Urinary System Notes Sheet
advertisement

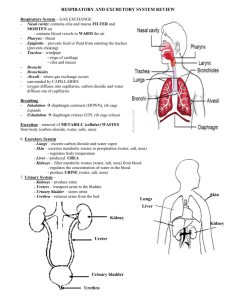
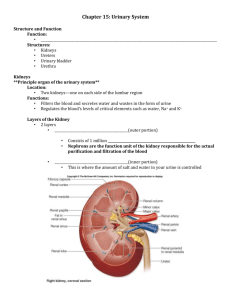
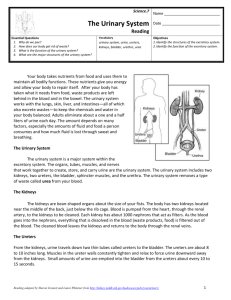
Name: __________________________________ Class #: ________ Class Period: ___________ Date: _____________ Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System 1. Maintains proper balance of water, salts and acids in body fluids 2. Filters _____________________________ to remove urea and other waste materials 3. Converts waste products and excess fluids into ______________________________ Urinary Organs 1. Two kidneys 2. Two ___________________________ 3. One bladder 4. One ___________________________ Kidneys Filter blood to remove waste and excess water; excreted as urine Has ______________________________ : renal cortex and medulla The renal cortex contains ________________________ Nephrons Form urine by the process of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion Each nephron contains a glomerulus which filters ______________________ entering the nephron Waste products pass through collecting tubes before entering the ureters Ureters and Urinary Bladder Ureters Narrow tubes about _________________ inches long that carry urine from a kidney to the urinary bladder _______________ ureter from each kidney to the bladder Urinary Bladder Reservoir (holding tank) for urine Holds about a pint of urine (_____________ cups) Urethra Tube extending from the urinary bladder to _________________________________________ Urinary sphincters control flow of urine from the bladder into the urethra, and out of the urethra through the urinary meatus Urination Normal process of excreting urine from the body __________________________ or voiding are other names Name: __________________________________ Class #: ________ Class Period: ___________ Date: _____________ Diagnostic Procedures 1. Catheterization – insertion of a sterile catheter through the ____________________ and into the urinary bladder. Commonly done to relieve urinary retention pressure, obtain sterile specimens for testing, and prevent incontinence during surgical procedures. 2. Cystoscopy – visual exam of the _________________________________________ using a cystoscope 3. KUB (kidneys, ureters, bladder) – radiographic study of these structures without use of contrast dye. 4. Urinalysis – laboratory examination of urine a. Urine __________________________ contain - sugar, albumin, blood, ketones, sediment, pus, or bilirubin b. Urine _____________________ contain – water, urea, creatinine, salts, acids, drugs