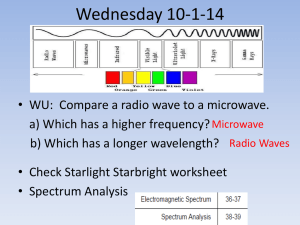
PHYSICS - Punakha HSS
advertisement

PHYSICS Paper-1 Three hours and a quarter (The first 15 minutes of the examination are for reading the paper only. Candidates must NOT start writing during this time) ……………………………………………………………………………………………… Answer ALL questions in Part I and NINE questions from Part II, choosing FOUR questions from section A, THREE questions from Section B and TWO questions from section C. All workings, including rough work, should be done on the same sheet as, adjacent to rest of the answer. The intended marks for questions are given in brackets [ ]. A list of physical constants is given in the end of the paper. ……………………………………………………………………………………………… Part I (40 marks) Answer all questions Question 1 (a) Each question is followed by four possible choices of answers. Choose the correct answer and write it on the answer booklet [10] (i). Two point charges (+e) and (–e) are kept inside a large metallic cube without touching its sides. Electric flux emerging out of the cube is: A. 𝝐 𝝐𝟎 𝝐 B. − C. D. 𝝐𝟎 zero 𝟐𝝐 𝝐𝟎 (ii) Which one of the following graphs represents variation of reactance ‘XC’ of a capacitor with frequency ‘f’ of an ac supply. (A) (B) XC XC f (C) f (D) XC XC f P.J. Sarma/Trial/XII Physics/2013 f Phss Page 1 of 8 (iii) When a charged particle is projected perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field, it describes a circular path in which: (A) Its speed remains constant (B) Its velocity remains constant (C) Its momentum remains constant. (D) Its kinetic energy increases. (iv) In Young’s double slit experiment, if sodium lamp is replaced by green light lamp, then the A B C D fringes will become brighter. fringes will become fainter. fringe width will increase. fringe width will decrease. (v) White light is passed through sodium vapours contained in a thin walled glass flask and the transmitted light is examined with the help of a spectrometer. The spectrum so obtained is: A B C D Absorption spectrum Solar spectrum Band spectrum Continuous spectrum (vi) Susceptibility is positive and large for a A ferromagnetic substance B non-magnetic substances C paramagnetic substance D diamagnetic substance (vii) Binding energy of a nucleus is of the order of: A B C D Electron volt (eV) Kilo electron volt (KeV) Mega electron volt (MeV) Joule (J) (viii) In which region of the electromagnetic spectrum lies the Lyman series of hydrogen? A B C D X-ray infrared visible ultraviolet (ix) The output of the two-input OR gate is 0 only when its A B C D either input is 1 either input is 0 both inputs are 1 both inputs are 0 P.J. Sarma/Trial/XII Physics/2013 Phss Page 2 of 8 (X) The rate of change of current 10 As-1 in a coil produces an e.m.f of 5 V. Then the Self inductance of the coil in henry is: A. 0.25 B. 0.5 C. 1 D. 1.25 (b) Choose the correct word/s given in the brackets and write them in your answer sheets. [6] (i) Critical temperature of a conductor is the temperature below which it’s ............. falls to zero and the conductor becomes a................ (capacity, resistivity, conductivity, resistor, superconductor). (ii) The amount of heat produced in a conductor due to a current flowing through it is ................... proportional to the square of.................. (inversely, directly,current, resistance). (iii) The p-type semiconductor is an.................... semiconductor obtained by adding a ...................... impurity. (extrinsic, intrinsic, trivalent, pentavalent). (iv) The combination of ............ and........... gate gives rise to NAND gate. (OR, NAND, AND, NOT). (v) The saturated photoelectric current depends upon....................while stopping voltage depends upon the ....................... of incident radiation. (intensity, wavelength, frequency, velocity). (vi) The wave particle duality of electromagnetic waves could be assured from.................. and..................... (Brewster’s law, polarization, Thomson’s experiment, photoelectric effect) (c) Match the items in column A with the items given in column B and rewrite the correct pairs in your answer sheet. Column A 1.Inductance 2.One atomic mass unit 3. Interference 4. Continuous spectrum 5. Characteristic curves 6. Bohr’s theory 7. Electric field 8. Spherical aberration [4]. Column B a. transistors b. object within focus c . 