Rubic for Student Growth
advertisement

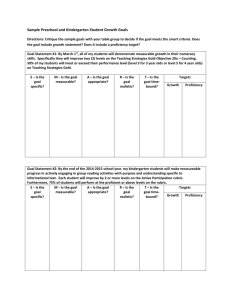
GOAL SETTING FOR STUDENT GROWTH PROCESS Step 3: Create and implement teaching and learning strategies. Step 4: Monitor student progress through ongoing formative assessment. Step 1: Determine needs. Step 2: Create specific learning goal based on preassessment. S M A R T Specific- The goal addresses student needs within the content. Measurable- An appropriate instrument or measure is selected to assess the goal. AppropriateThe goal is clearly related to the role and responsibilities of the teacher. Realistic- The goal is attainable. Time-boundThe goal is contained to a single school year/course. The goal is measurable and uses an appropriate instrument. The goal is standardsbased and directly related to the subject and students that the teacher teaches . The goal is doable, but rigorous and stretches the outer bounds of what is attainable. The goal is bound by a timeline that is definitive and allows for determining goal attainment. The goal is focused on a specfic area of need. Step 5: Determine whether the students achieved the goal. *Adapted for Kentucky from Stronge, J. H., & Grant, L. W. (2009). Student achievement goal setting: Using data to improve teaching and learning. Larchmont, NY: Eye on Education, Inc. 1 STUDENT GROWTH GOAL: Content Considerations Does the goal…….. Align with the needs identified from the data Show that it is congruent with Kentucky Core Academic Standards appropriate for the grade level and content area for which it is developed Target an enduring concept or skill or a subset of knowledge and skills Technical Considerations Does the goal……. Target at least one group of students? Contain both a growth and proficiency target? Match SMART criteria? Specific, Measurable, Appropriate, Realistic and Time-bound Allow high- and low- achieving students to adequately demonstrate their knowledge Provide access and opportunity for all students, including students with disabilities, ELLs and gifted/talented students ASSESSMENT: Content Considerations The assessment…….. Is it congruent with Kentucky Core Academic Standards appropriate for the grade level and content area for which it is developed? Does it target an enduring concept or skill or a subset of knowledge and skills? Is there a good match between the rigor of the standard and the method used to collect evidence? If the assessment is a rubric, does it describe the performance levels aligned with meeting mastery? Technical Considerations The assessment ……. Provides for opportunities for baseline and end of the year data? Provides for opportunities for formative assessment throughout the year – especially at mid-year? Allows high- and low- achieving students to adequately demonstrate their knowledge Provides access and opportunity for all students, including students with disabilities, ELLs and gifted/talented students Professional Growth Goal: Content Considerations Does the goal…….. Align with the needs identified in the self assessment? Answer the 3 guiding questions: What do I want to change about my practice that will effectively impact student learning? How can I develop a plan of action to address my professional learning? How will I know if I accomplished my objective Technical Considerations Were a variety of different sources of evidence used for the needs assessment? Is additional clarification needed about what the teacher will do? If so, additional plan information will be needed. 2 ELA sample goal During the 2014-15 school year, my 5th period 8th grade ELA students will improve their ability to write arguments that support claims and use textual evidence to support claims and refute counterclaims. All 8th graders in my 5th period class will improve by at least one level in their overall score on the district argumentation rubric. At least 70% of my students will score at the proficiency level (level 3) on the 4point rubric. Identify: Growth Target Proficiency Target SMART Criteria o Specific o Measurable o Appropriate o Realistic o Time Bound o Discuss: How do you determine if the goal is Appropriate and Realistic? What would you need to hear from the teacher or what evidence would you need? 3 Art sample goal _________________________________________________ During this school year, my third grade students will develop their use of art to convey meaning and their ability to discuss their art. The district approved 10-point rubric will be used to evaluate performance on a pre/post assessment task to determine growth. All students will move one performance level in their ability to use art to convey meaning and in their ability to discuss their art with others. 80% of students will achieve at least an average of a 7 on the post assessment task. ___________________________________________________ Identify: Growth Target Proficiency Target SMART Criteria o Specific o Measurable o Appropriate o Realistic o Time Bound Discuss: What does a principal need to know about a goal to give feedback on the technical components? What else do you need to know about the teacher’s process? 4 8th Grade Language Arts Think and Plan for Developing Student Growth Goals Purpose: This document is a summary form a teacher completes for conferencing with their administrator. The column to the right provides guidance, detail, and hyperlinks for completing the process and the template. Step 1: DETERMINE NEEDS Identify the context of the identified class, as selected by teacher in collaboration with principal, including student population. Guiding Questions I teach 5 classes of 8th grade Language Arts. The class selected for my SGG is a diverse class of 9 special education students and 8 that receive Title 1 services. 70% of the class receives free/reduced lunch. Identify the course-long interval of instruction (e.g., trimester, semester, one school year). Year long Identify the content area enduring skills*, concepts, and/or processes that your goal will target. (In the KCAS for Mathematics, the “Enduring Understandings” reflect the enduring learning advocated in the goal-setting for student growth process.) Content area examples: Reading, Writing, Speaking and Listening, Social Studies, Science, Reading Foundational Skills, PE, Health, World Language, Music, Art Writing arguments that support claims, including using textual evidence to support the claims and to refute counterclaims In collaboration with colleagues, identify the enduring skills*, concepts, and processes for my content area (facilitator’s guide, process pptx, example). Based on my content standards, what are the enduring skills*, concepts and processes students should master by the end of the school year/course? Do the identified skills, concepts and processes represent essential learning that: ENDURES beyond a single test date, is of value in other disciplines, is relevant beyond the classroom, is worthy of embedded, courselong focus, and may necessary for the next level of instruction (next grade or future course)? What does it look like for students to be performing at proficiency level on these skills, concepts and processes? How do I know? Pinpoint areas of need based on my current students' abilities. Are there any enduring skills*, concepts or processes my students lack overall? What are the biggest areas of need? What are my students’ abilities? How have I collected and analyzed evidence/data to determine patterns, trends, strengths and weaknesses for all students? (e.g., formative processes, analysis of student work, anecdotal notes, last year's data, previous teachers) Are the areas of need identified appropriate for a year-long/course-long student growth 5 List the sources of evidence you will use to establish baseline data and measure student growth. I used a rubric designed by my district ELA PLC based on the