copenhagen, Faculty of Life Sciences/Sino-Danish Breast Cancer Research Centre, Frederiksberg C, Denmark 2 Dako Denmark A/S, Glostrup, Denmark Background: Human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER-) 2 belongs to the family of epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFRs) with homology to HER1, HER3 and HER4. HER2 is overexpressed in approximately 20% of invasive human breast cancers (Wolff, Hammond et al. 2007). Over-expression of HER2 is associated with a poor prognosis; however, the protein can be targeted by anti-HER2 therapy (trastuzumab, Herceptin®) (Slamon, Leyland-Jones et al. 2001). Trastuzumab therapy is offered only to patients whose tumors over-express HER2 protein and/or show amplification of the HER2 gene. Accordingly, the expression level of HER2 protein and/or amplification of the HER2 gene are determined routinely in all newly diagnosed breast cancers. Essential to this testing of HER2 expression at the protein level is the availability of specific antibody-based test systems. Aim: The aim of the present study was to investigate the specificity of three clinically approved commercially available anti-HER2 antibodies towards members of the EGFR-family. Methods: We studied the antibody used in the Herceptest™ (Dako), the PATHWAY® antibody (Ventana Medical Systems, Inc.) and the Oracle™ antibody (Leica Microsystems). Antibody specificity was investigated by manually performed immunohistochemistry (IHC) and in competitive ELISAs. For IHC, Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells were transiently transfected with the intracellular domain of respectively HER1, HER2, HER3 and HER4 and all three antibodies were applied to sections of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) transfected cells. In ELISA, cross reactivity towards HER1 and HER4 was tested with peptides corresponding to the C-terminal part of HER1 and HER4. Results: In IHC experiments, all three antibodies stained cells transfected with HER2. Binding of the antibodies to HER2 was confirmed by competitive ELISA. However, in IHC experiments the PATHWAY® and the Oracle™ antibodies also stained cells transfected with HER4. Competitive ELISAs confirmed binding of the PATHWAY® antibody to HER4, whereas binding of the Oracle™ antibody to HER4 could not be confirmed in a competitive ELISA. None of the antibodies cross reacted with HER1 and HER3 homologous to the HER2 binding site of the antibodies. Conclusions: Two out of three clinically validated anti-HER2 antibodies were shown to cross react with HER4 in FFPE cells. As determination of HER2 over-expression and/or amplification guides therapy with trastuzumab, a valid test result by the use of specific antibodies is crucial to ensure proper personalized therapy with HER2-targeted therapy. These results warrant further investigation of anti-HER2 antibodies and of the procedures for clinical determination of HER2 protein expression. Abstract for SABCS 2010, Abstract No. 850345 Final Version References: Slamon, D. J., B. Leyland-Jones, et al. (2001). "Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2". Journal of Medicine 344(11): 783-792. Wolff, A. C., M. E. Hammond, et al. (2007). "American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Guideline Recommendations for Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer." J Clin Oncol 25(1): 118-145. Abstract for SABCS 2010, Abstract No. 850345 Final Version