931MeV d. henry e. volt per meter f. wave nature of light g. varying fringe width h. stationary orbits i. plano-convex lens j. bi-convex lens k. x-ray P.J. Sarma/Trial/XII Physics/2013 Phss Page 3 of 8 (d) State True or False and give reason for the false statement. [4] (i) Prisms are preferred over plane mirrors in the construction of a periscope. (ii) The wavelength soft X-rays is smaller than that of the hard X- rays (iii) No photoelectrons are emitted if the incident radiation has a frequency less than a threshold frequency. (iv) The forbidden energy gap of carbon in diamond structure is 0.7 eV. (e) Answer the following questions briefly: [2x8 =16] (i) A radioactive nuclide ‘Z’ undergoes a series of decays according to the scheme, 𝛼 β α 𝛾 Z Z1 Z2 Z3 Z4 If the mass number and the atomic number of ‘Z’ are 180 and 72 respectively, what are the corresponding numbers for Z4? (ii) Write down the expressions for K.E and P.E of an electron in Bohr’s model. (iii) In Young’s double slit experiment with monochromatic light, how is fringe width affected if, (i) the separation of the slits is decreased (ii) the screen is moved closer to the slits. (iv) With the help of a labelled ray diagram, show the formation of a secondary rainbow. (v) An oil drop weighing 1.0 x 10-15 N and carrying a charge of 8 x 10-19C is found to remain at rest in a uniform electric field of intensity ‘E’. Find ‘E’. (vi) Why does a capacitor blocks d.c. but allows a.c.? Explain. (vii) Show graphically the intensity distribution in the diffraction pattern of a single slit and label the axes. (viii) State two conditions which must be satisfied in order to apply tangent law in magnetism. PART II SECTION A (28 marks) Answer any four questions Question 2 (a) Define intensity of electric field at a point. [1] (b) State Gauss’ theorem. Give its mathematical expression. [2] (c) Prove that the electric potential at a point in the equatorial line of an electric dipole is zero. [2] P.J. Sarma/Trial/XII Physics/2013 Phss Page 4 of 8 (d) An isolated 16μF parallel plate air capacitor has a potential difference of 1000 V. A dielectric slab having relative permittivity (i.e.dielectric constant)=5 is introduced to fill the space between the two plates completely . Calculate: (i) the new capacitance of the capacitor. (ii) the new potential difference between the two plates of the capacitor. [2] Question 3 (a) Write one evidence to show that Ohm’s law is not a universal law. [1] (b) A p.d. of 10V is applied across a conductor of resistance 1kΩ. Find the approximate number of free electrons flowing through the conductor in one minute. [2] (c) State two important differences between Joule effect and Peltier effect. [2] (d) The resistance of a galvanometer is 10Ω. It can measure a maximum current of 1A. Draw a diagram to show how this galvanometer can be converted into a voltmeter reading up to 100V. Calculate the value of resistance connected. [2] Question 4 (a) What is polarization in a voltaic cell? How is this defect remedied? [2] (b) The length of a conductor is increased to three times. What is its effect on (i) drift velocity of electrons and (ii) resistivity if potential across the conductor is kept constant. [2] (c) Derive the expression τ = MBsinθ for a rectangular coil of area ‘A ‘carrying current ‘I’ placed in a magnetic field. The angle between the direction of field and normal to the plane of coil is θ. [3] Question 5 (a) The earth’s core contains iron. So it is a source of earth’s magnetism. Do you agree? [2] (b) Obtain the relation Bm = BHtanθ for a deflection magnetometer from a vector diagram of Bm and BH. [2] (c) A step-up transformer operates on a 220V line and supplies a current of 5A output. The ratio of the primary and secondary windings is 1:20. Calculate the: (i) (ii) P.d. across the secondary Power output [3] Question 6 (a) State any two differences between a moving coil galvanometer and a tangent galvanometer. [2] (b) State Ampere’s circuital law. Apply it to find an expression for magnetic field due to long straight conductor carrying current. [3] (c) What is meant by