7th Science Genetics and Bioengineering
advertisement

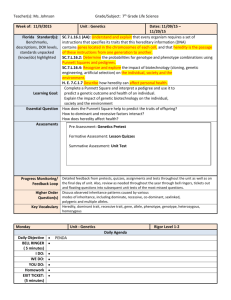
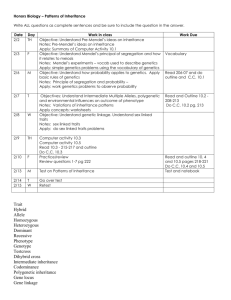
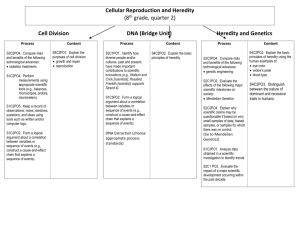
Unit Title: Genetics & Bioengineering 10 Days Science Lesson Plan Teacher: th 7 Grade Science Teacher Grade: 7th Grade Science Lesson Title: “Genetics & Bioengineering” – Reproduction of Flowers and Bioengineering “Genetics and Bioengineering” – Heredity & Punnett Squares STRANDS Embedded Inquiry Engineering & Technology Heredity LESSON OVERVIEW Summary of the task, challenge, investigation, career-related scenario, problem, or community link. Week 1: Students will begin their study of genetics and bioengineering. The scientific focus of this unit will be the principal mechanisms by which living things reproduce and transmit information between parents and offspring. This week we will learn about plant anatomy and the relationship between agriculture, bioengineering, and genetics. Students will compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction, investigate the anatomy and physiology of plants, and determine the different types of pollination. Students will also prepare to work with a local gardener at the end of the week to reinforce the reproductive anatomy and physiology of flowers and the breeding practices used in gardening. The students will begin formulating questions for the gardener’s visit to our school during class time this week. Week 2: Students will continue their study of Genetics and Bioengineering. Students will learn to differentiate between codominance, incomplete dominance, and sex-linked inheritance. Students will also study selective breeding and the impact of selective breeding on daily life. The students will work with hands-on projects to practice successfully modeling genetic crosses utilizing punnett squares. The students will also focus on pedigrees and the patterns of inheritance. Students will participate in a small group learning activity based on the Kentucky Derby to better understand the role of genetics and pedigrees. Hook for the week unit or supplemental resources used throughout the week. (PBL scenarios, video clips, websites, literature) MOTIVATOR Week 1: Students will work in small groups of three to complete the following PBL Scenario: You are a local grocer who owns a small business. The customers at your store are requesting more organic locally grown fruits and vegetables. As you are preparing to negotiate purchasing agreements for the upcoming business quarter you are researching ways to meet your customer’s requests and maintain your profit margin. To best communicate with the local gardeners and large gardening operations you are completing research to compare costs of organically grown produce and commercially grown produce. You will need to prepare a chart that illustrates the difference in customer cost for organically grown produce and commercially grown produce. This chart will also need the source information, such as location, growing conditions, pesticides used, fertilizer used, and if any genetic engineering or modifications have been made for these produce. Your chart must contain 5 most commonly sold fruits and the 5 most commonly sold vegetables. This chart must also be created in a way that is easy for the customers to read and understand. Week 2: The motivator for this week will be a Skype interview with a local alpaca farmer. This farmer will discuss the relationship between genetics, breeding, and agriculture. The Skype interview will introduce many of the important terms and concepts that will be included in this week’s lessons and allow students to learn about the local impact of genetics. DAY Objectives (I can….) 1 Materials & Resources Embedded Inquiry Materials: Embedded Technology / Engineering 1. Video Clip 2. Pre-Test (Heredity) 3. PPT – Bioengineering and Agriculture 4. Poster Supplies – poster board, markers, rulers, scissors, crayons, and pencils. 