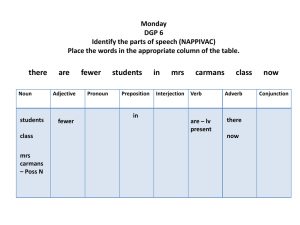
Chapter 2 Notes
advertisement

Mrs. Stahl 1 Chapter 2 Notes Vocabulary Review: Abiotic:_______________________________________________________________________________ Biotic:________________________________________________________________________________ Ecosystems:___________________________________________________________________________ Habitat:______________________________________________________________________________ Microhabitat:__________________________________________________________________________ Homeostasis:__________________________________________________________________________ Homeostasis with Marine Organisms: Problems-> ___________________________________________________________________________ Optimal Range->_______________________________________________________________________ Zones of Stress-> _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Zones of Intolerance-> _____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ What happens if an organism lives outside its optimal range? ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ Mrs. Stahl 2 Chapter 2 Notes Optimal Range Chart Physical Characteristics of Marine Environment ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ Sunlight- The basis of all life ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Mrs. Stahl 3 Chapter 2 Notes ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Sunlight and the Shoreline: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Temperature Ectotherms: _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Example-> ____________________________________________________________________________ They are sluggish when temperatures are low and very active when temperatures are high. Endotherms: _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Example-> ____________________________________________________________________________ Temperature also affects the distribution of organisms Tidal pools-> _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Salinity Definition-> _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Mrs. Stahl 4 Chapter 2 Notes Solutes-> substances that are dissolved in water. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Example-> In the open ocean spider crabs cannot regulate the salt concentration of their body fluids because their bodies absorb water and salt. Bays, estuaries, and tide pools are really affected because of evaporation. Water evaporates but the salt remains highly concentrated. Fiddler Crab-> able to adjust the salt content of their body tissues by regulating salt and water retention. Pressure ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Metabolic Requirements Nutrients-> _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Seawater-> _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Mrs. Stahl 5 Chapter 2 Notes Oxygen-> ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Cooler/ less salty water= more oxygen Warm / saline water= less oxygen Anaerobic organisms-> ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Aerobic organisms-> ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Too many nutrients cause issues such as run-off (eutrophication) which increases nutrient levels -> Explosion= algal blooms or photosynthetic plankton blooms -> plankton dies-> bacteria decomposes-> decomposition depletes water of oxygen -> organisms die-> decomposition-> massive die offs Metabolic Waste ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Populations- a group of the same species Example-> _________________________________________________ Characteristics: ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Mrs. Stahl 6 Chapter 2 Notes How is population determined? 1. ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Mark Recapture Captured-> tagged-> released-> wait a sufficient amount of time for the animals to mix back into the population = sample is taken again and the ration of marked: unmarked is documented. Example: Tag 10 nurse sharks-> release-> two weeks later catch 10 more-> and two of the 10 have tags= 20% of the entire population in the area-> population would be 50 sharks because 20% of 50 =10, and 10 is how many were tagged initially. Population Density The number of individuals per unit area or volume. Example-> the number of barnacles on a square meter of rock Three types of dispersion: clumped, uniform, and random Dispersion- pattern Clumped Uniform of spacing among individuals within the range Definition Example Random Mrs. Stahl 7 Chapter 2 Notes Changes in population size ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Examples-> _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Survivorship = life expectancy / longevity Type 1 Type 2 Type 3 Mrs. Stahl 8 Chapter 2 Notes Life History-> birth, reproduction, and death __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ Clutch Size # Events Age Q???? What would be the benefit of an organism reproducing once in its lifetime? ___________________________________________________________________________________ Terms to know!!!!!!! Biological fitness-> _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Opportunistic Species-> _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Equilibrium Species-> _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Population Growth Recruitment 1. Reproduction 2. Immigration (new individuals from other populations joining Mrs. Stahl 9 Chapter 2 Notes Phytoplankton Bloom- “J Curve” or exponential logarithmic growth Mrs. Stahl 10 Chapter 2 Notes Population Regulation What factors determine the carry capacity of an environment? __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ * ______________________________ * ______________________________ * ______________________________ Communities-> Populations of different species in the same habitat Example-> ____________________________ Niche-> “occupation” its role in the environment Examples-> 1. _____________________________________________________ 2. _____________________________________________________ 3. _____________________________________________________ Mrs. Stahl 11 Chapter 2 Notes What makes up a niche? 