Scheme of Work for Year 7 2012-2013
advertisement

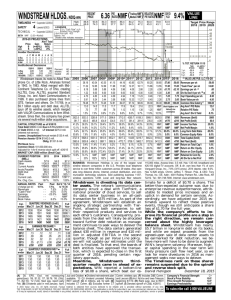
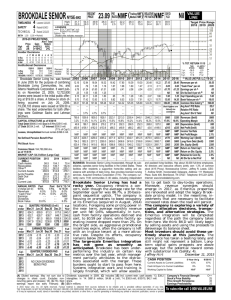
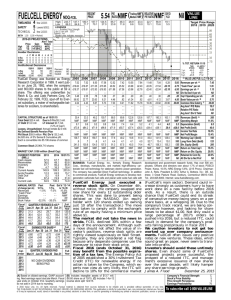
Scheme of Work for Year 7 2012-2013 The first few topics come from the Year 7 New Maths books and the remainder come from the Year 8 New Maths books. Please take care to read each topic carefully as I have sometimes missed sections of topics out. Throughout stress efficient use of a calculator and estimations to check that a sensible answer has been obtained. Lesson Sequen -ce 1 Topic (Level) Title Algebra 1 (4-6) Sequences and rules * To describe integer sequences * To generate terms of a simple sequence integer; sequence; term; rule; difference NMF: Lesson 1.1 pg 4 / 1A pg1 (5) Finding missing terms * To generate terms of a simple sequence, given a rule (see school presentation plan) sequence; term; difference NMF: Lesson 1.2 pg 6 / 1B pg 3 (6) Finding the general term (nth term) nth term; justify; generalisation NMF: Lesson 1.3 pg 8 / 1C pg 4 (4-6) Using letter symbols to represent functions * To generate sequences from patterns or practical contexts and describe the general term in simple cases * To use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variable function; mapping; expression; variable NMF: Lesson 1.5 pg 12/ 1E pg 8 Number 1 (5-6) Decimals Ordering Decimals Directed Numbers (5-6) Estimates Digit, order, place, tenth, hundredth, between thousandth ,compare, most, least, digit, significant Positive, negative, plus, minus, integer, directed number. Guess, estimate, approximate, roughly, nearly NMF: lesson 2.1 P.20 2.2 P.22/ 2A & 2B pg 17 and pg 23 (5-6) *To use decimal notation and place value. *To multiply and divide by powers of ten *To order and compare decimals in different context. *To understand negative numbers as positions on a number line. *To order, add and subtract integers. *To make and justify estimates and approximations of calculations. (4-6) Column method for addition, subtraction and multiplication Real life problems Difference, point, place, columns, tens, units, tenths, hundredths, deposit, profit, loss, credit, cost, selling NMF: lesson 2.5 P.28/ 2E pg 25 & 2F pg 27 Number 4 (4-6) Ratio and Proportion *To use efficient written methods to ad and subtract whole number and decimals with a focus on presentation. * To use known facts to derive unknown facts * To understand the relationship between ratio and proportion * To use direct proportion in simple contexts and to use ratio notation Proportion; ratio; cancel; simplest form; highest common factor NMF: Lesson 12.2 pg 146 / 12B pg 152 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Objectives Keywords Resources (teacher’s book)/ Pupils Book NOTES Fairly short as admin during these lesson. Focus on presentation of work Can use part of previous ex as starter Two exercises in one lesson. Use selective questions. NMF: lesson 2.3 P.24/ 2C pg 20 NMF: lesson 2.4 P.26/ 2D pg23 Emphasis on use for checking for sensible answers Two exercises in one lesson. Use selective questions. 10 11 12 (4-5) Algebra 2 (4-5) Calculating ratios and proportion Algebraic terms and expressions (4-6) Rules of algebra (4-6) Expanding and simplifying (5-6) Formulae Equations Geometry and Measures 1 (6) (6) Areas of some 2-D shapes Geometry and Measures 3 (5-6) Constructions 13 14 15 16 17 Surface area and volume of cuboids * To simplify ratios and divide a quantity into two parts in a given ratio *To use symbols to represent unknown numbers/variables *To substitute numbers into an expression *To understand that algebraic operations follow the rules of arithmetic. *To simplify expressions by collecting like terms. *To multiply out a single bracket. *To substitute integers into linear expressions and formulae. *To derive simple formulae. Ratio; cancel; lowest terms; simplest form Algebra, variable, substitute, term, expression NMF: Lesson 12.3 pg 148/ 12C pg 154 NMF: lesson 6.1 P.72/ 6A pg 78 Operation, convention Term, like terms, expansion, simplify NMF: lesson 6.2 P.74 / 6B pg 80 NMF: lesson 6.3 P.76 / 6C p82 Formula, substitution, expression NMF: lesson 6.4 P.78/ 6D pg 83 & 6E pg 85 * To derive and use formulae for the area of a triangle, parallelogram and trapezium * To