Literacy Design Collaborative (LDC) argumentation rubric to establish a baseline for my student growth goal and assessed students in a variety of ways. Students were given two different writing prompts in which they were provided texts to base their argument and then scored using the district argumentation rubric. Additionally, I collected student short responses to using texts to support claims or to refute counterclaims. Using this variety of assessments allowed me to get a truer picture of students’ abilities and where they fell overall on the rubric. goal? Decide on sources of evidence. After identifying an area or areas of need, choose the sources of evidence (e.g., rubrics, classroom assessments, performances, products, portfolios, projects, district learning checks) for collecting baseline, mid-term, and end of year/course data for the student growth goal. Note: At least three sources of evidence are recommended for contributing to baseline data. Do the sources of evidence provide the data needed to demonstrate proficiency for the identified area(s) of need? Can the sources of evidence be used to provide baseline data, comparable mid-term data, and end of year/course data? Do the sources of evidence require students to meet or exceed the true intent of the standards being assessed? (This addresses both rigor of the evidence and comparability.) Is there a good match between the rigor of the standard to be assessed and the method used to collect evidence? (For instance, if the best way to determine if students are meeting the rigor of a standard is a performance, then the task should be a performance that demonstrates where students are in meeting mastery of that standard. See Classroom Assessment for Student Learning resources on Target-Method Match.) Use baseline data to determine area(s) of need for the goal What did I learn from collection of data? How will I combine data to determine a baseline for my SGG? Step 2: CREATE A SPECIFIC LEARNING GOAL Specify the expected growth and proficiency. Include a growth target that expresses the growth you expect your students to make. All of my 8th graders will move at least one level in their overall score on the district argumentation rubric. Include a proficiency target. At least 70% of my students will score at the proficiency level (3) on the 4 point rubric. Decide on a student growth goal (SGG) that meets the SMART criteria. SPECIFIC Is the identified area of need significant enough for year-long/course-long instructional focus? Does the goal address learning that is representative of the enduring skills*, concepts and/or processes that: o ENDURES beyond a single test date, o is of value in other disciplines, o is relevant beyond the classroom, o is worthy of embedded, course-long focus, o may be necessary for the next level of instruction? 6 Write your student growth goal statement that meets the SMART criteria. Include both growth and proficiency. Explain the rationale for the goal. Include reference to baseline data and explanation of how targets meet the expectation for rigor. Students in this class overall scored low on the district argumentation rubric. 60% scored at level 1 and 40% scored at level 2. I believe this is because of a lack of exposure to strategies that support argumentation. Therefore, I believe that with targeted instruction, all students can improve by at least one level on the rubric and that it is doable to get at least 70% of the class at proficiency level (3) or above. Determine the measure for identifying H, E, L growth and for identifying proficiency. (Rubric, etc.) Define H, E, L growth and proficiency based on the identified measure. *See district certified evaluation plan. MEASURABLE Does the goal identify the sources of evidence/measures that will be used to show how all students will demonstrate growth? Do the sources of evidence provide the data needed to accurately measure where students are in mastering the grade level standards for the identified areas(s) of need? Which criteria were used for determining what amount of growth is rigorous for students? Why was this criteria selected? Does the goal include a growth target and proficiency target? APPROPRIATE Is the goal standards-based and directly related to the subject and students taught? Is there a good match between the goal and the level of rigor expected in the identified standards? REALISTIC Is the goal doable, but rigorous enough to stretch the outer bounds of what is attainable? TIMEBOUND Is the goal designed to stretch across the interval of instruction (e.g., trimester, semester, one school year)? Is there sufficient time within the interval of instruction to determine goal attainment? Sample Student Growth Goals 2014 High, Expected, Low determination Has the teacher identified “expected” as the desired outcome? How will the teacher address achievement of growth but not proficiency? How will the teacher address the achievement of proficiency but not growth? Step 3: CREATE AND IMPLEMENT TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES Describe professional learning (PL) needed to support students’ attainment of the student growth goal. (Include any PL needs in your Professional Growth Plan.) My school PLC team will be doing a study of teaching argument, including review and discussion of videos in PD360 and a book study of George Helix’s book, Teaching Argument Writing. Through our action research, our PLC will share student work samples and share strategies. Determine professional learning What professional learning is needed to support the SGG? How can a professional learning community/colleagues’ expertise provide support? Does the Professional Growth Plan (PGP) reflect the support needed to meet the goal? 7 Describe the instructional strategies for goal attainment, specifically what you will do instructionally to assure your students make gains projected in your student growth goal. Introduce writers’ notebooks where students will have regular opportunities to respond to text and authors’ claims Analyze and respond to good and weak models of arguments where authors’ have supported claims and/or addressed counterclaims Introduce peer response groups where students will use the rubric to provide feedback to each other’s claims and counterclaims Decide on instructional strategies for goal attainment How do I identify the instructional strategies that will most effectively support students in attaining the SGG? What resources and supports do I need to implement these strategies with my students? Step 4: MONITOR STUDENT PROGRESS THROUGH ONGOING FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT Describe your plan to monitor students’ progress toward goal attainment. I’ll review student prompts using the rubric and monitor students’ feedback to each other. Plan for progress monitoring How and when will I monitor progress towards the SGG throughout the year/course? What formative assessment processes will I use for progress monitoring? How will I involve students in progress monitoring? How will I provide all students multiple opportunities and/or assessment types to demonstrate learning of the selected standards? How will specific feedback occur regularly to move students forward in their learning? Step 5: DETERMINE WHETHER THE STUDENTS ACHIEVED THE GOAL Do no complete this box until the end of the growth goal timeline. Analyze results: Analyze the summative/postassessment data to determine goal attainment and reflect on next steps. What does the data reveal about student growth? What does the data show about instructional practices? How can these results inform professional growth? (Connect this back to Step 3.) 