5. iPads 6. Exit Ticket I can research bioengineering technologies that advance health and contribute to improvements in our daily lives Instructional Procedures Essential Question(s): 1. What are the principal mechanisms by which living things reproduce and transmit information between parents and offspring? Modified Project Day – Refer to Unit Plan Set Bell Work – 10 minutes Video Clip on the Bioengineering and Technology used in the study of genetics and heredity. Pre-Test Pre-Test – 5 minutes Plant Reproduction Heredity and Genetics Direct Instruction Bioengineering and Agriculture PPT – 20 minutes Focus: a. What is agriculture? b. How is bioengineering related to agriculture? c. What tools and technology are used in the bioengineering and agriculture? d. How does this relationship affect our daily life? Research – Posters Differentiated Instruction Differentiated Instruction: - Remediation: Peer Tutoring, Guided Notes, Visual Aids, Prompting, and Reduced assignment - Enrichment: Peer Tutoring Assessment Formative Assessment for lesson effectiveness: - Pre-Test and Exit Ticket - “Wanted” Poster Job Posting – “Wanted” advertisement – 15 minutes Students will work in pairs to create an advertisement for a job related to bioengineering and agriculture The poster must be colored and include details such as education requirements, job responsibilities and tasks, work environment, and salary. Closure Exit Ticket – 5 minutes Students will provide a list of two careers related to bioengineering that they are interested in pursing. This list will also contain the reason for their interest. Homework – Complete “Wanted” Advertisement 2 I can classify plants. Materials: I can identify the reproductive anatomy of a flowering plant. 1. Entrance Ticket with questions 2. PPT – Plant Anatomy and Types of Reproduction 3. Information Text – Types of Pollination. 4. Diagramming the Reproductive Parts of a Flower – construction paper, markers, colored pencils, and crayon. 5. iPads 6. Exit Ticket with questions. I can describe the reproductive physiology of a flowering plant. I can compare and contrast the fundamental features of sexual and asexual reproduction. I can classify methods of reproduction as sexual or asexual. I can classify organisms according to whether they reproduce sexually or asexually. I can compare and Essential Question(s): 1. What are the principal mechanisms by which living things reproduce and transmit information between parents and offspring? Topic – “Genetics & Bioengineering” – Plant Anatomy and Types of Reproduction Set Entrance Ticket – 15 minutes - Compare and Contrast the sepal and the pistil. - Name the locations of the flower’s egg and sperm. - How are the reproductive parts of a flower different from the reproductive system of other organisms? Direct Instruction Plant Anatomy & Types of Reproduction PPT – 25 minutes Focus: a. What are plants? b. How are plants classified? c. Describe the anatomy and physiology of plants, with a focus on reproductive structures. d. Compare and Contrast asexual and sexual reproduction. e. Classify methods of reproduction as sexual or asexual. f. Classify organisms according to whether they reproduce sexually or asexually. Reading Activity Types of Pollination – 10 minutes Students will complete independent read utilizing an information text regarding the different types of pollination. Students will then complete a think-pair-share activity to discuss what they have learned from the informational text. Individual Practice Diagraming the Reproductive Parts of a Flower – 15 minutes Differentiated Instruction: - Remediation: Creation Activity, Modified Notes, Prompting, Leveled Reading - Enrichment: Peer Tutoring and Creation Activity Formative Assessment for lesson effectiveness: Entrance & Exit Ticket Think-Pair-Share Diagramming the Reproductive Parts of a Flower contrast types of pollination. - Students will work individual to create a model of a flower. The students will research a flower (their choice) and then diagram and label the reproductive parts of this flower. This diagram must also include the function of each labeled anatomical part. Closure Exit Ticket – 5 minutes - Compare and Contrast the sepal and the pistil. - Name the locations of the flower’s egg and sperm. Homework – Complete Diagraming the Reproductive Parts of a Flower 3 I can identify the reproductive anatomy of a flowering plant. I can describe the reproductive physiology of a flowering plant. Materials: 1. Bell Work question (chart) incorporated into PPT 2. Video Clip – Reproductive Parts of Flowers 3. Flower Dissection Lab Procedures 4. Flower Dissection Lab Materials – Dissection Pans and Tools, Variety of Flowers (Roses, Peonies, Tulip, etc.) 5. Exit Ticket – Post-Test (10 Multiple Choice Questions) Essential