calculate areas of compound shapes * To know and use the formula for the area of a rectangle and to calculate the perimeter and area of shapes made from rectangles * To calculate the surface area of cubes and cuboids * To know and use the formula for the volume of a cuboid and to calculate volumes and surface areas of cuboids and shapes made from cuboids * To make accurate mathematical constructions * To construct a triangle using SAS and ASA * To construct the midpoint and perpendicular bisector of a line segment and the bisector of an angle Base; eight; perpendicular height; parallelogram; trapezium Cube; cuboid; surface area; volume; cubic millimetre; cubic centimetre; cubic metre; formula NMF: Lesson 3.2 pg 36 / 3B pg 36 Construct; protractor; ruler; bisect; bisector; mid-point; perpendicular bisector; construction line NMF: Lesson 11.2 pg 138/ 11B pg 144 Mirror line; object; image; reflection; transformation Centre of rotation; object; image; rotation NMF: Lesson 14.2 pg 168 & 14.3 pg 170/ 14B pg 176 & 14C pg 178. Two exercises in one lesson. Use selective questions. NMF: Lesson 3.4 pg 40/ 3D pg 42. LEVELS TEST 1 HALF TERM 18 Geometry and Measures 4 (4-6) Reflections Rotations * To understand and use the language and notation associated with reflections and rotations * To recognise and visualise the symmetries of a 2-D shape * To transform 2-D shapes by reflecting in given mirror lines * To transform 2-D shapes by rotating about a given point Two exercises in one lesson. Use selective questions. 19 (5-6) Translations Enlargements * To understand and use the language and notation associated with translations & enlargement. * To recognise and visualise the symmetries of a 2-D shape * To transform 2-D shapes by translating * To transform shapes using reflection, rotation and translation * To enlarge 2-D shapes, given a centre of enlargement and a positive integer scale factor Centre of enlargement; enlarge; image; object; scale factor translation; image; object NMF: Lesson 14.4 pg 172 & 14.5 pg 174 / 14D pg 180 & Ex 14E pg 182 Two exercises in one lesson. Use selective questions. YEAR 8 BOOK 20 Number and Algebra 1 (5-6) (4-7) Multiplying & dividing negative numbers * To multiply by negative numbers * To divide by negative numbers Positive, negative, BODMAS NMF: Lesson 1.1 pg 4 / 1A pg 1 HCF and LCM * To find the highest common factor of two integers * To find the lowest common multiple of two integers. * To apply Integers between 1 and 10 to various powers. * To apply the second and third roots to various integers * To write a number as a product of its prime factors * To find the HCF and LCM of two numbers by finding their prime factors. * To identify alternate and corresponding angles * To calculate missing angles using alternate and corresponding angles. * To calculate interior and exterior angles in regular polygons * To learn the properties that define various quadrilaterals Factor, multiple, integer, prime, HCF, LCM NMF: Lesson 1.2 pg 6 / 1B pg 3 Power, Index, Root, Square, cube NMF: Lesson 1.3 pg 8 / 1C pg 6 Prime, factor, multiple, Factor Tree, HCF, LCM NMF: Lesson 1.4 pg 10 / 1D pg 8 Alternate, supplementary, complimentary, corresponding, intersect, parallel, angle Interior, exterior, sum, polygon, regular, Parallel, bisect, symmetry, rotational, equal, diagonal, adjacent, right angle Numerator, denominator, terminating, recurring NMF: Lesson 2.1 pg 22 / 2A pg 23 Common denominator, mixed number, top-heavy fraction NMF: Lesson 4.2 pg 50/ 4B pg 56 21 (5-6) Powers and Roots (6-7) Prime Factors 22 23 24 25 Geometry & Measures 1 (6) (6) (6) 26 27 Number 2 (6-7) (5-6) 28 Alternate and Corresponding angles Interior and Exterior Angles of Polygons The geometric properties of quadrilaterals Fractions and Decimals Adding and Subtracting fractions * To recognise that a recurring decimal is a fraction * To convert a fraction to a decimal * To order fractions and decimals * To add and subtract fractions NMF: Lesson 2.2 pg 24 / 2B p26 NMF: Lesson 2.4 pg 28 / 2D p30 Use the proper names 2C can be used for extension NMF: Lesson 4.1 pg 48 / 4A p55 Revision of mixed and top heavy fraction needed (5-6) Multiplying and Dividing fractions (6) Percentages (5-6) Percentage Increase and Decrease Algebra 2 (4) Algebraic