8 Elementary Art Example Think and Plan Guidance for Developing SGGs Purpose: This document is a summary form a teacher completes for conferencing with their administrator. The column to the right provides guidance, detail, and hyperlinks for completing the process and the template. Step 1: DETERMINE NEEDS Identify the context of the identified class, as selected by teacher in collaboration with principal, including student population. Guiding Questions There are 27 students in this 3rd grade class. Seven students have IEPs, 2 students share an assistant. We meet for 45 minutes once a week. Identify the course-long interval of instruction (e.g., trimester, semester, one school year). The class is a year-long class. Identify the content area enduring skills*, concepts, and/or processes that your goal will target. (In the KCAS for Mathematics, the “Enduring Understandings” reflect the enduring learning advocated in the goal-setting for student growth process.) Content area examples: Reading, Writing, Speaking and Listening, Social Studies, Science, Reading Foundational Skills, PE, Health, World Language, Music, Art the elements and principles of design of visual art are intentionally applied in creating works of art. responding to or critiquing works of art involves an understanding of elements, principles and structures appropriate to each area of the arts. In collaboration with colleagues, identify the enduring skills*, concepts, and processes for my content area (facilitator’s guide, process pptx, example). Based on my content standards, what are the enduring skills*, concepts and processes students should master by the end of the school year/course? Do the identified skills, concepts and processes represent essential learning that: ENDURES beyond a single test date, is of value in other disciplines, is relevant beyond the classroom, is worthy of embedded, courselong focus, and may necessary for the next level of instruction (next grade or future course)? What does it look like for students to be performing at proficiency level on these skills, concepts and processes? How do I know? Pinpoint areas of need based on my current students' abilities. Are there any enduring skills*, concepts or processes my students lack overall? What are the biggest areas of need? What are my students’ abilities? How have I 9 List the sources of evidence you will use to establish baseline data and measure student growth. At the beginning of the year, students were asked to create a piece of art and discuss their choices of technique and medium selection. An initial scoring by the teacher and student (self-assessment) were obtained using the district’s 10-point rubric. I noticed that students weren’t able to make a claim about their work and support it. As a class, the use of correct terminology (elements, techniques, procedures and response) in their discussion and self-assessment was limited. Evidence gathered through the discussion, my scoring and their self-assessment allowed me to gather baseline ratings for each student. collected and analyzed evidence/data to determine patterns, trends, strengths and weaknesses for all students? (e.g., formative processes, analysis of student work, anecdotal notes, last year's data, previous teachers) Are the areas of need identified appropriate for a year-long/course-long student growth goal? Decide on sources of evidence. After identifying an area or areas of need, choose the sources of evidence (e.g., rubrics, classroom assessments, performances, products, portfolios, projects, district learning checks) for collecting baseline, mid-term, and end of year/course data for the student growth goal. Note: At least three sources of evidence are recommended for contributing to baseline data. Do the sources of evidence provide the data needed to demonstrate proficiency for the identified area(s) of need? Can the sources of evidence be used to provide baseline data, comparable mid-term data, and end of year/course data? Do the sources of evidence require students to meet or exceed the true intent of the standards being assessed? (This addresses both rigor of the evidence and comparability.) Is there a good match between the rigor of the standard to be assessed and the method used to collect evidence? (For instance, if the best way to determine if students are meeting the rigor of a standard is a performance, then the task should be a performance that demonstrates where students are in meeting mastery of that standard. See Classroom Assessment for Student Learning resources on Target-Method Match.) Use baseline data to determine area(s) of need for the goal What did I learn from collection of data? How will I combine data to determine a baseline for my SGG? 10 Step 2: CREATE A SPECIFIC LEARNING GOAL Specify the expected growth and proficiency. Include a growth target that expresses the growth you expect your students to make. All students will move one performance level in their ability to use art to convey meaning and in their ability to discuss their art with others. All students will move one performance level in their ability to use art to convey meaning and in their ability to discuss their art with others. Include a proficiency target. 80% of students will achieve at least an average of a 7 on the post assessment task. Write your student growth goal statement that meets the SMART criteria. Include both growth and proficiency. Explain the rationale for the goal. Include reference to baseline data and explanation of how targets meet the expectation for rigor. I noticed that the students weren’t able to communicate about art using specific art vocabulary. I found that 45% of the students scored less than an average of 5 on the pre-assessment task. By focusing on communication through and about their art during the school year, I feel the students will show growth on those two areas. I feel it is reasonable to expect that all students will move one performance level on the postassessment. Decide on a student growth goal (SGG) that meets the SMART criteria. SPECIFIC Is the identified area of need significant enough for year-long/course-long instructional focus? Does the goal address learning that is representative of the enduring skills*, concepts and/or processes that: o ENDURES beyond a single test date, o is of value in other disciplines, o is relevant beyond the classroom, o is worthy of embedded, course-long focus, o may be necessary for the next level of instruction? MEASURABLE Does the goal identify the sources of evidence/measures that will be used to show how all students will demonstrate growth? Do the sources of evidence provide the data needed to accurately measure where students are in mastering the grade level standards for the identified areas(s) of need? Which criteria were used for determining what amount of growth is rigorous for students? Why was this criteria selected? Does the goal include a growth target and proficiency target? APPROPRIATE Is the goal standards-based and directly related to the subject and students taught? Is there a good match between the goal and the level of rigor expected in the identified standards? REALISTIC Is the goal doable, but rigorous enough to stretch the outer bounds of what is attainable? TIMEBOUND Is the goal designed to stretch across the interval of instruction (e.g., trimester, semester, one school year)? Is there sufficient time within the interval of instruction to determine goal attainment? Sample Student Growth Goals 2014 Determine the measure for identifying H, E, L growth and for identifying proficiency. (Rubric, etc.) Define H, E, L growth and proficiency based on the identified measure. *** Please follow district directed guidance for calculating the HEL rating. High, Expected, Low determination Has the teacher identified “expected” as the desired outcome? How will the teacher address achievement of growth but not proficiency? How will the teacher address the achievement of proficiency but not growth? 