Question(s): 1. What are the principal mechanisms by which living things reproduce and transmit information between parents and offspring? Topic – “Genetics & Bioengineering” – Plant Anatomy Set Bell Work – 5 minutes - Students will complete a chart that provides either the name of the reproductive part of a flower or its function. Direct Instruction Reproductive Parts of Flowers Video Clip – 10 minutes - Students will take notes in their science notebook. - Students will learn about the lesson’s objectives: - I can identify the reproductive anatomy of a flowering plant. - I can describe the reproductive physiology of a flowering plant. Laboratory Activity – Flower Dissection Hands-on lab (Partners) – 30 minutes - Students will work in pairs to dissect a flower. - This lab experience will allow student to have hands-on experience with locating the reproductive anatomy of a flower. - The students will answer the accompanying lab questions that focus on the function and physiology of the reproductive parts of flowers. Closure Exit Ticket – 5 minutes - Students will complete a 10 question multiple choice post-test regarding the reproductive parts of flowers and their function. Differentiated Instruction: - Remediation: Peer Tutoring, Heterogeneous Grouping, Visual, Hands-on, and Verbal learning activities - Enrichment: Peer Tutoring, Heterogeneous Grouping, Visual, Hands-on, and Verbal learning activities Formative Assessment for lesson effectiveness: Set & Closure - Bell Work and Exit Ticket Flower Dissection Lab and Accompanying Questions 4 I can compare and contrast types of pollination. I can explain the relationship among genes, chromosomes, and inherited traits. I can describe a gene. I can describe a chromosome. I can describe how traits are inherited. Materials: 1. Bell Work question incorporated into PPT 2. iPads 3. Construction Paper, Colored Paper, Colored Pencils, Markers, and Scissors 4. PPT – Mendel and the Pea Plants 5. Exit Ticket – printed for students to complete Essential Question(s): 1. What are the principal mechanisms by which living things reproduce and transmit information between parents and offspring? Topic – “Genetics & Bioengineering” – Types of Pollination & Mendalian Genetics Set Bell Work – 5 minutes - What are the different types of pollination? - How does one differentiate between the types of pollination? Student Research Project Independent Research Project – 25 minutes - Student will work independently to research Gregor Mendal. - Each student will create a book cover sleeve for a hypothetical upcoming biographical book to be written about Gregor Mendal. - These cover sleeves must neat, colored, and include a title, cover art, and summary used for the back portion of the cover. - All of the information must be accurate with sources recorded on the inside of the cover sleeve. Direct Instruction Relationship between Mendalian Genetics and Flowers – 20 minutes - Students will take notes in their science notebook. - Students will learn about the lesson’s essential questions. Closure Exit Ticket – 10 minutes - Students will prepare to work with a local gardener during class tomorrow to reinforce the reproductive anatomy and physiology of flowers and the breeding practices used in gardening. - The students will formulate questions for the gardener’s visit to our school during class time this week. (A minimum of 5 questions.) 5 Project Day – Refer to Unit Plan Differentiated Instruction: - Remediation: Peer Tutoring, Heterogeneous Grouping, Visual, and Verbal learning activities - Enrichment: Peer Tutoring, Heterogeneous Grouping, Visual, Hands-on, and Verbal learning activities Formative Assessment for lesson effectiveness: Student Research Project 6 I can compare and contrast heterozygous and homozygous. I can compare and contrast dominant alleles and recessive alleles. I can compare and contrast genotype and phenotype. I can describe each of the laws of inheritance? I can explain how punnett squares are used as a prediction tool? Materials: 1. Bell Work – questions incorporated into PPT 2. Heredity and Genetics PPT 3. Punnett Square Manipulatives – charts and colored tokens 4. Punnett Square Practice Review Sheets 5. Exit Ticket – 10 multiple choice questions on Heredity and Genetics 6. Heredity Vocabulary Review Essential Question(s): 1. Compare and contrast heterozygous and homozygous. 