networkvulnerabilitiesteam
advertisement
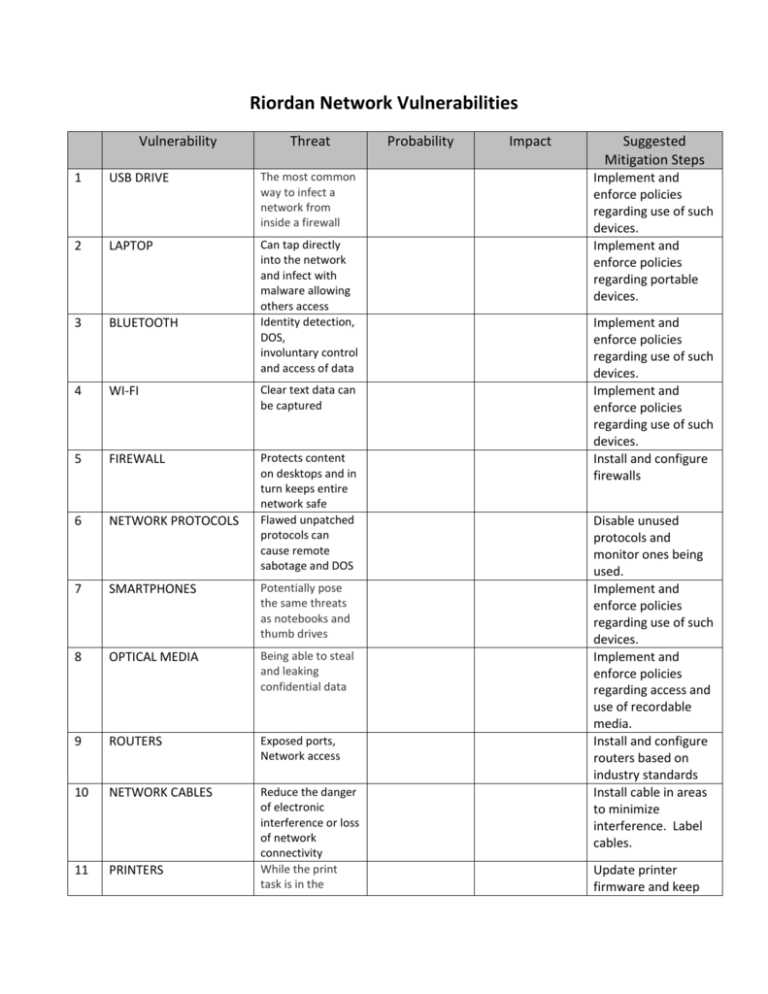
Riordan Network Vulnerabilities Vulnerability Threat 1 USB DRIVE The most common way to infect a network from inside a firewall 2 LAPTOP 3 BLUETOOTH Can tap directly into the network and infect with malware allowing others access Identity detection, DOS, involuntary control and access of data 4 WI-FI Clear text data can be captured 5 FIREWALL 6 NETWORK PROTOCOLS Protects content on desktops and in turn keeps entire network safe Flawed unpatched protocols can cause remote sabotage and DOS 7 SMARTPHONES Potentially pose the same threats as notebooks and thumb drives 8 OPTICAL MEDIA Being able to steal and leaking confidential data 9 ROUTERS Exposed ports, Network access 10 NETWORK CABLES 11 PRINTERS Reduce the danger of electronic interference or loss of network connectivity While the print task is in the Probability Impact Suggested Mitigation Steps Implement and enforce policies regarding use of such devices. Implement and enforce policies regarding portable devices. Implement and enforce policies regarding use of such devices. Implement and enforce policies regarding use of such devices. Install and configure firewalls Disable unused protocols and monitor ones being used. Implement and enforce policies regarding use of such devices. Implement and enforce policies regarding access and use of recordable media. Install and configure routers based on industry standards Install cable in areas to minimize interference. Label cables. Update printer firmware and keep Vulnerability Threat queue, the data is unencrypted and vulnerable to theft 12 FAX MACHINES Unsecure faxing will put you at risk for confidential and identity theft 13 SAN STORAGE Network availability 14 EMPLOYEES 15 SERVERS Individuals having access to restricted area of the network Open to brute force attacks, botnets, cross-site scripting and DOS 16 WORKSTATIONS 17 VIDEO CONFRENCING 18 THEFT 19 IMPERSONATION 20 LAPTOPS/TABLETS 21 USB DEVICES Can be used by attackers as "slave" machines in coordinated attacks. Machines set to auto answer will allow the attacker to essentially gain a front-row seat inside corporate meetings Attacker steals privilege information to gain access Attacker poses as a service provider or custodial crew to physically gain access Portable and easy to hide and attach to network. MP3 Players, etc Probability Impact Suggested Mitigation Steps an update inventory of all printers and drivers Implement and enforce policies regarding information distribution Limit access to data storage based on classification and need to know. Maintain a strict access control policy for restricted areas. Harden servers against cyber attacks using industry standard or better. Harden workstations against cyber attacks using industry standard or better. Should be hardened disable auto answer to prevent eaves dropping. Access control and password policy Security awareness training and policy Implement and enforce portable device policy Implement strict policies regarding USB devices. Vulnerability 22 FIRE ALARM 23 ELECTRICAL POWER 24 AIR CONDITION SYSTEM 25 POOR MAINTENANCE Threat Probability Fire retardant system does not work when needed No backup power in case of public power outage Cooling system fail causing equipment to overheat and fail Do not know when unauthorized equipment is attached to the network Impact Suggested Mitigation Steps Test fire alarm system periodically Backup generators and UPS for critical systems Service and maintain heating and cooling system. Inventory and label all equipment and document change management Logical Network Vulnerabilities 1 DATABASE SQL Injection, DOS Attacks, Database Exposure and Privilege elevation 2 VPN Confidential information can be inadvertently downloaded. Unobstructed route for Malware. 