self- induction? Write the expression for its co-efficient. [2] P.J. Sarma/Trial/XII Physics/2013 Phss Page 5 of 8 Question 7 (a) An ac voltage 𝐸 = 𝐸0 sin 𝑤𝑡 is applied across a pure inductor of inductance L. Show mathematically that the current flowing through it lags behind the applied voltage by a phase angle of π/2. [3] (b) An a.c voltage V = 200 sin 314t is applied across a series C-R circuit, where C = 318.2 μF and R = 7Ω. Calculate: (i) the capacitive reactance (ii) the impedance and (iii) the phase angle. [3] (c) Where is the power dissipation in an a.c circuit? [1] Section B (18 marks) Answer any three questions Question 8. (a) Derive Snell’s law of refraction for a parallel beam incident on a plane surface of a refracting medium using ‘Huygen’s principle’. [3] (b) Two coherent sources of light are placed 0.12mm apart and the fringes are observed on a screen 70cm far. The 4th bright fringe is found at a distance of 10.5 mm from the central bright fringe. Calculate the wavelength of light used. [3] Question 9 (a) A diverging lens of focal length F is cut into two identical parts each forms a planoconcave lens. What is the focal length of each part? [2] (b) Define dispersive power. Obtain an expression for the dispersive power of the material of prism in terms of refractive indices. [3] (C) Name the characteristics of electromagnetic waves that (i) increases (ii) remains constant in the electromagnetic spectrum as one moves from radio wave region towards u-v region. [1] Question 10 (a) Draw a labelled diagram of an astronomical telescope showing the formation of image at infinity. [2] (b) A ray of light is incident on the surface of a glass plate of μ = √3 at the polarizing angle . Calculate the polarizing angle and the angle of refraction of the ray. [2] (c) State the conditions for the formation of a pure spectrum. [2] P.J. Sarma/Trial/XII Physics/2013 Phss Page 6 of 8 Question 11 (a) Define luminous intensity. Name a unit in which it is measured. [2] (b) The radii of curvature of a double convex lens are 15cm and 30cm. It’s refractive index is 1.5. Find the focal of the lens. [2] (c) Define Chromatic aberration in lenses. Give the condition for achromatism. [2] SECTION C (14 marks) Answer any two questions Question 12 (a) An electromagnetic wave of wavelength λ is incident on a photosensitive surface of negligible work function. If the photoelectrons emitted from this surface have the 2𝑚𝑐 de-Broglie wavelength λ1, prove that 𝜆 = ( ℎ ) 𝜆21 [3] (b) Differentiate between the following pairs i) Pair-production and Pair- annihilation ii) Nuclear fusion and nuclear fission reactions [2] (c) Draw labeled circuit diagram of a full-wave rectifier and show graphically the input and output waveforms. [2] Question 13 (a) When ultraviolet light of wavelength 300nm is incident on a metal plate, a negative potential of 0.54 volt is required to stop the emission of photo electrons. Calculate the energy of the incident photon and the work function for the metal in eV. Calculate the maximum frequency and corresponding wavelength of X-rays produced in a tube maintained at 13.26 kV. [3] (b) How is the intensity of X-rays increased in an X-ray tube? [1] (C) Starting with the law of radioactive disintegration, show that: 𝑁 = 𝑁0 𝑒 −𝜆𝑡 , where the terms have their usual meaning. [3] Question 14 (a) State any two postulates of Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom. [2] (b) Draw a circuit diagram of a n-p-n transistor as an amplifier (common emitter) and write the expression for the voltage gain. [2] (c) Calculate the binding energy of deuteron in MeV if mass of neutron = 1.008665u ; mass of 1H1 = 1.007825u and mass of 1H2 = 2.014103u. [3] P.J. Sarma/Trial/XII Physics/2013 Phss Page 7 of 8 [PHYSICAL CONSTANTS AND RELATIONS] Permittivity of free space єo = 8.85 x 10-12 Fm-1 Planck’s constant h = 6.63 x 10-34 Js Electron charge e = 1.6 x 10-19 C 1 electron volt 1eV = 1.60 x 10-19J Speed of electromagnetic wave c = 3.00 x 108 ms-1 Energy equivalent of 1u = 931 MeV Mass of an electron me = 9.10 x 10-31kg Unified mass atomic unit u = 1.66 x 10-27kg 1/4πєo = 9.0 x 109 S.I. units π = 3.14 Rydberg’s constant R = 1.097 x 107m-1 P.J. Sarma/Trial/XII Physics/2013 Phss Page 8 of 8