11 Step 3: CREATE AND IMPLEMENT TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES Describe professional learning (PL) needed to support students’ attainment of the student growth goal. (Include any PL needs in your Professional Growth Plan.) Because I am the only elementary art teacher in my district, I have reached out to several elementary art teachers in my school’s cooperative to create a PLN. I have identified a need to learn more about formative assessment in the elementary classroom – this will help me monitor growth in my classroom, and support our school’s Program Review. Describe the instructional strategies for goal attainment, specifically what you will do instructionally to assure your students make gains projected in your student growth goal. I have developed a self-assessment component for the artist statements. The students and I created a rubric that highlights specific vocabulary and reinforces a series of questions students can respond to when talking about and responding to art. At the beginning of each class I share a work of art and the students respond to it in their sketchbooks. Determine professional learning What professional learning is needed to support the SGG? How can a professional learning community/colleagues’ expertise provide support? Does the Professional Growth Plan (PGP) reflect the support needed to meet the goal? Decide on instructional strategies for goal attainment How do I identify the instructional strategies that will most effectively support students in attaining the SGG? What resources and supports do I need to implement these strategies with my students? Step 4: MONITOR STUDENT PROGRESS THROUGH ONGOING FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT Describe your plan to monitor students’ progress toward goal attainment. I will routinely check student sketchbooks for vocabulary and correct use of terminology. The students share responses and use component of the larger rubric to provide feedback to their peers. I have created a checklist to accompany the rubric that hangs in the classroom; we refer to it regularly during whole group critiques. Plan for progress monitoring How and when will I monitor progress towards the SGG throughout the year/course? What formative assessment processes will I use for progress monitoring? How will I involve students in progress monitoring? How will I provide all students multiple opportunities and/or assessment types to demonstrate learning of the selected standards? How will specific feedback occur regularly to move students forward in their learning? Step 5: DETERMINE WHETHER THE STUDENTS ACHIEVED THE GOAL Do no complete this box until the end of the growth goal timeline. Analyze results: Analyze the summative/postassessment data to determine goal attainment and reflect on next steps. What does the data reveal about student growth? What does the data show about instructional practices? How can these results inform professional growth? (Connect this back to Step 3.) 12 Sample SGG Rubric #1 District Student Growth Goal (SGG) Rubric ‘SPECIFIC’ Does the SGG focus on a specific area of need based on an enduring skill or understanding/overarching goal? ‘MEASURABLE’ Is an appropriate measure selected to assess the goal? S.M.A.R.T. STRUCTURE OF THE STUDENT GROWTH GOAL ACCEPTABLE NEEDS REVISION Identifies an area of need pertaining to Identifies a specific area of need, but current students’ abilities lacks supporting data for current students Includes growth and proficiency targets that establish and differentiate expected performance for ALL students (e.g. Spec. Ed, GT, ELL etc.) Includes both a growth target and a proficiency target, but fails to differentiate expected performance for one or both targets Includes only a growth or a proficiency target ACCEPTABLE Uses appropriate measures for base-line, mid-course, and end of year/course data collection. NEEDS REVISION Uses measures that fail to clearly demonstrate performance for the identified skill. INSUFFICIENT Uses no baseline data or uses irrelevant data. Is anchored in baseline data and Identifies multiple measures that demonstrate where students are in meeting or exceeding the intent of the standard(s) being assessed ‘APPROPRIATE’ Appropriate/Attainable Is the SGG rigorous, realistic, and standards based? ACCEPTABLE Aligned to KCAS grade level standards (or international, national state, local or industry recognized standards) appropriate for the grade level and content area for which it was developed. Address critical content, enduring skill(s) which students are expected to master necessary for advancement to future coursework ‘RELIABLE’ Is the SGG results-oriented and relevant? Is the data collected comparable across similar classrooms, across the district? ‘TIME-BOUND’ Does the SGG specify an appropriate instructional interval? INSUFFICIENT Is not focused on a specific area of need Only allows students to demonstrate competency of part, but not all aspects of the standards being assessed. NEEDS REVISION Congruent to content, but not aligned to grade level standards. Does not assess the level of competency intended in the standards INSUFFICIENT Is not congruent or appropriate for grade level/content area standards Focuses on a standards-based skill that does not match enduring skill criteria Goal is too narrow; focusing on a narrow skill or topic. Goal is written in a general context and encompasses too much content. Goal lists multiple enduring skills/overarching goals of adopted state standards ACCEPTABLE Includes growth and proficiency targets that are rigorous for students, but attainable with support. Rigor is determined by past performance of students, year’s growth, percentage of students who attain the target or other measures. NEEDS REVISION Includes targets that are achievable, but fail to stretch attainability expectations INSUFFICIENT Includes targets that do not articulate expectations AND/OR targets are not achievable Uses comparable criteria across similar classrooms (classrooms that address the same standards) to determine progress toward mastery of standards/enduring skills n/a For similar classrooms, data collected for the student growth goal: does not reflect common criteria used to determine progress ACCEPTABLE Is appropriate for the instructional interval defined and explicitly states yearlong/course-long interval of instruction NEEDS REVISION Specifies less than/more than a yearlong/course-long interval of instruction INSUFFICIENT Fails to specify an interval of instruction 13 Sample SGG Rubric #2 14 Sample Student Growth Rubric #3 STRUCTURE OF THE GOAL The student growth goal: Focuses on a standards-based enduring skill which students are expected to master ACCEPTABLE The student growth goal: Focuses on a standards-based enduring skill NEEDS REVISION The student growth goal: Focuses on a standards-based skill that does not match enduring skill criteria INSUFFICIENT The student growth goal: Is not standards-based Identifies a specific area of need supported by data for current students Identifies a specific area of need, but lacks supporting data for current students Is not focused on a specific area of need Includes a growth target that establishes growth for ALL students; a proficiency target that establishes the mastery expectation for students Includes both a growth target and a proficiency target, but fails to differentiate expected performance for one or both targets Includes only a growth or a proficiency target Uses appropriate measures for base-line, mid-course, and end of year/course data collection Uses measures for collecting baseline, midcourse, and end of year/course data that matches the skill being assessed Uses measures that fail to clearly demonstrate performance for the identified skill Uses no baseline data or uses irrelevant