Medical Roots

Medical Roots.
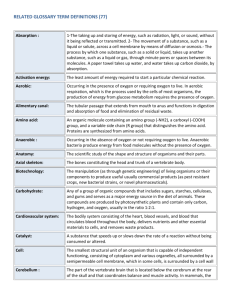
1.
Aden- Gland; a cell, or group of cells, or organ of endothelial origin that selectively removes materials from the blood, concentrates or alters them, and secretes them for further use in the body or for elimination from the body.
2.
Adren- adrenal glands; either of a pair of complex endocrine organs near the anterior medial border of the kidney consisting of a mesodermal cortex that produces glucocorticoid.
3.
Appendix- appendix; bodily outgrowth or process.
4.
Arthr- joints; The point of contact between elements of an animal skeleton whether movable or rigidly fixed together with the surroundings and supporting parts.
5.
Blephar- Eyelid; movable lids of skin and muscle that can be closed over the eyeball.
6.
Bucc- Cheek; the fleshy side of the face below the eye and above and to the side of the mouth.
7.
Cephal- Head; the division of the humans body that contains the brain, the eyes, the ears, the nose, and the mouth.
8.
Cervix- Neck; the back part of the neck.
9.
Chloe- bile; a yellow or greenish viscid alkaline fluid secreted by the liver and passed into the duodenum where it aids especially in the emulsification and absorption of fats called also fel.
10.
Col- Colon; the part of the large intestine that extends from the cecum to the rectum.
11.
Crani- Cranium; the skull, or brain case.
12.
Cyst- Urinary Bladder; a distensible membranous sac that serves the temporary retention of the urine.
13.
Dactyl- A finger or a toe.
14.
Derm- Skin; the 2 layered covering of the body consisting of an outer ectodermal epidermis that is more less cornified and penetrated by the openings of sweat and sebaceous glands and an inner mesodermal dermis that is composed largely of connective tissue and is richly supplied with blood vessels and nerves.
15.
Enter- intestine; the tubular portion of the alimentary canal that lies posterior to the stomach from which it is separated by the pyloric sphincter and consist of a slender but long anterior.
16.
Gingival- gum; a narrow space between the free margin of the gingival epithelium and the adjacent enamel of a tooth.
17.
Hemo- Blood, (AmE); The fluid that circulates in the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins of a vertebrate animal carrying nourishment and oxygen to and bringing away a waste products from all parts of the body.
18.
Histo- Tissue; an aggregate of cells usually of a particular kind together with their substance that form one of the structural materials of a plant or an animal and that in animals include connective tissue, epithelium, muscle tissue, and nerve tissue.
19.
Lapar- abdominal wall, flank; A fleshy part of the side between the ribs and the hip.
20.
Lipo- Fat; notable for having an unusual amount of fat.
21.
Mast- Breast; either of the pair mammary glands extending from the front of the chest in the pubescent and adult females of human and some other mammals.
22.
Naso- nose; The part of the face that bears the nostrils and covers the anterior part of the nasal cavity; this part together with the nasal cavity.
23.
Myelo- Bone marrow; a softly highly vascular modified connective tissue that occupies the cavities and cancellous part of most bones and occurs in 2 forms.
24.
Neuro- Nerves; any of the filamentous bands of nervous tissue that connects parts of the nervous system with the other organs.
25.
Odont- Tooth; Any of the hard bony appendages that are borne on the jaws and serve especially for the prehension and mastication of food.
26.
Ophthalm- Eye; An organ of sight. A nearly spherical hollow organ that is lined with a sensitive retina.
27.
Oss- Bony; consisting of or resembling bone.
28.
Oto- Ear; The characteristic vertebrate organ of hearing and equilibrium consisting in the typical mammal of a sound-collecting outer ear separated by the tympanic membrane from a sound-transmitting middle ear that in turn is separated from a sensory inner ear by membranous fenestrae.
29.
Phleb- Vein; Any of the tubular branching vessels that carry blood from capillaries toward the heart and have thinner walls than the arteries and often valves at intervals to prevent reflux of the blood which flows in a steady stream and is in most cases dark-colored due to the presence of reduced hemoglobin.
30.
Pleura- Ribs; either of a pair of 2-walled sacs of serous membrane each of which lines one lateral half of the thorax.
31.
Pod- Foot; The terminal part of the vertebrate leg upon which an individual stands.
32.
Pulmon- Lung; A mechanical device for regularly introducing fresh air into and withdrawing stale air from the lungs.
33.
Ren- Kidney; One of a pair of vertebrate organs situated in the body cavity near the spinal column that excrete waste products of metabolism.
34.
Salpingo- Fallopian tube; surgical excision of a fallopian tube and an ovary.