1. 2. 3. 4. __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Biological Interactions Competition-> _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Can Be: ___________________________________ __________________________________ ___________________________________ __________________________________ No two groups of organisms can use exactly the same resources in exactly the same place at the same time. Results of competition Mrs. Stahl 12 Chapter 2 Notes Predator- Prey Interactions ___________________________________________________________ Plants-> herbivores-> omnivores / carnivores If there is not enough vegetation herbivores will decline (starvation) -> vegetation increases-> herbivores increase. Carnivores and their prey (they switch when prey declines) Some predators focus on species that are abundant because they expend less energy Carnivores eats lots of one species Prey replenishes Carnivore starves Prey Prey declines Keystone Species-> they keep the entire ecosystem in check. Example-> ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Sea Otters: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Mrs. Stahl 13 Chapter 2 Notes Symbiosis: “living together” Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Definition Example Energy Flow Through Ecosystems Producers / Autotrophs -> _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Mrs. Stahl 14 Chapter 2 Notes Equation for Photosynthesis: _____________________ + _____________________ -> __________________+ ________________ Not all producers are photosynthetic, some are chemosynthetic (use energy from chemical reactions) Ex.-> Bacteria inhabit deep sea vents Consumers / Heterotrophs-> rely on others for food Detritivores-> ______________________________________________________________________ Decomposers->_____________________________________________________________________ Mrs. Stahl 15 Chapter 2 Notes Biomass pyramid Food Chain vs. Food Web Food Web Biogeochemical Cycles-> cycles of nutrients needed for life Hydrologic Cycle-> Water Equator= supplies the greatest amount of evaporation in all the oceans due to excessive eat and sunlight. Water vapor is carried north and south from the equator and west to east within each hemisphere. When air masses cool and rise = precipitation Mrs. Stahl 16 Chapter 2 Notes Sea Salt= precipitation nuclei= sea salt enters the air because of waves crashing. They then collect water droplets and when they get heavy enough they fall back onto the ground as precipitation. Carbon Cycle: Carbon is essential for all living things Backbone of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids Living organisms produce carbon when they respire Organism dies Decomposers breakdown tissues (CO2) Marine producers use the CO2 in photosynthesis to make carbohydrates Carbohydrates are used to make other materials CO2 reacts with seawater to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) which forms hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions Bicarbonate ions are absorbed by marine life and they combine with calcium carbonate (shells and skeletons) The calcium carbonate collects in the sediment and becomes limestone. The limestone appears on land through geological processes where it becomes weathered (wind / rain) -> washes back into the ocean. Mrs. Stahl 17 Chapter 2 Notes Nitrogen Cycle Producers require nitrogen for protein synthesis, growth, and reproduction Ammonia= NH3, ammonium=NH4, nitrite=NO2, nitrate= NO3 Producers use energy from photosynthesis to concentrate the nitrogen in their tissues and then turn that energy into amino acids-> proteins Nitrogen is then passed in the form of proteins to consumers Proteins and amino acids get processed and released through uric acid, urea, and ammonia Atmosphere= 79% Thunderstorms-> produce nitrates that enter through precipitation Major nitrogen fixing organism in the ocean is cyanobacteria Run-off from land contains nitrogen from fertilizers, sewage, and dead biotic factors= huge growth of phytoplankton The Biosphere-> the Earth= all communities and ecosystems Kelp forests, estuaries, salt marshes, mangrove swamps, rocky shores, sandy shores, coral reefs, open ocean Estuary-____________________________________________________________________ Intertidal Zone-______________________________________________________________ Ocean ZonesPelagic Zone-___________________________________________________________________ Benthic-_______________________________________________________________________ Neritic-________________________________________________________________________ Open Ocean-___________________________________________________________________ Photic Zone-____________________________________________________________________ Aphotic Zone-___________________________________________________________________ Shelf Zone-______________________________________________________________________ Bathyal Zone-____________________________________________________________________ Abyssal Zone-____________________________________________________________________ Hadal Zone-_____________________________________________________________________ Epifauna-_______________________________________________________________________ Mrs. Stahl 18 Chapter 2 Notes Infauna-_______________________________________________________________________ Label the: Intertidal Pelagic Zone Abyssal Zone Benthic Zone Shelf Zone Oceanic Zone Neritic Zone Bathyal Hadal Photic Zone Aphotic Zone