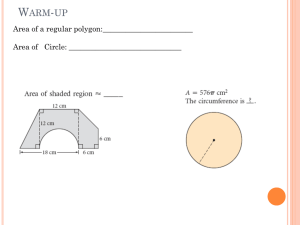
Lesson 1.6 Circles notes
advertisement
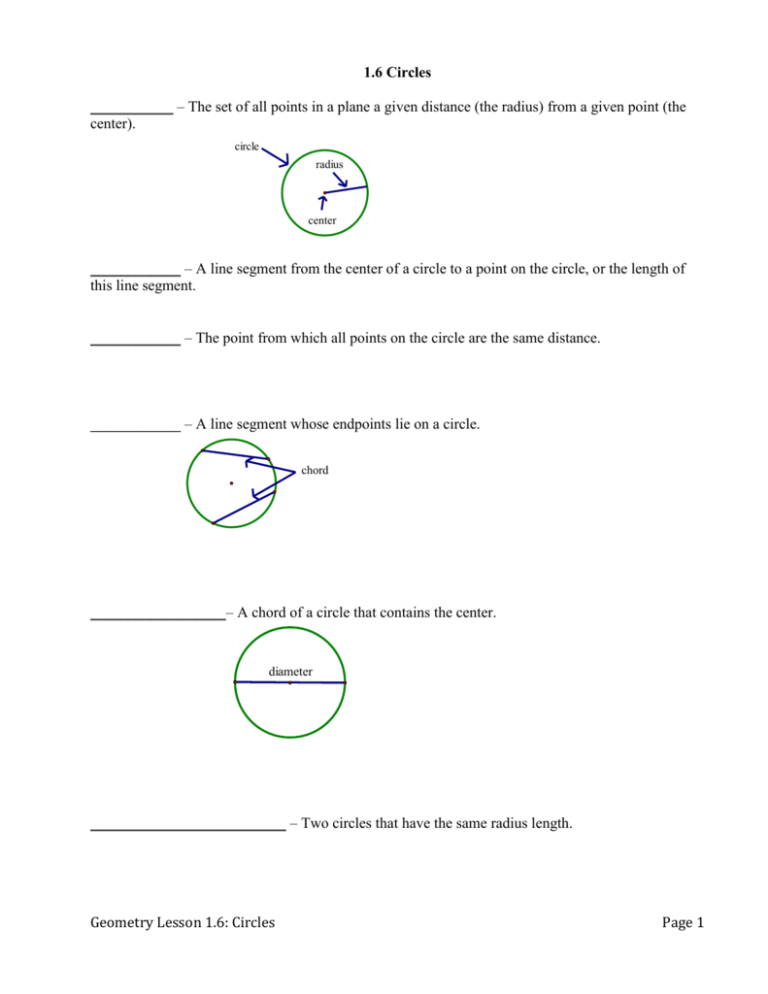
1.6 Circles ___________ – The set of all points in a plane a given distance (the radius) from a given point (the center). circle radius center ____________ – A line segment from the center of a circle to a point on the circle, or the length of this line segment. ____________ – The point from which all points on the circle are the same distance. ____________ – A line segment whose endpoints lie on a circle. chord __________________– A chord of a circle that contains the center. diameter __________________________ – Two circles that have the same radius length. Geometry Lesson 1.6: Circles Page 1 _____________________________ – Two or more circles having the same center. _____________________ – A line that lies in the plane of a circle and that intersects the circle at exactly one point. point of tangency tangent line ___________________________ – The point where a tangent line intersects the circle. ________________ – A line that intersects a circle in two points. It contains a chord of the circle. secant Geometry Lesson 1.6: Circles Page 2 ________ – Two points on the circle (the endpoints of the _______) and the points of the circle between them. An angle intercepts an _______ if the sides of the angle intercept the circle at the endpoints of the __________. The _________ is included by the chord with the same endpoints. ______________________ – An arc whose measure is less than the measure of a semicircle (180). A minor arc is named with 2 points, the endpoints. ______________________ – An arc whose measure is greater than the measure of a semicircle (180). A major arc is named using 3 points, the endpoint and any point on the arc between the endpoints. ___________________________ - An arc of a circle included by a diameter. Half of a circle (180). A semicircle is named using 3 points, the endpoints and any point on the semicircle between the endpoints. ________________________ – An angle whose vertex is the center of a circle and whose sides pass through the endpoints of a chord or arc. minor arc major arc central angle _____________________ – The measure of the central angle that intercepts an arc, measured in degrees. Geometry Lesson 1.6: Circles Page 3 Example 1: D F G B C A E H I a) Name 2 chords. b) Name 2 radii. c) Name a diameter. d) Name a tangent. e) Name a secant. Geometry Lesson 1.6: Circles Page 4 Example 2: BC is a diameter m BAE = 46 m DAC = 73 D C B A E a) Name a central angle. b) Name a minor arc and find its measure. c) Name a major arc and find its measure. d) Name a semicircle. pp. 70 – 71 => 1 – 10; 18 - 20 Geometry Lesson 1.6: Circles Page 5