3 MAN-IN-THE-MIDDLE Use cryptography and Hashed Message Authentication Codes 4 PRIVILEGE ESCALATION Attacker monitors and steals Information in real time Individual gains access to network higher functions due to misconfiguration 5 PHISHING Used by an attacker to collect sensitive information to gain access Segment network and encrypt data 6 FOOTPRINTING Attacker use default username and weak or blank password to gain access to the network Strong password, do not use blank password or weak Check Roles, Use strong ACLs; and use standard encryption Vulnerability Threat 7 HIJACKING Attacker can take over your internet browser downloading additional malware 8 SOCIAL ENGINEERING 9 PASSWORDS 10 DIGITIAL CERTIFICATE 11 OPERATING SYSTEM 12 TCP/IP 13 EMAIL Attackers will trick users into revealing their passwords Easy guessable passwords, hackers gain initial access to a system. Attackers hack into certificate authorities and issue false certificates for legitimate websites If not patched regularly the network is open to security vulnerabilities Vulnerable to a variety of attacks ranging from password sniffing to denial of service Spyware, Virus, Phishing, and spam 14 WEB BROWSERS 15 INSTANT MESSAGING 16 SECURITY MISCONFIG Attacker can take over your browser making you vulnerable if the browser plug-ins are not fully patched Vulnerable to firewall tunneling, identity theft, data security leaks, and authentication spoofing Attackers can access networks virtually without Probability Impact Suggested Mitigation Steps Use session and communication encryption. Apply patch to fix vulnerabilities Security awareness training. Enforce strong password; lock out and audit trails Revoke PKI and maintain list of revoked keys to id false certificates. Harden OS Disable unnecessary protocols Conduct cyber security awareness to educate end user of email threats. Configure secure web permissions; Use .Net Framework access control Strong password, do not cache password, Configure based on industry standard. Vulnerability Threat attracting attention Probability Impact Suggested Mitigation Steps Avoid custom configuration Input validation Use HTMLEncode and URLEncode functions to encode any output Update definition files and patches. 17 WEB APPLICATIONS DOS, Elevation of privilege, Information disclosure, and impersonation 18 MALWARE 19 SOFTWARE DEFECT Can infect networked resources and possibly bring down the network Allows data to be viewed by unauthorized people 20 SPOOFING An attacker pretends to be an entity to take over communication between systems 21 DOS ATTACK An attack on a network that causes a loss of service to users Resource and bandwidth throttling techniques. Validate and filter input. 22 SNIFFER ATTACK Segment network. Encrypt data. 23 BUFFER OVERFLOW Can read, monitor, and capture network data exchanges Exploits poorly written software to allow attackers to take over the target system 24 REMOTE ACCESS Without the appropriate security measures (SSL VPN), all Apply updates and patch vulnerabilities. Or uninstall and replace. Strong authentication. Do not store secrets Do not pass credentials in plaintext over the wire. Protect authentication cookies with SSL. Validate input Inspect API managed code. Use the /GS flag to compile code Configure remote access with the necessary security parameters to ensure Vulnerability 25 3 NO ANTIVIRUS Created a table of 50 vulnerabilities and threat pairs relevant to the organization Threat Probability Impact communications are being transmitted in clear text Not Protected against virus and other malware attacks 0.00 Suggested Mitigation Steps secure communication. Install, configure and update antivirus software. 0.70 0.85 1.00 Comment: Trying to find 50 vulnerabilities is not an easy task. Not every item is a vulnerability. Some are attacks, some are threats, and some are vulnerabilities. 0.85











