Spectrum Analysis - cms14-15
advertisement
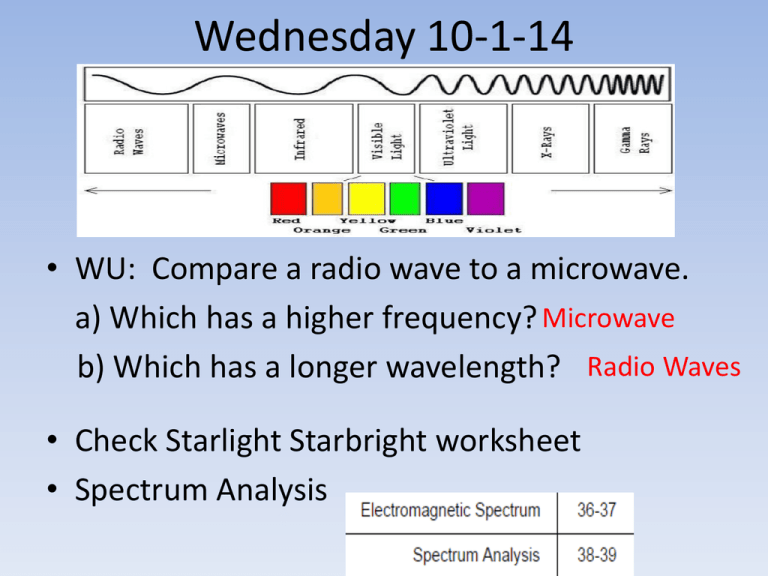
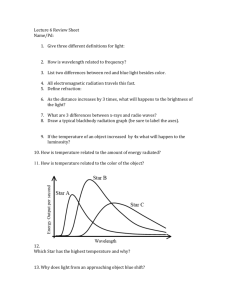
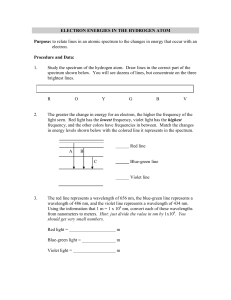
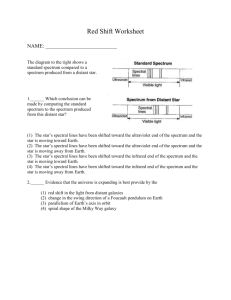
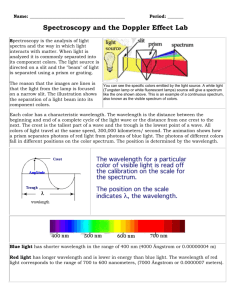
Wednesday 10-1-14 • WU: Compare a radio wave to a microwave. a) Which has a higher frequency? Microwave b) Which has a longer wavelength? Radio Waves • Check Starlight Starbright worksheet • Spectrum Analysis To Do Quizlet has been moved to Friday Grade Star Light, Star Bright Update SN Spectrum Analysis HW: Universe CBA Review All missing assignments must be turned in by Thursday – no exceptions! • • • • • • Color in the above spectrum on your sheet What color has the largest wavelength? Red Smallest wavelength? Violet What color has the highest frequency? Violet Lowest frequency? Red What color would you expect to see if its wavelength were: – 600 nanometers? Orange – 450 nanometers? Blue – 650 nanometers? Red • Skip to part 3 (we’ll come back to part 2) Below are the bright line spectra of four elements and the spectrum of an unknown gas. 700 a) Which elements are in the unknown? Explain. Hydrogen and Helium. The unknown has all of the hydrogen and helium lines. b) Why are you able to exclude the presence of the other elements? The unknown does not contain all of the lines for lithium or sodium c) Young stars are mostly hydrogen with a small abundance of helium and other elements. Is the unknown a likely spectrum for a young star? Explain your answer. Yes this is likely to be a young star because it contains hydrogen and helium 400 -Spectrums A, B, and C are from identical stars. -A represents a spectrum from an unmoving star. -B and C show stars in motion with respect to us 1. 2. 3. 4. What is the approximate range in nanometers that the black lines fall in for each spectrum. A = 550-570 B= 600-650 C= 430-470 C – Blue shifted Which spectrum is that of a star moving toward Earth? Explain. (smaller B – Red shifted Moving away from Earth? wavelength) (longer wavelength) In comparison to A, which is moving faster. B or C? Justify your answer. C, it is shifted farther from original