Topic XXVIII – Genetic Diseases and Human Genetics
advertisement

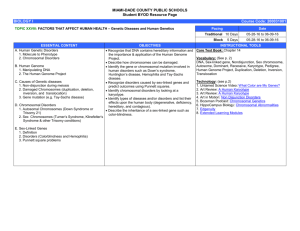
MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page BIOLOGY I HONORS Course Code: 200032001 TOPIC XXVIII: FACTORS THAT AFFECT HUMAN HEALTH – Genetic Diseases and Human Genetics Pacing Date Traditional 10 Days Block ESSENTIAL CONTENT A. Human Genetic Disorders 1. Molecule to Phenotype 2. Chromosomal Disorders 5 Days 05-28-16 to 06-09-16 INSTRUCTIONAL TOOLS Recognize that DNA contains hereditary information and Core Text Book: Chapter 14 the importance & application of the Human Genome Vocabulary: Project. DNA, Sex-linked gene, Nondisjunction, Sex chromosome, Describe how chromosomes can be damaged. B. Human Genome Autosome, Dominant, Recessive, Karyotype, Pedigree, Identify the gene or chromosomal mutation involved in 1. Manipulating DNA Human Genome Project, Duplication, Deletion, Inversion, human disorders such as Down’s syndrome, 2. The Human Genome Project Translocation Huntington’s disease, Hemophilia and Tay-Sachs disease. Technology: C. Causes of Genetic diseases Recognize disorders caused by sex-linked genes and 1. Non-disjunction during meiosis 1. Untamed Science Video: What Color are My Genes? predict outcomes using Punnett squares. 2. Damaged Chromosomes (duplication, deletion, 2. Art Review: A Human Karyotype . Identify chromosomal disorders by looking at a inversion, and translocation) 3. Art Review: A Human Karyotype karyotype. 3. Gene mutation (e.g. Tay-Sachs disease) 4. Art in Motion: Non Disjunction Disorders Identify types of diseases and/or disorders and list their effects upon the human body (degenerative, deficiency, 5. Bozeman Podcast: Chromosomal Genetics D. Chromosomal Disorders 6. HippoCampus Biology: Chromosomal Abnormalities hereditary, and contagious). 1. Autosomal Chromosomes (Down Syndrome or 7. Edgenuity State the goals of the Human Genome Project and Trisomy 21) 8. Extended Learning Modules explain what we have learned so far. 2. Sex Chromosomes (Turner’s Syndrome, Klinefelter’s Describe the inheritance of a sex-linked gene such as Syndrome & other Trisomy conditions) color-blindness. E. Sex-Linked Genes 1. Definition 2. Disorders (Colorblindness and Hemophilia) 3. Morgan and Fruit fly eye color 4. Punnett square problems F. Examining Human Chromosomes & 1. Traits 2. Karyotype 3. Pedigree (automosal or sex-linked, dominant or recessive; e.g. Huntington’s disease) OBJECTIVES 05-28-16 to 06-09-16 MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page BIOLOGY I HONORS SC.912.L.16.2 Course Code: 200032001 Human Karyotyping Video Standard: SC.912.L.15.15 Audio Video Standard: SC.912.L.16.2 Audio The Human Genome Project Heredity: How Our Parents' Genes Affect Us DNA and the Human Genome Project Nondisjunction Evolution: Sources of Variability: Recombination Choromosomal Alteration That May Closing Remarks: Sex-Linked Occur During Meiosis: Investigating the Inheritance Process of Nondisjunction The Effects Produced by Chromosomal Introduction: Chromosomal Alterations Alterations Discovery of Down Syndrome Genetic Disease Patterns of Inheritance Survey and Data Analysis: Dominant and Recessive Traits for Hairline, Thumb, and Earlobes Research Results Introduction: Sex-Linked Inheritance Research on the Genetic Make-up of the Fruit Fly Drosophila Karyotype: A Key to the Study of SexLinked Inheritance Evolution: Sources of Genetic Variability: Mutation Heredity: Sex-Linked Genetic Conditions in Humans Inherited Human Traits and Patterned Sex-Linked Inheritance Color Blindness Organizing Information About SexLinked Inheritance in Pedigree Charts Hemophylia Closing Remarks: Sex-Linked Inheritance Heredity: Sex Linkage Heredity: Problems Using Sex Chromosomes & Sex Linkage Sex-Linked Traits Single Gene Disorders Incomplete Dominance in Snapdragons Incomplete Dominance in Humans and Plants Reviewing Key Terms That Relate to Patterns of Inheritance Multiple Alleles and Co-Dominance in Human Blood Types Rabbit Breeding MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page BIOLOGY I HONORS Standard: SC.912.L.16.2 Standard: HE.912.C.1.7 Course Code: 200032001 Image Video Mosaic Down syndrome; nondisjunction in early embryo Human trisomies Mutation types; protein changes Translocation Mutation DNA sequence; nature of mutation Base pairing errors; generation of mutations Base substitution mutation Insertion and deletion mutations Down syndrome; distinguishing between types Mosaic Down syndrome; nondisjunction in early embryo Down syndrome; mapping effects of extra DNA Trisomy; gene dosage effects Multifactorial Disorders Heredity: How Our Parents' Genes Affect Us Basic Facts About Cancer Obesity Diabetes Hunting Down the Genes Involved in Disease DNA and the Genetics of Cancer Families and Genetic Disease Genetic Case Study: Addison's Disease Cystic Fibrosis Human trisomies X-linked dominant trait; pedigrees Colorblindness pedigrees; X-linked recessive trait Probability of colorblind child - Punnett square Probability of colorblind child - answer Karyotype Chromosomes Risk Factors for Heart Disease DNA Screening High & Low Risks for Cancer High & Low Risks for Cardiovascular Disease High & Low Risks for Diabetes MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Student BYOD Resource Page BIOLOGY I HONORS Course Code: 200032001 Video Mapping the Human Genome No Interest in the Gym? It May Be Genetic Gene Therapy Offers New Hope to Cancer Patients Researchers Discover Genes Linked to Deadly Cancers For Mixed Race Patients, Few Bone Marrow Donors Researchers Map DNA of Fetus from Blood and Saliva of Parents Genetic Test Can Help Tailor Breast Cancer Treatment Cracking the Genetic Code: The First "Book of Life" Human Chromosome #21 Mapped, Linked to Down Syndrome Scientists Discover New Gene That Could Help Pinpoint Cause of Alzheimer's Disease Searching Genes, Genome, for Health Predispositions Researchers Map First Human Chromosome: #22 "Fountain of Youth" Anti-Aging Gene Found in Earthworms Dawn of the "Genetics Age" May Help Those With Inherited Diseases No Bull: Genetic Manipulation Lets Breeders Select for Female Cows Scientists Isolate Specific Gene That Causes Muscular Dystrophy Efforts Using Gene-Splicing to Develop Bacteria-Produced Insulin