data Explicitly states year-long/course-long interval of instruction Specifies a year-long/course-long interval of instruction Specifies less than a year-long/course-long interval of instruction Fails to specify an interval of instruction Identifies an area of need pertaining to current students’ abilities Includes growth and proficiency targets that establish and differentiate expected performance for ALL students RIGOR OF THE GOAL ACCEPTABLE NEEDS REVISION INSUFFICIENT The student growth goal: Is congruent to KCAS grade level standards and appropriate for the grade level and content area for which it was developed The student growth goal: Is congruent and appropriate for grade level/content area standards The student growth goal: Is congruent to content, but not to grade level standards The student growth goal: Is not congruent or appropriate for grade level/content area standards Identifies measures that demonstrate where students are in meeting or exceeding the intent of the standard(s) being assessed Identifies measures that allow students to demonstrate their competency in performing at the level intended in the standards being assessed Identifies measures that only allow students to demonstrate competency of part, but not all aspects of the standards being assessed Identifies measures that do not assess the level of competency intended in the standards Includes growth and proficiency targets that are challenging for students, but attainable with support Includes growth and proficiency targets that are doable, but stretch the outer bounds of what is attainable Includes targets that are achievable, but fail to stretch attainability expectations Includes targets that do not articulate expectations AND/OR targets are not achievable COMPARABILITY OF DATA Data collected for the student growth goal: ACCEPTABLE For similar classrooms, data collected for the student growth goal: NEEDS REVISION Uses comparable criteria across similar classrooms (classrooms that address the same standards) to determine progress toward mastery of standards/enduring skills Reflects use of common measures/rubrics to determine competency in performance at the level intended by the standard(s) being assessed INSUFFICIENT For similar classrooms, data collected for the student growth goal: n/a Does not reflect common criteria used to determine progress 15 Science Student Growth Goals – 3 Levels More Practice Rubric Activity This school year, all of my 6th grade science students will demonstrate measurable growth in their ability to apply the scientific practices. Each student will improve by two or more levels on the districts’ science rubric in the areas of engaging in argument from evidence, and obtaining, evaluating and communicating information. 80% of students will perform at level 3 on the 4-point science rubric. This school year, all of my 6th grade students will make measureable progress in their knowledge of science. All students will improve on their final exam and 75% of students will score a B or higher. For the current school year, all of my students will make measureable progress in their ability to obtain and combine information about ways individual communities use science ideas to protect the Earth’s resources and environment (KCAS, 5-ESS31). All students will improve one level from the pre to the post assessment and 75% of students will meet expectations for the standard. 16 Social Studies Student Growth Goals – 3 Levels More Practice Rubric Activity For the current school year, all of my students will make measurable progress in historical argumentation and appropriate use of relevant historical evidence. All students will move up at least 1 level and 75% of students will achieve at the 3 or higher level on the reading/research and development areas of the LDC Argumentation Rubric. For the current school year, all of my students will make measureable progress in their understanding of U.S. History. All students will improve on their U.S. History End of Course Assessment and 75% of students will meet or exceed the College Readiness Benchmark. For the current school year, all of my students will make measureable progress in their understanding of the immediate and long-term influences of Reconstruction on the lives of African Americans and U.S. society as a whole (ACT Quality Core for US History). All students will improve one level from the pre to the post assessment and 75% of students will meet expectations for the standard. 17 World Language Student Growth Goals – 3 Levels More Practice Rubric Activity During this school year all of the students in my French II classes will demonstrate performance at least one level above their baseline for interpretive listening, interpersonal speaking, interpretive reading and interpersonal writing, and they will expand the breadth of their vocabulary topic areas. Data from individual performance assessments, designed by teacher teams around speaking and listening, reading and writing competencies in the target language will provide multiple data points for baseline and throughout the year. At least 70% of my students will meet or exceed the Intermediate-Low competency level for at least two modes of communication, as measured by the KY World Language Standards rubric. During this school year all of my students will make measureable progress in French. All students will improve on their final exam and 75% of students will receive a B or higher. For the current school year, all of my students will make measureable progress in their ability to write in French about themselves using learned phrases and memorized expressions (Kentucky Standard for World Language Proficiency, NM.PW.2). All students will improve one level from the pre to the post assessment and 75% of students will meet expectations for the standard. 18 Sample Student Growth Goals – March 2014 Goal Criteria From CEP The goal is congruent with Kentucky Core Academic Standards appropriate for the grade level and content area for which it was developed represents or encompasses an enduring skill, process or concept that students are expected to master by taking a particular course (or courses) in school will allow high and low achieving student to adequately demonstrate their knowledge provides access and opportunity for all students, including students with disabilities, ELLs, and gifted/talented students SMART Specific – the goal is focused on a specific area of student need within the content. Measurable – the goal will be assessed using an appropriate instrument. Appropriate – the goal is standards-based and directly related to the responsibilities of the teacher. Realistic – the goal is doable, while rigorous, stretching the outer bounds of what is attainable. Time-bound – the goal contained to a simple school year/course. *Note that analysis of pre-assessment data is needed to truly determine if the goal is SMART. Science During this school year, all of my 8th -grade science students will grow in their ability to use models to explain, predict, and investigate the natural and designed world, including identifying the limitations of the models. Based upon the Grades 6-8 Using Models Analytic Rubric, all students will improve in each of the scoring elements by at least one performance level as demonstrated on the district approved performance task. Furthermore, 80 percent of students will score proficient on the district approved performance task as indicated by the rubric. Health and PE During the 8th-grade nine weeks course, all students will grow in their ability to analyze the influence of family, peers, culture, media, technology, and other factors on health behavior. Using a standards-based four -point rubric created by the District Health/PE Vertical Team, students’ current level of understanding will be determined with a constructed