Chemistry 100 Practice Exam III
advertisement
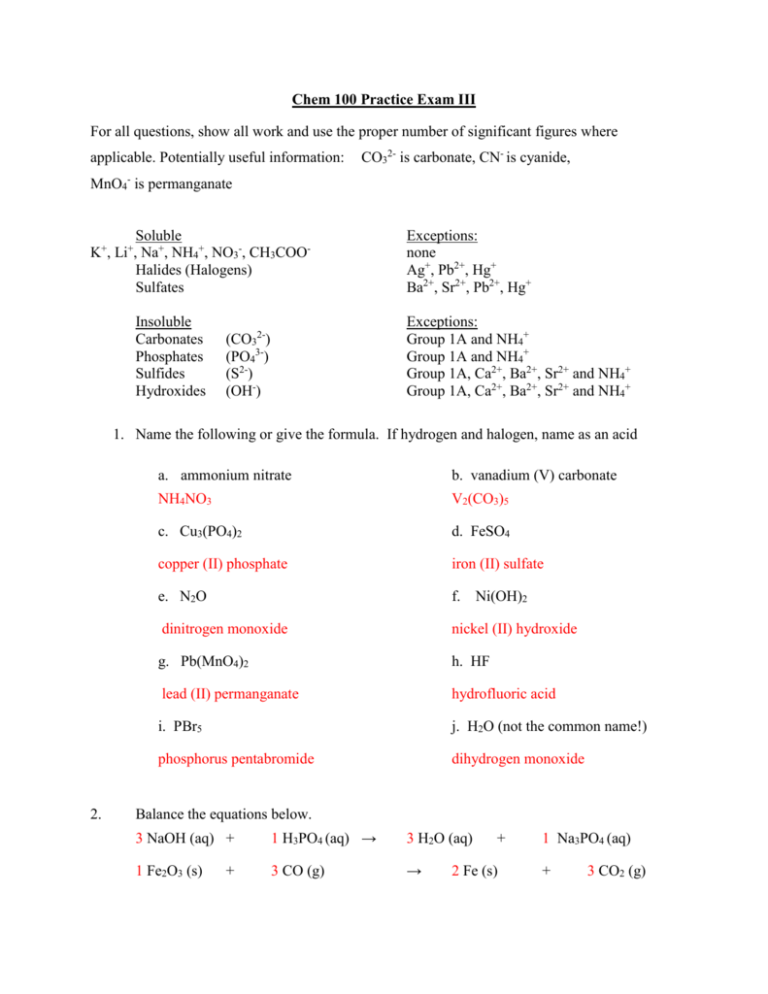
Chem 100 Practice Exam III For all questions, show all work and use the proper number of significant figures where applicable. Potentially useful information: CO32- is carbonate, CN- is cyanide, MnO4- is permanganate Soluble K , Li , Na+, NH4+, NO3-, CH3COOHalides (Halogens) Sulfates + + Insoluble Carbonates Phosphates Sulfides Hydroxides Exceptions: none Ag+, Pb2+, Hg+ Ba2+, Sr2+, Pb2+, Hg+ Exceptions: Group 1A and NH4+ Group 1A and NH4+ Group 1A, Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+ and NH4+ Group 1A, Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+ and NH4+ (CO32-) (PO43-) (S2-) (OH-) 1. Name the following or give the formula. If hydrogen and halogen, name as an acid 2. a. ammonium nitrate b. vanadium (V) carbonate NH4NO3 V2(CO3)5 c. Cu3(PO4)2 d. FeSO4 copper (II) phosphate iron (II) sulfate e. N2O f. dinitrogen monoxide nickel (II) hydroxide g. Pb(MnO4)2 h. HF lead (II) permanganate hydrofluoric acid i. PBr5 j. H2O (not the common name!) phosphorus pentabromide dihydrogen monoxide Ni(OH)2 Balance the equations below. 3 NaOH (aq) + 1 H3PO4 (aq) → 3 H2O (aq) 1 Fe2O3 (s) 3 CO (g) → + + 2 Fe (s) 1 Na3PO4 (aq) + 3 CO2 (g) 1 B2H6 (g) + → 3 O2 (g) 2 HBO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) 4 C3H5O9N3 (l) (nitroglycerin) → 12 CO2 (g) + 6 N2 (g) + 1 O2 (g) + 10 H2O (g) 3. Draw Lewis structures for the two molecules CS2 and SiBr2O. What is the shape around the central atom in each molecule? Can’t draw on this computer, but carbon disulfide is linear, carbon double bonded to each sulfur and two lone pairs on each sulfur. Silicon in center, double bond to oxygen, each bromine has a single bond to silicon. Each Br with 3 lone pairs, O w/ 2 lone pairs and this is trigonal planar. 4. For the molecules above, indicate any polar bonds and tell me whether the molecule itself is polar or not. 1st molecule, δ+ on the C, δ- on both S’s; molecule is non-polar because both bonds in linear molecule are polar 2nd molecule, δ+ on Si, δ- on both Br’s and O; according to our chem. 100 theory, this molecule is non polar because it is trigonal planar and has three polar bonds (technically, this is polar because the three polar bonds are not all equal – but this is more detail than I said you would be responsible for) 5. Examine the reactions below. For each reaction that produces a precipitate, tell me what the precipitate is. If no solid is produced, write NR. Pick one of the reactions that does make a precipitate and write molecular, total ionic, and net ionic equations for that reaction. a. Ba(NO3)2 (aq) + NH4OH (aq) → b. SrCl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) → NR SrSO4 (s) + 2 NaCl (aq) Sr2+ (aq) + 2 Cl- (aq) + 2 Na+ (aq) + 1 SO42- (aq) → SrSO4 (s) + 2 Na+ (aq) + 2 Cl- (aq) Sr2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) → c. SrSO4 (s) 4 K3PO4 (aq) + 3 Pb(CH3COO)4 (aq) → 1 Pb3(PO4)4 (s) + 12 KCH3COO (aq) 12 K+ (aq) + 4 PO43- (aq) + 3 Pb4+ (aq) + 12CH3COO- (aq) → 1 Pb3(PO4)4 (s) + 12K+ (aq) + 12 CH3COO- (aq) 3 Pb4+ (aq) + 4 PO43- (aq) → 1 Pb3(PO4)4 (s) 6. Balance the following reactions. 1 Ag2S (s) + 1 BaCl2(aq) + 6 CO2 (g) + 2 HCl (aq) + 2 HCl (aq) 1 Na2CO3(aq) 6 H2O (l) 1 CaCO3 (s) 2 AgCl (s) + 1 BaCO3 (s) + 1 C6H12O6 (s) + 1 CaCl2 (aq) +1 CO2 (g) + 1 H2S (g) 2 NaCl (aq) 6 O2 (g) 1 H2O (l)