2. Compare and contrast dominant alleles and recessive alleles. 3. Compare and contrast genotype and phenotype. 4. What are the laws of inheritance? 5. How are punnett squares used as a prediction tool? Topic – “Genetics and Bioengineering” – Heredity and Punnett Squares Set Bell Work – 5 minutes Students will respond the following questions: - Compare and contrast heterozygous and homozygous. - Compare and contrast dominant alleles and recessive alleles. - Compare and contrast genotype and phenotype. Think-Pair-Share Direct Instruction and Whole Class Discussion Heredity and Genetics – 20 minutes - Students will take notes in their science notebook. - Students will learn about the lesson’s essential questions. - Homozygous and Heterozygous - Dominant alleles and Recessive alleles - Genotypes and Phenotypes - Laws of Inheritance - Punnett Squares Punnett Square Manipulatives Hands-On Activity – 20 minutes Students will work in pairs to complete this hands-on activity. Students will utilize manipulates that include punnet squares, shapes, and tokens. Students will complete a Punnett Square practice review sheet using manipulates. Closure Exit Ticket – 5 minutes Students will complete a 10 multiple choice questions on Heredity and Genetics. Homework – Complete Heredity Vocabulary Review (Independent Practice) Differentiated Instruction: - Remediation: Peer Tutoring, Guided Notes, Visual Aids, Prompting, Handon activity, and Reduced Assignment - Enrichment: Peer Tutoring and Hand-on activity Formative Assessment for lesson effectiveness: - Bell Work and Exit Ticket - Punnett Square Practice with Manipulates 7 I can define codominance. I can describe incomplete dominance. I can explain the difference between codominance, incomplete dominance, and “regular” monohybrid crosses. I can describe each of the laws of inheritance? I can explain how punnett squares are used as a prediction tool? Materials: 1. Bell Work – sheet for questions 2. Sharing Activity – white board and expo markers 3. Types of Inheritance Video Clip 4. Types of Inheritance PPT 5. Heredity Vocabulary Review 6. Expo Boards 7. Expo Markers 8. Exit Ticket Essential Question(s): 1. What is codominance? 2. What is incomplete dominance? 3. How are codominance and incomplete dominance different than “regular” monohybrid crosses? 4. What are the laws of inheritance? 5. How are punnett squares used as a prediction tool? Topic – “Genetics and Bioengineering” – Types of Inheritance Set Bell Work – 5 minutes - Students will respond to the following questions: - What is codominance? 2. What is incomplete dominance? 3. How are codominance and incomplete dominance different than “regular” monohybrid crosses? - Share and Discuss – 10 minutes Direct Instruction Types of Inheritance Video Clip – 20 minutes Direct Instruction and Class Discussion Types of Inheritance PPT – 20 minutes - Students will take notes in their science notebook. - Students will learn about the lesson’s essential questions. - What is codominance? - What is incomplete dominance? - How are codominance and incomplete dominance different than “regular” monohybrid crosses? - What are the laws of inheritance? - How are punnett squares used as a prediction tool? Whole Class Review Heredity Vocabulary Review (Independent Practice)– 10 minutes - Students will review the vocabulary independent practice. - Students will utilize expo boards and markers to create concept maps that utilize the review terms. - The class will discuss any misconceptions. Closure Exit Ticket – 5 minutes - Students will create a Venn diagram to compare and contrast codominance and incomplete dominance. Differentiated Instruction: - Remediation: Peer Tutoring, Guided Notes, Visual, Hands-on, and Verbal learning activities - Enrichment: Peer Tutoring, Visual, Hands-on, Link to High School Content Subjects, and Verbal learning activities Formative Assessment for lesson effectiveness: Bell Work and Exit Ticket Class Review of the Heredity Vocabulary Review (concept maps and discussion) 8 I can define codominance. I can describe incomplete dominance. I can explain the difference between codominance, incomplete dominance, and “regular” monohybrid crosses. I can describe each of the laws of inheritance? I can explain how punnett squares are used as a prediction tool? I can define an inherited disorder. I can describe how inherited disorders are passed from parents to offspring. I can create a pedigree to illustrate patterns of inheritance, Materials: 1. Bell Work – sheet for questions 2. Sharing Activity – white board and expo markers 3. Pedigrees and Patterns of Inheritance PPT 4. Types of Inheritance Practice 5. Whiteboards 6. Expo Markers 7. Closure 8. Exit Ticket Family History for Pedigree Construction 9. Pedigree Practice #1 Essential Question(s): 1. What is codominance? 