response performance task on how these factors affect behavior. Applying the same rubric to the post assessment, students will be given a performance task in which they will be asked to identify and explain how these factors influence health behaviors. Each student will improve by moving one level on the rubric. Furthermore, 80 percent of students will score Meets Expectations (Proficient) on the rubric. Social Studies For the current school year, all of my students will make measurable progress in historical argumentation and appropriate use of relevant historical evidence. All students will move up at least one level and 75 percent of students will achieve at the three or higher level on the reading/research and development areas of the LDC Argumentation Rubric. French II During this school year all of the students in my French II classes will improve their linguistic competency performance. Students will move at least one performance level in: interpretive listening, interpersonal speaking, interpretive reading and interpersonal writing based on the KY World Language Standards rubric. At least 70 percent of my students will meet or exceed the Intermediate-Low competency level for at least two modes of communication, as measured by the KY WL Standards rubric. LDC Writing - Multiple Content Areas For the 2012-13 school year, my students will make measurable progress in writing arguments to support claims. On the District 8th-Grade Writing Assessment each student will improve by at least one performance level in three or more scoring elements of the LDC argumentation rubric. Eighty percent of my students will score an average of a three or higher on a summative rating of the LDC argumentation rubric. Elementary By the end of the 2013-14 school year, all of my 4th grade students (100%) will show growth in summarizing key ideas and details in what they read. Each student will improve by two or more levels on the rubric developed by my PLC team for summarization. In addition, 90 percent of students will score proficient or above on the rubric by the end of the year. By the end of the 2014-15 school year, my 3rd-grade students will make measurable progress in reading and comprehending informational text at the high end of the grade 2-3 text complexity band. Each student will improve by two or more levels on the Reading Comprehension rubric. Furthermore, 75 percent of students will perform at the proficient or above levels on the rubric. 19 Music During this school year, my 5th-grade students in Music class will grow in their ability to read and notate music. Each student will increase by one performance level in two or more areas of the Elementary Music Assessment Rubric. Eighty percent of students will score proficient on two or more areas of the rubric. Family Consumer Science During this school year, my students in Culinary and Food Services class will grow in their understanding of food safety and sanitation. Every student will increase one performance level in all scoring elements of the district Food Safety and Sanitation Performance Task Rubric. Growth data will be obtained using a Pre & Post Performance Assessment Task at the beginning and end of the course. Furthermore, 65 percent of students will demonstrate proficiency by obtaining SERVSAFE Certification. Math During this school year, my 7th-grade students will use the eight Math Practices to further their understanding of proportional relationships. This will be demonstrated by growth by at least one level on the rubric (from the repeated common assessments) developed by the district Math PLC. Furthermore, 70 percent of my students will show mastery by reaching level four or higher on the rubric. Multimedia During this school year, my Advanced Multimedia students will demonstrate measurable growth in effectively communicating with digital media tools by moving at least one performance level (three levels: learner, skilled, master) on the appropriate rubric used for the district approved Adobe Dreamweaver/Flash/Photoshop Performance Task Assessment. Seventy percent of the students will demonstrate proficiency by obtaining an Adobe Certification in Dreamweaver, Flash or Photoshop. * This teacher has 80 students enrolled in this course. She teaches Flash, Dreamweaver, or Photoshop in the same class setting. She has included all three Adobe programs in her goal. Art During this school year, my 3rd-grade students will develop their use of art to convey meaning and their ability to discuss their art. The district approved 10-point rubric will be used to evaluate performance on a pre/post assessment task* to determine growth. All students will move one performance level in their ability to use art to convey meaning and in their ability to discuss their art with others. Eighty percent of students will achieve at least an average of a seven on the post-assessment task. *At the beginning of the year, students were asked to create a piece of art and discuss their choices of technique and medium selection. An initial scoring by the teacher and student (selfassessment) were obtained using the district’s 10-point rubric. In final portfolio presentations students will show their pieces and discuss their choices of technique and medium selection with the class, one visiting artist, and the teacher. The portfolio and presentation will be scored by the visiting artist, the teacher, and students will also complete a self-assessment using the 10-point rubric. 20 STUDENT GROWTH/PGP GOAL/PLAN CONFERENCE Sample Agenda & Framework for Analysis of Goals & Plan 1. Overview of needs assessment Teacher shares what was learned through the needs assessment and how it helped create a focus for the goals. 2. Student Growth Goal/Plan Teacher shares the goal/plan Principal analyzes goal/plan considering: Does the student growth goal: Align with the identified needs from the data? Match SMART criteria? Have both growth and proficiency targets? Does the assessment Provide for pre/post data? Accurately measure what students should be mastering? Reach the level of rigor expected of the standard? Expected by the district? Match a variety of cognitive levels and include a sufficient number of items to provide data? Describe performance levels aligned with meeting mastery if a rubric? Does the student growth plan: Align with the goal? Address all aspects of the goal? Identify how the student learning will be accomplished? Identify relevant/focused activities? Identify appropriate materials/resources? Reflect manageable timelines? Will the teacher achieve the goal through the identified plan? Sample Follow-up Questions What did you learn from the data you reviewed? What data sources did you use to help you decide upon your goal? Why? Goal: Why do you think this goal will cause an increase in student performance? Which students do you think will benefit most as you accomplish your goal? Why? What evidence will you gather to determine your progress toward meeting your goal? Assessment Explain how you know that the assessment matches the level of rigor expected in the standards. How do you know that the assessment accurately measures what students should be mastering? Plan: Why do you think the activities you chose will produce results? How will you use the identified resources/ materials? Identify any barriers that you might need to plan for as you implement your plan? Principal provides feedback through sharing evidence, asking questions and providing specific feedback. Principal and teacher collaborate together to refine the goal/plan. 21 3. PGP Goal/Plan Teacher shares the goal/plan Principal analyzes goal/plan considering: Does the professional growth goal: Align with the identified needs from the data? Answer the 3 questions? Does the professional growth plan: Align with the goal? Address all aspects