here - Musgrove Park Hospital
advertisement

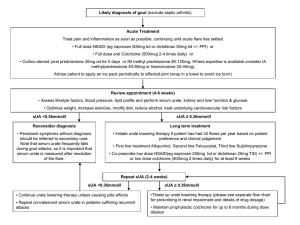
GOUT TREATMENT ALGORITHM 1,2 Typical 1st Likely diagnosis of gout (exclude septic arthritis) MTP joint involvement or crystals on Synovial Fluid polarising microscopy L ACUTE TREATMENT Suppress pain and reduce inflammation until acute flare has subsided. Use one of the following Full-dose NSAID Colchicine* (500 microgram 3-4 times daily reducing course) Avoid if eGFR<30 ml/min Reduce dose by 50% if eGFR < 60 ml/min Corticosteroid (intra-articular, intramuscular) oral (0.5mg/Kg for 5-10 days) Advise patient to use an ice-pack 6-week appointment: sUA ≥ 360 µmol per litre REDUCE RISK FACTORS Switch thiazide /loop diuretic to ACE or Losartan (uricosuric) if possible Reduce alcohol intake (beer especially) Reduce intake fructose/corn syrup in food and drinks Check fasting lipids 6-week appointment: sUA < 360 µmol per litre LONG-TERM TREATMENT Initiate sUA-lowering therapy if patient has had ≥2 flares per year, based on patient preference and clinical judgement. Allopurinol 100mg od +. prophylactic low-dose colchicine Add (500 microgram twice daily) for up to the first six months of treatment (3 months may be sufficient). Alternatives NSAID (but not aspirin) if no contraindications or Prednisolone 10 mg od RECONSIDER DIAGNOSIS Persistent symptoms without definitive diagnosis should be discussed with secondary care Patient education - increased fluid intake 6-week appointment: sUA ≥ 360 µmol per litre Increase allopurinol depending upon sUA Doses as high as 900 mg per day are sometimes required. Start low and slowly increase. Maintain prophylactic colchicine (500 microgram twice daily) . 6-week appointment: sUA < 360 µmol per litre Continue with sUA-lowering therapy Retest sUA every six months to one year Stop colchicine 1 month after hyperuricaemia corrected If allopurinol intolerant (side effects sufficient to warrant discontinuation) or allergic to allopurinol then initiate Febuxostat 80 mg od. If sUA >360 after 2-4 weeks increase to 120MG od Gout flares while taking sUA lowering therapy Suppress pain and reduce inflammation. Do not interrupt sUA lowering therapy unless there is a clinical reason *Colchicine is the preferred treatment for patients who have concomitant conditions and who are taking medications that contraindicate the use of NSAIDs + Allopurinol dosage reduction in renal failure:/elderly: start low (1.5 mg per unit of eGFR) or 50 mg od and increase gradually 1. Zhang W, Doherty M, Pascual E et al. EULAR evidence based recommendations for gout. Part I: Diagnosis. Report of a task force of the Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis 2006; 65: 1301–11. Part II: Management. Report of a task force of the Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT), Ann Rheum Dis 2006; 65: 1312–24. 2. Jordan KM, Cameron JS, Snaith M et al. British Society for Rheumatology and British Health Professionals in Rheumatology guideline for the management of gout. Rheumatology 2007; 46: 1372-4. 3. Khanna D et al 2012 American College ofRheumatology Guidelines for management of gout Parts 1 and 2 Arthritis Care & Research 2012 64 :1447-1461 This treatment algorithm has been produced as an educational service by A. Menarini Pharma UK SRL and adapted locally by Cathy Laversuch and Shaun Green.