Shorthand Like Terms 32 (5-7) Expanding Brackets 33 (6) Using Algebra with Shapes 34 (5-7) Index Notation 29 30 * To calculate fractions of quantities * To multiply and divide an integer by a fraction *To express one given number as a percentage of another * To calculate percentage increase and decrease Fraction, improper, mixed number, half, third, quarter NMF: Lesson 4.3 pg 52 / 4C pg 58 Percentage, denominator, equivalent fraction Increase, decrease, reduction, VAT NMF: Lesson 4.4 pg 54 / 4D pg 59 NMF: Lesson 4.5 pg 56 / 4G pg 61 * To recognise that letter symbols play different roles in equations, formulae, and functions. * To simplify or transform linear expressions by collecting like terms * To expand a single term over a bracket * To expand brackets and collect like terms * To multiply out single brackets and collect like terms * To use index notation for small positive integers Expression, term, like terms, simplify symbol, operation, equal NMF: NMF: Lesson 5.1 pg 64 & Lesson 5.2 pg 66 / Ex 5A pg 71 & Ex 5B pg 73 Multiply out, expand, factorise Perimeter, area, expansion, simplify Power, index, indices, cancelling NMF: Lesson 5.3 pg 68 5C pg 74 NMF: Lesson 5.4 pg 70 / EX 5D pg 76 NMF: Lesson 5.5 pg 72/ 5E pg 79 31 31 SMSC – opportunity to consider the rate at which credit card debts increase, repayment of loans and mortgages, how taxes work Two exercises in one lesson. Use selective questions. LEVELS TEST 2 CHRISTMAS 35 Statistics 1 (6-7) (6-7) Probability & Probability Scales *To work out different probabilities *To understand the probability scale *To know probabilities sum to 1 Probability, event, outcome, success, fraction, random, predictable NMF: Lesson 3.1 pg 34 -37 / Ex 3A pg 38 & pg 40 Mutually Exclusive events *To understand what mutually exclusive events are NMF: Lesson 3.2 pg 38/ 3C p42 Calculating probabilities *To work with sample space diagrams *To work with two way tables Experimental probabilities *To understand the difference between theoretical and experimental probability *To calculate theoretical and experimental probability Mutually exclusive, Probability, event, outcome, success Probability, event, outcome, success, sample space, two way table Probability, event, outcome, success, experimental, theoretical 36 (6) 37 (6-7) 38 NMF: Lesson 3.3 pg 40 / 3D pg 44 NMF: Lesson 3.4 pg 42 / 3E pg 48 Two exercises in one lesson. Use selective questions 39 Geometry and Measures 2 (6) (6-7) The Circle * To understand the definition of a circle. * To recognise and name the various parts of a circle Circumference of a Circle (6-7) Area of a Circle (7) Surface Area and Volume of Prisms (5) Imperial Units *To learn the formula to calculate a circles circumference * To use the formula to calculate the circumference *To learn the formula to calculate a circles area * To use the formula to calculate the area * To convert between area and volume measures * To calculate surface area and volume of right prisms * To know rough metric equivalents of imperial measures in common use. * To convert between metric and imperial units * To find a function given a set of inputs and outputs * To find an inverse of a function * To plot the graph of a function in all four quadrants * To recognise that the equation of a straight line is y = mx +c * To calculate the gradient and intercept of straight lines * To construct and plot graphs given real life situations * To interpret and use the graphs to make predictions *To read and write positive integer powers of 10 *To multiply and divide integers and decimals by 0.1, 0.01 and powers of 10 * Round decimals to the nearest whole number or to 1 or 2 decimal places * To round positive numbers to any given power of 10 * To round decimals to the nearest whole number or a given number of decimal places 40 41 42 43 44 45 Algebra 3 (6 - 7) Finding a function from Inputs and Outputs (6-7) Graphs of Functions (6-7) Gradient of a Straight Line (6-7) Real-Life Graphs 46 47 Number 3 (4-7) Powers of 10 Large Numbers 48 (5-6) 49 Working with Decimals Centre, circumference, arc, radius, diameter, chord, tangent, segment, sector, semicircle Circumference, diameter, pi, radius NMF: Lesson 6.1 pg 76 / 6A pg 83 area, diameter, pi, radius NMF: Lesson 6.3 pg 80 / 6C pg 87 Prism, cross