Chapter 20 Outline
advertisement
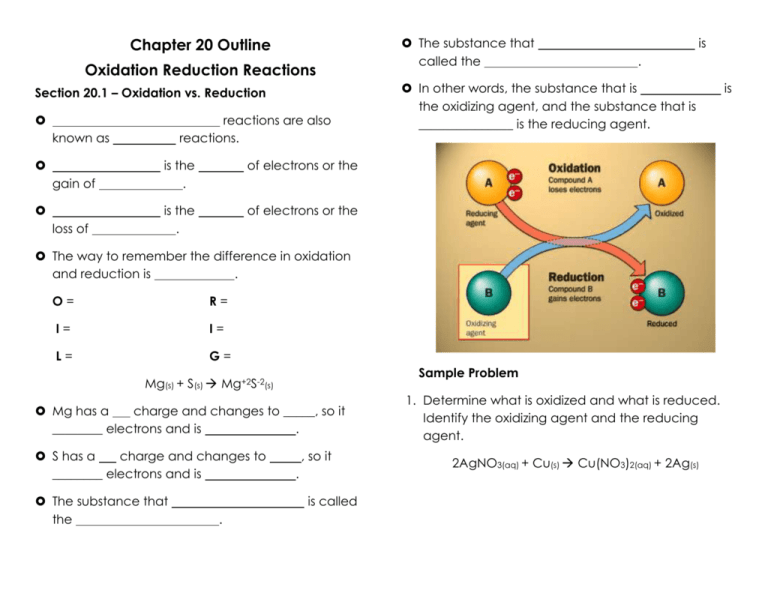
Chapter 20 Outline Oxidation Reduction Reactions Section 20.1 – Oxidation vs. Reduction reactions are also reactions. known as of electrons or the gain of is the . of electrons or the loss of is the . The substance that called the is . In other words, the substance that is the oxidizing agent, and the substance that is _______________ is the reducing agent. The way to remember the difference in oxidation and reduction is . O= R= I= I= L= G= Sample Problem Mg(s) + S(s) Mg+2S-2(s) Mg has a charge and changes to _____, so it ________ electrons and is . S has a charge and changes to ________ electrons and is The substance that the , so it . is called . 1. Determine what is oxidized and what is reduced. Identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent. 2AgNO3(aq) + Cu(s) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s) is Practice Problem 1. Determine which substance is oxidized and which is reduced. Identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent. 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) 2Al2O3(s) Section 20.1 Assessment 1. Define oxidation and reduction in terms of loss or gain of oxygen. 2. Define oxidation and reduction in terms of loss or gain of electrons. 3. How do you identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent in a redox reaction? Section 20.2 – Oxidation Numbers An is a positive or negative ______________ assigned to an atom to indicate its ______________ of oxidation or reduction. A atom’s oxidation number is the _____________ that it would have if the electrons in the bonded were assigned to the atom of the more element. Rules for Oxidation Numbers 1. The oxidation number of a equal to its is . Ex: Br- = Fe+3 = 2. The oxidation number for is ________________________ where it is except in . Ex: HCl, H = NaH, H = 4. Determine which substance is oxidized and which is reduced. Identify the oxidizing agent and reducing agent. Mg(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) Mg(NO3)2(aq) + Cu(s) 3. The oxidation number for in where it is Ex: MgO, O = H2O2, O = is . except 4. The oxidation number of a element is . Ex: Ag = N2 = 5. For a , the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal . Ex: NaCl = H2O = 6. For a , the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal the _____________________ of the ion. Ex: CO3-2, O = , so C = Sample Problem 1. What is the oxidation number of each element in Na2SO4? Practice Problems 1. Assign the oxidation numbers for each element in SO2. 2. Assign the oxidation number for each element in (NH4)2S. In some , it is necessary to look at instead of just using charges. Sample Problem 1. Identify which atoms are oxidized and which are reduced in the reaction. 2KNO3(s) 2KNO2(s) + O2(g) Practice Problem 1. Identify which atoms are oxidized and which are reduced in the reaction. 2HNO3(aq) + 6HI(aq) 2NO(g) + 3I2(s) + 4H2O(l) Section 20.2 Assessment 1. What is the general rule for assigning oxidation numbers? 2. Identify which atoms are oxidized and which are reduced. 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) 2NaCl(s)








