8th Unit Planning
advertisement
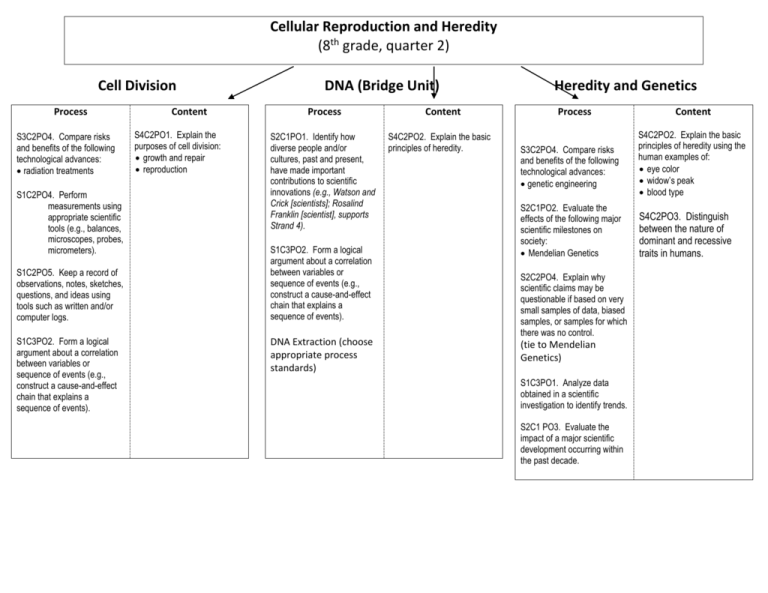
Cellular Reproduction and Heredity (8th grade, quarter 2) Cell Division Process S3C2PO4. Compare risks and benefits of the following technological advances: radiation treatments S1C2PO4. Perform measurements using appropriate scientific tools (e.g., balances, microscopes, probes, micrometers). S1C2PO5. Keep a record of observations, notes, sketches, questions, and ideas using tools such as written and/or computer logs. S1C3PO2. Form a logical argument about a correlation between variables or sequence of events (e.g., construct a cause-and-effect chain that explains a sequence of events). Content S4C2PO1. Explain the purposes of cell division: growth and repair reproduction DNA (Bridge Unit) Process S2C1PO1. Identify how diverse people and/or cultures, past and present, have made important contributions to scientific innovations (e.g., Watson and Crick [scientists]; Rosalind Franklin [scientist], supports Strand 4). S1C3PO2. Form a logical argument about a correlation between variables or sequence of events (e.g., construct a cause-and-effect chain that explains a sequence of events). DNA Extraction (choose appropriate process standards) Content S4C2PO2. Explain the basic principles of heredity. Heredity and Genetics Process Content S3C2PO4. Compare risks and benefits of the following technological advances: genetic engineering S4C2PO2. Explain the basic principles of heredity using the human examples of: eye color widow’s peak blood type S2C1PO2. Evaluate the effects of the following major scientific milestones on society: Mendelian Genetics S4C2PO3. Distinguish between the nature of dominant and recessive traits in humans. S2C2PO4. Explain why scientific claims may be questionable if based on very small samples of data, biased samples, or samples for which there was no control. (tie to Mendelian Genetics) S1C3PO1. Analyze data obtained in a scientific investigation to identify trends. S2C1 PO3. Evaluate the impact of a major scientific development occurring within the past decade.











