Nutrition Unit STUDY GUIDE
advertisement

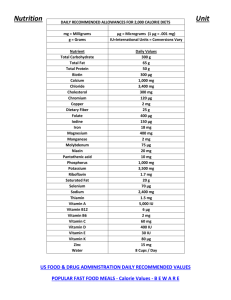
Nutrition Unit STUDY GUIDE Types of NUTRIENTS ENERGY UNITS METABOLISM o BMR – Basal Metabolic Rate FATS o Saturated o Unsaturated o Trans o Cholesterol Minerals, Vitamins, Supplements, electrolytes Amino Acids Glycogen Scurvy, Anemia Dehydration Homeostasis Nutrient Density Understand Food Pyramid Daily Recommended Values o Based on how many calories? Components of a food label Body Mass Index Obesity Fad Diets Types of Diets Anti-Oxidants VOCABULARY: 1. Amino Acids: small units that are bound together chemically to form proteins. 2. Metabolism: the chemical process by which the body breaks down food to release energy. 3. Carbohydrate: a nutrient made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen that supply energy. 4. Calories: unit for the amount of energy released when nutrients are broken down. 5. Protein: a nutrient that contains nitrogen as well as carbon, hydrogen and oxygen; needed for the growth and repair of body tissues. 6. Nutrients: a substance in food that the body needs to regulate bodily functions, promote growth, repairs body tissues and obtains energy. 7. Fats: a nutrient made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; supplies energy, forms cells, maintains body temperature and protects nerves. 8. Fiber: a type of complex carbohydrate that is found in plants and is necessary for the proper functioning of the digestive system. 9. Trans Fat: the type of fat produced when manufacturers add hydrogen to the fat molecules in the vegetable oil. 10. Cholesterol: a waxy, fat like substance that is found only in animal products. 11. Vitamins: a nutrient that is made by living things is required in small amounts and assists in chemical reactions in the body. 12. Fat Soluble Vitamins: which dissolve in fatty material. Vitamins A, D, E 13. Sodium: mineral, important in functioning of the heart and water balance can raise blood pressure. 14. Mineral: a nutrient that occurs naturally in rocks or soil; needed by the body in small amounts. 15. My Pyramid Plan: a plan that groups foods according to types and indicates how much of each type should be eaten daily for a healthy diet. 16. Unsaturated Fats: a fat with at least one unsaturated bond in place where hydrogen can be added to the molecule. 17. Nutrient-Dense Food: a food that contains lots of vitamins and minerals relative to the number of calories but is low in saturated fat, Trans fat, added sugar and salt. 18. Antioxidant: a vitamin that helps protects healthy cells from the damage caused by the normal aging process as well as certain types of cancer. 19. Dehydration: a serious deduction in the body’s water content. 20. Saturated Fats: a fat that has all the hydrogen the carbon atoms can hold. 1. Overweight: term used to describe a person who is heavier than the standard for the person’s height. 2. Body Composition: a measure of how much body fat a person has as compared to muscle and bone. 3. Body Mass Index (BMI): a ratio of a person’s weight to height. BMI = [weight / height^2]* 703 4. Hunger: a feeling of discomfort caused by the body’s need for nutrients. 5. Appetite: a desire for food based more on emotional and other factors than on nutritional need. 6. Vegan: a person who does not eat food from any animal source. 7. Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): the rate at which a person uses energy when the body is at rest. 8. Nutrient Dense Food: a food that contains lots of vitamins and minerals relative to the number of calories but is low in saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, and salt. 9. Daily Values: recommendations that specify the amounts of certain nutrients that the average person should obtain every day. 10. Fasting: refraining from eating 11. Food Allergy: the immune systems response to the proteins in certain foods. 12. Fad Diet: Popular diets that may help a person lose or gain weight but without proper regard for nutrition and other health issues. 13. Obesity: condition in adults who have a body mass index of 30 or higher. 14. Type 2 Diabetes: is a disease in which the body does not properly use insulin, a substance that controls blood glucose levels. 15. Anorexia: eating disorder in which a person doesn’t eat enough food to maintain a healthy weight. 16. Food Intolerance: the inability to digest a particular food or food additive. 17. Mega Dose: over dosage. Not a wise investment. 18. Bulimia: an eating disorder in which a person has uncontrolled eating binges followed by purging. 19. Food Labels: lists specific nutritional facts about the food including calories, nutritional content, and ingredients