section, volume, surface area NMF: Lesson 6.4 pg 82 / 6D pg 89 Metric, imperial, convert, capacity, length, mass NMF: Lesson 6.5 pg 84/ 6E pg 92 SMSC – use of imperial units in context Function, input, out, inverse NMF: Lesson 7.2 pg 90/ 7B pg 99 Can use Exercise 7A as starter Coordinates, axes, equation NMF: Lesson 7.3 pg 92/ 7C pg 101 NMF: Lesson 7.4 pg 94/7D pg 104 Also include y=x, y=c & x= c c∈ R Gradient, intercept, coordinates, axes NMF: Lesson 6.2 pg 78/ 6B p85 Travel graph, average speed NMF: Lesson 7.5 pg 96/ 7E pg 106 Round, decimal, power of 10 Place value, power, million, billion NMF: Lesson 8.1 pg 102 &: Lesson 8.2 pg 104 / 8A p113 & 8B pg 115 Integer, tenths, hundredths, decimal, rounding NMF: Lesson 8.4 pg 108/ 8D pg 118 Two exercises in one lesson. Use selective questions (5-6) Multiplying and dividing decimals 50 * To multiply decimals and integers by integers and decimals * To divide decimals and integers by integers and decimals Long division, long multiplication, column method, chunking NMF: Lesson 8.6 pg112 / 8F pg 123 If too short then use Ex 8E on efficient calculator use or the National Test Questions Transformation, map, reflect, rotate, translate NMF: Lesson 9.2 pg 120/ 9B 131 Explain congruent shapes prior to starting the exercise Object, image, enlarge, centre of enlargement, scale factor, negative enlargement Plane, solid, symmetry, axis NMF: Lesson 9.3 pg 122/ 9C p136 LEVELS TEST 3 Half Term Geometry and Measures 3 (5-6) (7) Combinations of Transformations (7) Planes of Symmetry (5-7) Shape and Ratio Geometry and Measures 5 (5 - 6) (7) Map Scales 57 (5-6) Bearings 58 Algebra 4 (5-6) (5-7) Equations involving negative numbers Equations with unknowns on both sides Substituting into expressions and Substituting into formulae 51 Enlargements 52 53 54 55 Loci 56 59 (5-7) 60 61 (5-7) Creating your own expressions and formulae * To transform shapes by rotation, reflection and translation * To transform a shape with a combination of the above * To enlarge a 2D shape given a centre of enlargement and a positive integer scale factor * To identify reflection symmetry in 3D shapes * To apply the relationship between ratio and proportion to shape sizes. * To simplify ratios * To use and interpret maps and scale drawings in the context of mathematics and other subjects. * To find simple loci to produce shapes and paths Ratio, length, are, volume, simplest form NMF: Lesson 9.4 pg 124 / 9D pg 138 NMF: Lesson 9.5 pg 126/ 9E pg 140 Map, scale drawing, map scale, map ratio, scale factor NMF: Lesson 15.4 pg 206 / 15D pg 220 NMF: Lesson 15.5 pg 208 / 15E pg 222 * Use bearings to specify a direction from one position to another * To construct and solve linear integer equations with negatives * To construct and solve linear integer equations with unknowns on both sides * To substitute positive integers into expressions involving small powers * To substitute integers into simple formulae Equidistant, locus, loci, angle bisector, perpendicular bisector Bearing, north, compass, back bearing Equation, linear, unknown, solve, negative Equation, linear, unknown, solve, negative Expression, substitution, variable Formula, variable * To create and derive simple formulae Expression, formula NMF: Lesson 10.6 pg 140/ 10F pg 153 LEVELS TEST 4 Easter NMF: Lesson 15.6 pg 210/ 15F pg 225 NMF: Lesson 10.2 pg 132/ 10 B pg 144 NMF: Lesson 10.3 pg 134/ 10 C pg 148 NMF: Lesson 10.4/5 pg 136 – 138 / 10D pg 149 & 10En pg 151 Two exercises in one lesson. Use selective questions 62 Statistic 2 (7) Statistical Surveys (6) Stem and Leaf Diagrams (7) Interpreting graphs and diagrams (6) Scatter graphs (6-7) Analysing Data 63 64 65 66 67 Algebra 5 (4-7) Expand and Simplify (7) Solving Equations by Trial and Improvement 69 (5-7) Constructing Equations 70 (6) Problems with Graphs (6) Real-life graphs (7) Change of Subject 68 71 72 73 74 . Solving Problems (6) (6) (6) 75 Number and Measures Using algebra, graphs and diagrams to solve problems Logic and Proof * To write a questionnaire with appropriate questions * To plan and collect data accurately and efficiently * To create stem-and-leaf diagrams given a set of data. * to calculate statistics for sets of discrete and continuous data * To interpret a range of graphs and diagrams