6_SS_Government and Social Class Unit 7: Eastern Civ. Defining
advertisement

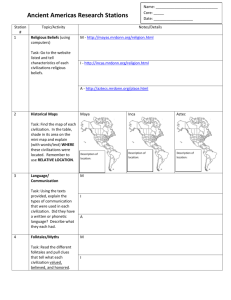
6_SS_Government and Social Class Unit 7: Eastern Civ. Defining Success OBJECTIVE: What will WWBAT draw similarities between the progressions of your students be development in India to other civilizations we have studied this able to do by the end year. (Reason for permanency of settlement, form of government) of class? WWBAT describe how the caste system in India works as a point of contrast between India and other civilizations (introduction to lesson 7.8 – Religion and Culture) KEY IDEAS: What 3-5 1. India was established along 2 river valleys and in a moderate key knowledge or region (climate-wise) with a variety of resources skills will students 2. Indians used irrigation and division of labor to establish large need to master the population centers objective? 3. India’s organization and success was managed early on by a series of dynasties 4. India is different from other civilizations we have studied because of the origins of their social class system (Hinduism’s belief in reincarnation and karma, more on this in 7.8 LP) and and the finality of it (connection to current events project coming up). 5. Diagram social class (caste) system for India. ASSESSMENT: How will you assess to determine which students mastered the objective? Lesson Cycle Caste Activity Compare/Contrast to modern social class structure of United States Untouchables conversation Unit exam Do Now: (15 min) MATERIALS Attendance, review HW (art forgery) Cards with Caste Activity castes (class INTRODUCTION OF NEW MATERIAL: How will you convey the knowledge and/or set: 7 sets of 4) skill of the lesson? What will you student be doing to process this My information? Review 6 signs of a civilization (in table groups, per different civilizations) classroom library You can use the books off my shelf for details but no technology! Describe the following for your civilization of choice: 1) What are their resources? (physical geography included) 2) What was the sequence of events that allowed for this civilization to grow and eventually lead up to an established division of labor? 3) What was their social class structure like? 4) Describe their form of government, and general attitude toward law and order 5) What were their religious beliefs? 6) Any other cultural practices you would like to include? (values, virtues, fashion, inventions, ideas/philosophical contributions, etc.) GUIDED PRACTICE: In what ways will your learners attempt to explain or do what you have outlined? How will you monitor and coach their performance? Table groups will present their summaries for: 1) Mesopotamia 2) Greece 3) Egypt 4) Hohokam 5) Aztec 6) Maya 7) Inca 8) China 9) India INDEPENDENT PRACTICE: In what ways will your different learners attempt the objective on their own? How will you gauge mastery? Students will silently list the ‘themes’ they heard (similarities between civilizations) and turn in as an exit ticket CLOSING: How will you have students summarize what they’ve learned? How will you reinforce the objective’s importance and its link to past and future learning? Organization DIFFERENTIATION: How will you differentiate your instruction to reach the diversity of learners in your classroom? Skills used: Verbal/Creative Recall (in role-play) Research skills (main idea, summarizing, textual evidence) Presentation skills (oral) Compare/Contrast (summary) NOTES TEMPLATE: NAME OF GROUP MEMBERS: Civilization Chosen: 1) What are their resources? (physical geography included) 2) What was the sequence of events that allowed for this civilization to grow and eventually lead up to an established division of labor? 3) What was their social class structure like? 4) Describe their form of government, and general attitude toward law and order 5) What were their religious beliefs? 6) Any other cultural practices you would like to include? (values, virtues, fashion, inventions, ideas/philosophical contributions, etc.) SUMMARY: WHAT THEMES DID YOU HEAR? i.e. what are some of the things a lot of civilizations had in common?