Lewis Structures
advertisement

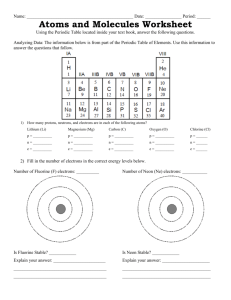
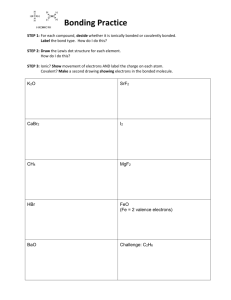
Guidelines for Constructing LEWIS STRUCTURES: For Covalent Compounds 1. Determine the # of each kind of atom from the molecular formula. 2. Determine the TOTAL # of valence electrons available to use by counting the number of valence electrons for each atom in the compound and then adding all the total of all the electrons Special NOTE for polyatomic ions: Add one electron for each negative charge Subtract one electron for each positive charge. 3. Determine the # of valence electrons needed to satisfy the octet rule for all atoms EXCEPT hydrogen, H. The maximum number of valence electrons required for hydrogen is 2. The maximum number of valence electrons required to satisfy the octet rule for all other atoms is 8. 4. Determine the # of bonds by subtracting the # of available electrons from the # of needed electrons. 5. Determine the # of bonds by dividing the # of bonding e-s by 2 because there are 2 electrons in a single bond. 6. Place the chemical symbol of the element present in the smallest amount in the center of the molecule and arrange all other atoms around it using the number of bonds calculated in #5 above. Represent each bond by a single line between the bonded atoms. Then add the nonbonding electrons so that every atom (EXCEPT H) has access to 8 electrons. Hydrogen should have access to 2 electrons. Special NOTE for polyatomic ions: Place square brackets around the [structure] and put the charge outside the brackets in the upper right-hand corner. Lewis Structure Practice You are to complete the following Lewis structures showing work to support your structure. Refer to the guidelines. Silicon tetrachloride and the phosphate ion have been done for you as examples. This is an important fundamental aspect of this course upon which several other concepts are built. Instructions: Draw the Lewis structure for each of the following molecules or ions. Show your work, meaning calculations of: Available (valence) electrons Needed electrons REMEMBER: hydrogen only needs two Bonding electrons # of bonds Be sure to show the Nonbonding electrons also!! 1. silicon tetrachloride, SiCl4 Atoms present: Si Cl Available (valence) electrons 4 7 Needed electrons 8 8 Bonding electrons 40e - 32e = 8e # of bonds 8e-/2e- per bond = 4 bonds Cl 7 8 2. nitrogen triiodide, NI3 Atoms present: Available electrons Needed electrons Bonding electrons # of bonds N I I H H S 3. hydrogen sulfide, H2S Atoms present: Available electrons Needed electrons Bonding electrons # of bonds 4. carbon dioxide, CO2 I Cl 7 8 Cl 7 8 Total e32 40 Atoms present: Available electrons Needed electrons Bonding electrons # of bonds C O O 5. acetylene, C2H2 Atoms present: Available electrons Needed electrons Bonding electrons # of bonds 6. sulfur dioxide, SO2 Atoms present: Available electrons Needed electrons Bonding electrons # of bonds 7. phosphate ion, PO4-3 Atoms present: P O Available electrons 5 6 Needed electrons 8 8 Bonding electrons 40e - 32e = 8e# of bonds 8e /2e per bond = 4 bonds 8. carbonate ion, CO3-2 Atoms present: Available electrons Needed electrons Bonding electrons # of bonds Extra O 6 8 O 6 8 O 6 8 e3 Total e32 40