relating to statistical data * To discuss and critique statements made about the data * To plot a scatter diagram give a set of data * To interpret the graph in relation to its correlation * To discuss, analyse and write about the results of a statistical enquiry * Simplify expressions by collecting like terms * Expand and simplify single brackets * Expand and solve linear equations * to find an approximate solution to a nonlinear equation through trial and improvement * To construct and solve linear equations given a problem * To find the gradient, y-intercept and equation of straight line graphs. * To construct linear functions arising from real-life situations. * To interpret graphs arising from real-life situations * To rearrange a formula to make another variable the subject * To identify mathematical features in a given problem and use them to solve the problem *Use graphs and set up equations to solve simple problems involving direct proportion * Use logical argument to interpret the mathematics in a given context * Give accurate solutions to a problem Problem, hypothesis, survey, experiment, questionnaire, observation, data NMF: Lesson 11.1 pg 144/ 11A pg 159 Range, mean, median, mode, average, stem-and-leaf diagram NMF: Lesson 11.2 pg 146 / 11B pg 161 Interpret, criticise, secondary data, NMF: Lesson 11.3 pg 148 / 11C pg 162 Scatter graph, correlation, positive, negative NMF: Lesson 11.4 pg 150 / 11D pg 165 Hypothesis, data, analysis, report, conclusion Expression, equation, expand, simplify, like terms NMF: Lesson 11.5 pg 152 / 11E pg 166 NMF: Lesson 13.1 pg 172 / 13A pg 185 Linear, non-linear, powers, trial and improvement NMF: Lesson 13.2 pg 174 / 13B pg 187 Equation, construct, solve NMF: Lesson 13.3 pg 176/ 13C pg 188 NMF: Lesson 13.4 pg 178/ 13D pg 190 NMF: Lesson 13.5 pg 180 / 13E pg 192 Gradient, intercept, rise, run Axes, relationship, variable Subject, transform, express in terms of Investigate, solve, problem, numbers, measures, conversions, bound, consecutive Algebra, graph, equation, flowchart Solution, proof, trial and improvement, integer, consecutive, best value, counter-example NMF: Lesson 13.6 pg 182/ 13F pg 194 NMF: Lesson 14.1 pg 188/14A pg 201 NMF: Lesson 14.2 pg 190/ 14B pg 203 NMF: Lesson 14.3 pg 192/ 14C pg 205 SMSC – use real data and interpret it in context Use for revision prior to EOY test Half Term SUMMER EXAM 7 16. Statistics 3 (6-7) Collecting Data for Frequency Tables * To decide on types of data and relevant degrees of accuracy * To plan how to collect the data * To design a survey to collect data * To calculate the mean of a set of numbers given an assumed mean * To understand what happens to the mean and range of a set of numbers when an operation is applied to the set *To construct and interpret frequency diagrams (6) Assumed Mean and Working with Stats (6) Drawing Frequency Diagrams (6) Comparing Data * To compare two distributions using the range, mean, median and mode (6-7) Comparing sets of Data (6-7) Experimental and Theoretical Probability * To compare two or more distributions and make inferences from appropriate statistics * to compare estimated experimental probabilities with theoretical probabilities Data, frequency table, class interval, data collection, sample size, bias, primary source, secondary source Mean, assumed mean, range NMF: Lesson 16.1 pg 218/ 16A pg 236 Bar chart, line graph, frequency diagram, time series, continuous, discrete Comparison, distribution, mean, range, variation, consistency, mode, median Comparison, percentage bar chart, distribution Biased, event, sample space, experimental, theoretical NMF: Lesson 16.3 pg 222/ 16C pg 240 SMSC – use reallife data and interpret in context NMF: Lesson 16.2 pg 220/ 16B pg 237 Short exercise maybe combine with next NMF: Lesson 16.4 pg 224/ 16D pg 241 NMF: Lesson 16.5 pg 226/ 16E pg243 NMF: Lesson 16.6 pg 228 / 16F pg 245 There are 4 Levels tests plus 1 Summer Exam. There should be enough spare lesson time, to go over tests and exams and still complete the syllabus. If your class struggles for some reason to understand a lesson, do not feel you have to continue to the next lesson regardless. Functional Maths exercises can be left for cover lessons or for when you are ahead of the scheme of work.