Vocabulary Genetics - Madison County Schools
advertisement

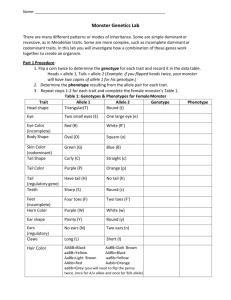
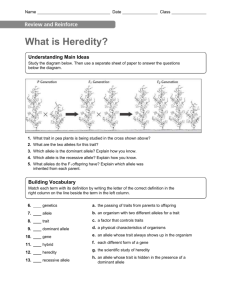
Genetics: The Science of Heredity 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. Heredity Trait GeneticsPurebredGeneAlleleDominant alleleRecessive alleleHybrid Punnett squarePhenotypeGenotypeHomozygousHeterozygousIncomplete dominanceCodominnaceMultiple allelesPolygenic inheritance Meiosis – Genetics: The Science of Heredity 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. HeredityTraitGeneticsPurebredGeneAlleleDominant alleleRecessive alleleHybrid Punnett squarePhenotypeGenotypeHomozygousHeterozygousIncomplete dominanceCodominnaceMultiple allelesPolygenic inheritance Meiosis - Genetics: The Science of Heredity 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. HeredityTraitGeneticsPurebredGeneAlleleDominant alleleRecessive alleleHybrid Punnett squarePhenotypeGenotypeHomozygousHeterozygousIncomplete dominanceCodominnaceMultiple allelesPolygenic inheritance Meiosis – Genetics: The Science of Heredity 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. HeredityTraitGeneticsPurebredGeneAlleleDominant alleleRecessive alleleHybrid Punnett squarePhenotypeGenotypeHomozygousHeterozygousIncomplete dominanceCodominnaceMultiple allelesPolygenic inheritance Meiosis – Genetics: The Science of Heredity 1. Heredity- the passing of traits from parents to offspring 2. Trait-a specific characteristic that an organism can pass to its offspring through its genes 3. Genetics- the scientific study of heredity 4. Purebred- an offspring of many generations that has the same form of a trait 5. Gene-a sequence of DNA that determines a trait and is passes from parent to offspring 6. Allele- the different forms of a gene 7. Dominant allele-an allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present 8. Recessive allele- an allele that is hidden whenever the dominant allele is present 9. Hybrid –an offspring of crosses that has two different allele for a trait 10. Punnett square- a chart that shows all the possible combination of alleles that can result from a genetic cross 11. Phenotype- an organisms physical appearance or visible traits 12. Genotype- an organisms genetic makeup, or allele combinations 13. Homozygous- have two identical alleles for a particular gene 14. Heterozygous- having two different alleles for a particular gene 15. Incomplete dominance-a situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele 16. Codominance-a situation in which both alleles for a gene are expressed equally 17. Multiple alleles- there or more possible alleles of a genet that determines a trait 18. Polygenic inheritance – the inheritance of traits that are controlled by two or more genes, such as height in humans. 19. Meiosis – the process that occurs in the formation of sex cells by which the number of chromosomes is reduced to half