of the goal? Identify how the teacher learning will be accomplished? Identify relevant and focused activities? Identify appropriate materials/resources? Reflect manageable timelines? Will the teacher achieve the goal through the identified plan? Will you know if the teacher achieved the goal using the identified evidence at the end of the year? Principal provides feedback through sharing evidence, asking questions and providing specific feedback. Principal and teacher collaborate together to refine the goal/plan. 4. Identify supports needed Goal: Why do you think this goal will cause a change in teaching practice? Now that you have realized _____, what will you do about it? Describe how your goal will provide a “stretch” for you? How will this impact what you do in the future? What do you expect to be different in your classroom after you meet your goal? What evidence will you gather to determine your progress toward meeting your goal? Plan: Why do you think the activities you chose will produce results? Predict how your practices will change. How will you use the identified resources/ materials? How will you collaborate with others as you learn? How will you share your learning? Describe the types of assistance you will need to meet these goals? How will our conversation influence the completion of your professional growth plan? Things to consider as you meet with teachers: What patterns are you seeing across the school in the identified goals/plans? How can you group teachers to support each other in this process? What implications do the identified goals and plans have for the school as a whole? How can you best utilize your resources to support teachers? Support students? What implications do the teacher goals have on your own PGP and SGG? 22 Sample Professional Growth Goals Each goal and action plan together should answer the following questions. The goal samples that follow include reference to the actions to be taken in order to meet the goal. 1. What do I want to change about my practice that will effectively impact student learning? 2. How can I develop a plan of action to address my professional learning? 3. How will I know if I accomplished my objective? Any content area – student engagement For the 2012 – 13 school year, I will improve my ability to engage students in their learning by attending and implementing Rigor and Relevance training, researching and implementing strategies for engaging students in rigorous learning, and refining my use of student involved formative assessment practices. These will be measured through pre and post assessments, student work samples, interim assessments, peer and principal observations and conferences, and self-reflection. Science Any Content area – learning styles During the 2012-2013 school year, I will increase student engagement by using a learning styles inventory with every student and designing lessons that address the different styles within my class. I will research teaching strategies to engage the different learning styles and study So Each May Learn by Silver. Measures of success will include student work products, observation, and student and teacher self-reflection. Any content area – formative assessment For the 2012 – 2013 school year, I will improve writing instruction in my science classroom by implementing and reflecting on strategies learned during a summer writing workshop for teachers. I’ll incorporate writing strategies for describing observations, explaining scientific phenomena, explain cause & effect occurrences, and drawing conclusions from experiments. Indicators of success will be student work samples, analysis of student’s writing products, and self-reflection. Reading in any content area During this school year, I will study Classroom Assessment for Student Learning, by Rick Stiggins, and embed formative assessment practices in my daily instruction. Indicators of success will include classroom observation, self-reflection, analysis of student assessment data, and observable student engagement. During the school year, I will learn to integrate literacy strategies in my instruction. I will implement learning from a literacy workshop and from reading professional literature. Measures of success will include results from analysis of student work samples, selfreflection, student surveys, and observation. During the school year, I will improve my questioning techniques to engage students in higher level critical thinking and problem solving. I will implement learning from study of Thinking Strategies. Growth will be evidenced through lesson plans, observation, self-reflection, and student work samples. Any content area - questioning 23 Special Education Teacher Leadership During the 2012-2013 school year, I will increase my knowledge of supporting students with autism. I will research on-line resources, consult with district/state/cooperative special education coordinators, observe a mentor teacher, and participate in an on-line short course on autism. This will be evidenced by notes and self-reflection, anecdotal notes on my interactions with autistic students, and the short course certificate. This school year, I will learn best practices for mentoring new teachers in my building. I will participate in the district study group and Cognitive Coaching PD and attend a KYVL online course for mentoring teachers. Evidence of success will include district PD certificate, course completion certificate, mentee teacher surveys, self-reflection on mentoring opportunities. Literacy Design Collaborative (LDC) teachers Math Design Collaborative (MDC) teachers This school year, I will implement what I am learning through LDC to support students in meeting the Common Core standards. I will design action research around implementing LDC modules as intended, analyze student work, and reflect on impact on students. Success criteria includes self-reflection, student surveys, analysis of student before & after work samples, and completed modules. During the 2011-2012 school year, I will improve my ability to think more deeply about mathematical concepts using what I am learning through MDC about math formative assessment lessons. I will engage my students in more critical thinking and problem solving about mathematics and help students persevere when struggling to learn new concepts. This will be evidenced by formative assessment lessons student work samples, observation, and self-reflection. Any content area - technology Writing in any content area During the school year, I will increase student use of technology for learning in my classroom. I will collaborate with a district technology cadre to learn ways to integrate learning with technology in instruction. We will also study Kajder’s book Adolescents and Digital Literacies and other resources. Evidence of success includes lesson plans, student work samples, and self-reflection. During the 2011-2012 school year, I will learn to incorporate online writing tools in my writing workshop. After collaborating with the technology resource teacher to investigate Google Docs and other on-line tools, my students will have opportunities to write independently, collaboratively and give/receive feedback using the tools. This will be evidenced by student writing samples, lesson plans, and reflection. 