35.
Spondyl- Vertebrae; Any of the bony or cartilaginous segments that make up the spinal column and that have a short more or less cylindrical body whose ends articulate by pads or elastic or cartilaginous tissue with those of adjacent vertebrae and a bony arch that encloses the spinal cord.
36.
Thorac- Chest; The part of the body enclosed by the ribs and the sternum.
37.
Valv- A bodily structure that closes temporarily a passage or orifice permits movement of fluid in one direction only.
38.
Vena- Large Veins; Either of 2 large veins by which the blood is returned t the right atrium of the heart.
39.
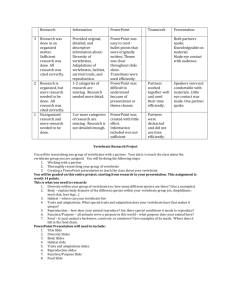
Cardi- Heart; A structure in an invertebrate animal functionally analogous to the vertebrate heart.
40.
Later- Side; of or relating to the side, lying at or extending toward the right or left side.
41.
Angi- Blood Vessels; Any of the vessels through which blood circulates in the body.
42.
Arter- Artery; Any of the tubular branching muscular- and elastic- the body.
43.
Aur- Ear; the characteristic vertebrate organ or hearing and equilibrium consisting in the typical mammal of sound- collecting outer ear separated by the tympanic membrane.
44.
Bronchus- Either of the two primary divisions of the trachea that lead respectively into the right and the left lung.
45.
Cereber- Brain; A nervous center in the invertebrates comparable in positions and function to the vertebrate brain.
46.
Cheil- lip; Either of a pair of fleshy folds surrounding an orifice.
47.
Chondr- Cartilage; A usually translucent somewhat elastic tissue that composes most of the skeleton of vertebrate embroys.
48.
Cost- Ribs; Ribs with the beading that is characteristic of rickets.
49.
Cut- Skin; To penetrate with or as if with an edged instrument.
50.
Cyt- Cell; A small usually microscopic mass of protoplasm bounded externally by a semipermeable membrane.
51.
Dent- Teeth; any of the hard and bony appendages that are borne on the jaws.
52.
Dors- Back; The rear part of the human body especially from the neck to the end of the spine.
53.
Gastro- Stomach; A saclike expansion of the alimentary canal of a vertebrate.
54.
Gloss- Tongue; A process of the floor of the mouth that is attached basally to the hyoid bone.
55.
Hepat- Liver; Any various large compound glands associated with the digestive tract of invertebrate.
56.
Hyster- Uterus; An organ in female mammals for containing and usually for nourishing the young during development prior of birth.
57.
Lingua- Tongue; A process of the floor of the mouth that is attached basally to the hyoid bone.
58.
Mamm- Breast; The fore or ventral part of the body between the neck and the abdomen.
59.
Myo- Muscle; A body tissue consisting of long cells that contract when stimulating and produce motion.
60.
Myring- Eardrum; The part of your ear that you hear through.
61.
Nephr- Kidney; Any of various excretory organs of invertebrate mammals.
62.
Ocular- Eye; Is they part of the head that you see through.
63.
Oophor- Ovary; One of the typically paired essential female reproductive organs that produce eggs and in vertebrates female sex hormones.
64.
Orch- Testis; A typically paired male reproductive gland that produces sperm and secretes testosterones and that in most mammals in contained within the scrotum at sexual maturity.
65.
Osteo- Bone; One of the hard parts of the skeleton of a vertebrate.
66.
Pedes- Foot; The terminal part of the vertebrate leg upon which an individual stands.
67.
Phren- Mind; The element or complex of elements in an individual that feels, perceives, thinks, wills, and especially reasons.
68.
Pneum- Lungs; One of the usually paired compound saccular thoracic organs that constitute the basic respiratory organ of air- breathing vertebrates.
69.
Proct- Anus or Rectum; The posterior opening of the alimentary canal.
70.
Pyelo- Pelvis; A basin-shaped structure in the skeleton of many vertebrates that is formed by the pelvic girdle and adjoining bones of the spine.
71.
Rhino- Nose; The part of the face that bears the nostrils and covers the anterior part of the nasal cavity.
72.
Splen- Spleen; A highly vascular ductless organ that is located in the left abdominal region near the stomach or intestine of most vertebrates and is concerned with final destruction of red blood cells, filtration and storage of blood, and production of lymphocytes.
73.
Stoma- Stomach; Any various small simple bodily openings especially in a lower animal.
74.
Utero- Uterus; in the uterus, before birth.
75.
Vaso- Vessel; A conducting tube in the xylem of a vascular formed by the fusion and loss of end walls of a series of cells.
76.
Ventra- Ventral; of or relating to the belly.