2. What is incomplete dominance? 3. How are codominance and incomplete dominance different than “regular” monohybrid crosses? 4. What are the laws of inheritance? 5. How are punnett squares used as a prediction tool? 6. What are pedigrees? 7. How can a pedigree illustrate patterns of inheritance? Topic – “Genetics and Bioengineering” – Pedigrees and Patterns of Inheritance Set Bell Work – 5 minutes - Students will complete a set of questions (5 multiple choice) based on the state standards associated with pedigrees. - Share and Discuss – 10 minutes Partners Practice – Codominance, Incomplete Dominance, and Sex-Linked Inheritance Types of Inheritance Partner Practice – 30 minutes - Students will work with a partner to begin practicing punnett squares that focus on a variety of inheritance. - The following method will be used to introduce this practice activity. - The teacher will model how to correctly complete a practice problem. - The students will help the teacher correctly complete a practice problem. - The teacher will help the students correctly complete a practice problem. - The students will model how to correctly complete a practice problem. - The students will then practice with a partner to complete their review work. Direct Instruction & Class Discussion Pedigrees and Patterns of Inheritance PPT – 20 minutes - Students will take notes in their science notebook. - Students will learn about the lesson’s essential questions. - What are pedigrees? - How can a pedigree illustrate patterns of inheritance? Closure Exit Ticket – 5 minutes - Students will construct a pedigree given family history information. Homework – Complete “Pedigree Practice #1” 9 Project Day – Refer to Unit Plan Differentiated Instruction: - Remediation: Peer Tutoring, Guided Practice, Visual, Authentic Learning Activities, Guided Notes, and Verbal learning activities Formative Assessment for lesson effectiveness: Bell Work and Exit Ticket Guided Practice – Types of Inheritance Practice Pedigree Practice #1 - Enrichment: Peer Tutoring, Guided Practice, Visual, Hands-on, Authentic Learning Activities, and Verbal learning activities 10 I can define codominance. I can describe incomplete dominance. I can explain the difference between codominance, incomplete dominance, and “regular” monohybrid crosses. I can describe each of the laws of inheritance? I can explain how punnett squares are used as a prediction tool? I can define an inherited disorder. I can describe how inherited disorders are passed from parents to offspring. I can create a pedigree to illustrate patterns of inheritance, Materials: 1. Bell Work – sheet for questions 2. Sharing Activity – white board and expo markers 3. iPads 4. Brochure – construction paper, colored paper, markers, colored pencils, rulers, scissors, and pencils. 5. Exit Ticket Essential Question(s): 1. What is codominance? 2. What is incomplete dominance? 3. How are codominance and incomplete dominance different than “regular” monohybrid crosses? What are the laws of inheritance? How are punnett squares used as a prediction tool? What are pedigrees? How can a pedigree illustrate patterns of inheritance? Topic – “Genetics and Bioengineering” – Pedigrees and Patterns of Inheritance 4. 5. 6. 7. Set Bell Work – 5 minutes - Students will respond to the following questions: - What are the laws of inheritance? - How are punnett squares used as a prediction tool? - Share and Discuss – 10 minutes Class Discussion The Kentucky Derby Project – 15 minutes - Students will discuss what they have learned from this project. - Students will also discuss the science requirements of this project. Whole Class Review Independent Practice “Pedigree Practice #1” – 10 minutes Direct Instruction – Utilizing Pedigrees and Punnett Squares for Prediction & Genetic Engineering – 15 minutes - Students will take notes in their science notebook. - Students will learn about the lesson’s essential questions. - Pedigrees - Family History and Patterns of Inheritance - Genetic Engineering and Technology Research Project Utilizing Pedigrees and Punnett Squares for Prediction & Genetic Engineering – 10 minutes - Students will research how engineering and technology is related to the study of genetics and heredity. - Students will create a brochure that includes five technological or engineering advances that are related to the study of genetics and heredity. - Students will work in groups of two. - Students will complete this assignment for homework. Closure Differentiated Instruction: - Remediation: Peer Tutoring, Practice Review, Visual Learning, Guided Notes and Authentic Learning Activities - Enrichment: Peer Tutoring, Visual, Learning, and Authentic Learning Activities Formative Assessment for lesson effectiveness: Bell Work and Exit Ticket Class Discussion – Kentucky Derby Project Whole Class Review – Pedigree Practice #1 “Utilizing Pedigrees and Punnett Squares for Prediction & Genetic Engineering” (Research Project) Exit Ticket – 5 minutes - Students will reflect and respond to the following questions: - How is bioengineering related to genetics and heredity? - Provide a minimum of two specific examples with a description of its relationship to bioengineering. Homework – Complete “Utilizing Pedigrees and Punnett Squares for Prediction & Genetic Engineering” (Research Project) STANDARDS Embedded Inquiry Grade Level Expectations: GLE 0707.Inq.1 GLE 0707.Inq.2 GLE 0707.Inq.3 GLE 0707.Inq.4 GLE 0707.Inq.5 State Performance Indicators SPI 0707.Inq.1 SPI 0707.Inq.2 SPI 0707.Inq.3 SPI 0707.Inq.4 SPI 0707.Inq.5 Identify what you want to teach. Reference State, Common Core, ACT College Readiness Standards and/or State Competencies. Design and conduct open-ended scientific investigations. Use appropriate tools and techniques to gather, organize, analyze, and interpret data. Synthesize information to determine cause and effect relationships between evidence and explanations. Recognize possible sources of bias and error, alternative explanations, and questions for further exploration. Communicate scientific understanding using descriptions, explanations, and models. Design a simple experimental procedure with an identified control and appropriate variables. Select tools and procedures needed to conduct a moderately complex experiment. Interpret and translate data in a table, graph, or diagram. Draw a conclusion that establishes a cause and effect relationship supported by evidence. Identify a faulty interpretation of data that is due to bias or experimental error. Embedded Technology & Engineering Grade Level Expectations: GLE 0707.T/E.1 Explore how technology responds to social, political, and economic needs. GLE 0707.T/E.2 Know that the engineering design process involves an ongoing series of events that incorporate design constraints, model building, testing, evaluating, modifying, and retesting. GLE 0707.T/E.3 Compare the intended benefits with the unintended consequences of a new technology. GLE 0707.T/E.4 Describe and explain adaptive and assistive bioengineered products. State Performance Indicators SPI 0707.T/E.1 SPI 0707.T/E.2 SPI 0707.T/E.3 Identify the tools and procedures needed to test the design features of a prototype. Evaluate a protocol to determine if the engineering design process was successfully applied. Distinguish between the intended benefits and the unintended consequences of a new technology. SPI 0707.T/E.4 Standard 4 – Heredity GLE 0707.4.1 GLE 0707.4.2 GLE 0707.4.3 GLE 0707.4.4 State Performance Indicators SPI 0707.4.1 SPI 0707.4.2 SPI 0707.4.3 SPI 0707.4.4 Differentiate between adaptive and assistive engineered products (e.g., food, biofuels, medicines, integrated pest management). Compare and contrast the fundamental features of sexual and asexual reproduction. Demonstrate an understanding of sexual reproduction in flowering plants. Explain the relationship among genes, chromosomes, and inherited traits. Predict the probable appearance of offspring based on the genetic characteristics of the parents. Classify methods of reproduction as sexual or asexual. Match flower parts with their reproductive functions. Describe the relationship among genes, chromosomes, and inherited traits. Interpret a Punnett square to predict possible genetic combinations passed from parents to offspring during sexual reproduction.