24 1.A In planning and practice, teacher makes content errors or does not correct errors made by students. Teacher displays extensive knowledge of the important concepts in the discipline and the ways they relate both to one another and to other disciplines. Teacher displays little or no understanding of the range of pedagogical approaches suitable to student’s learning of the content. Teacher displays solid knowledge of the important concepts in the discipline and the ways they relate to one another. Teacher is familiar with the important concepts in the discipline but displays lack of awareness of how these concepts relate to one another. Teacher’s plans and practice reflect familiarity with a wide range of effective pedagogical approaches in the discipline, anticipating student misconceptions. Teacher’s plans and practice display little understanding of prerequisite relationships important to student’s learning of the content. Teacher’s plans and practice indicate some awareness of prerequisite relationships, although such knowledge may be inaccurate or incomplete. Teacher’s plans and practice reflect a limited range of pedagogical approaches to the discipline or to the students. Teacher’s plans and practice reflect accurate understanding of prerequisite relationships among topics and concepts. Teacher’s plans and practice reflect familiarity with a wide range of effective pedagogical approaches to the discipline. Teacher’s plans and practice reflect understanding of prerequisite relationships among topics and concepts and provide a link to necessary cognitive structures needed by students to ensure understanding. 1.B The teacher also purposefully seeks knowledge from several sources of students’ backgrounds, cultures, skills, language proficiency, interests, and special needs and attains this knowledge about groups of students. Teacher actively seeks knowledge of students’ levels of development and their backgrounds, cultures, skills, language proficiency, interests, and special needs from a variety of sources. This information is acquired for individual students. Teacher demonstrates little or no understanding of how students learn and little knowledge of students’ backgrounds, cultures, skills, language proficiency, interests, and special needs and does not seek such understanding. Teacher indicates the importance of understanding how students learn and the students’ backgrounds, cultures, skills, language proficiency, interests, and special needs, and attains this knowledge about the class as a whole. Teacher understands the active nature of student learning and attains information about levels of development for groups of students. 1.C All outcomes represent rigorous and important learning in the discipline. All the instructional outcomes are clear, are written in the form of student learning, and suggest viable methods of assessment. Most of the outcomes are suitable for most of the students in the class in accordance with global assessments of student learning. Most outcomes represent rigorous and important learning in the discipline. Outcomes are stated as activities rather than as student learning. Outcomes reflect only one type of learning and only one discipline or strand and are suitable for only some students. Outcomes reflect several different types of learning and opportunities for coordination. Outcomes reflect several different types of learning and, where appropriate, represent opportunities for both coordination and integration. Outcomes reflect several types of learning, but teacher has made no attempt at coordination or integration. Outcomes represent low expectations for students and lack of rigor, and not all of them reflect important learning in the discipline. Outcomes represent moderately high expectations and rigor. Outcomes take into account the varying needs of groups of students. Outcomes take into account the varying needs of individual students. Some outcomes reflect important learning in the discipline and consist of a combination of outcomes and activities. The outcomes are clear, are written in the form of student learning, and permit viable methods of assessment. 1.D Teacher displays awareness of resources – not only through the school and district but also through sources external to the school and on the 25 Internet – available for classroom use, for the expansion of his or her own knowledge, and for students. Teacher displays basic awareness of school or district resources available for classroom use, for the expansion of his or her own knowledge, and for students, but no knowledge of resources available more broadly. Teacher displays extensive knowledge of resources – not only through the school and district but also in the community, through professional organizations and universities, and on the Internet—for classroom use, for the expansion of his or her own knowledge, and for students. Teacher is unaware of school or district resources for classroom use, for the expansion of his or her own knowledge, or for students. 1.E The series of learning experiences is poorly aligned with the instructional outcomes and does not represent a coherent structure. The lesson’s or unit’s structure is clear and allows for different pathways according to diverse student needs. The lesson or unit has a recognizable structure; the progression of activities is uneven, with most time allocations reasonable. The lesson or unit has a clear structure, with appropriate and varied use of instructional groups. The learning activities have reasonable time allocations; they represent significant cognitive challenge, with some differentiation for different groups of students. The activities are not designed to engage students in active intellectual activity and have unrealistic time allocation. Instructional groups do not support the instructional outcomes and offer no variety. Teacher coordinates knowledge of content, of students, and of resources, to design a series of learning experiences aligned to instructional outcomes and suitable to groups of students. Some of the learning activities and materials are suitable to the instructional outcomes and represent a moderate cognitive challenge but with no differentiation for different students. Instructional groups partially support the instructional outcomes, with an effort by the teacher at providing some variety. Plans represent the coordination of in-depth content knowledge, understanding of different students’ needs, and available resources (including technology), resulting in a series of learning activities designed to engage students in high-level cognitive activity. Learning activities are differentiated appropriately for individual learners. Instructional groups are varied appropriately with some opportunity for student choice. 1.F Approach to the use of formative assessment is rudimentary, including only some of the instructional outcomes. The approach to using formative assessment is well designed and includes student as well as teacher use of the assessment information. Teacher intends to use assessment results to plan future instruction for individual students. Assessment criteria and standards are clear. Teacher has a well-developed strategy for using formative assessment and has designed particular approaches to be used. Assessment criteria and standards have been developed, but they are not clear. Assessment methodologies have been adapted for individual students, as needed. Assessment procedures are not congruent with instructional outcomes; the proposed approach contains no criteria or standards. Some of the instructional outcomes are assessed through the proposed approach, but others are not. Teacher has no plan to incorporate formative assessment in the lesson or unit nor any plan to use assessment results in designing future instruction. Teacher intends to use assessment results to plan for future instruction for the class as a whole. Teacher intends to use assessment results to plan for future instruction for groups of students. Teacher's plan for student assessment is aligned with the instructional outcomes; assessment methodologies may have been adapted for groups of students. Teacher's plan for student assessment is fully aligned with the instructional outcomes and has clear criteria and standards that show evidence of student contribution to their development. 26