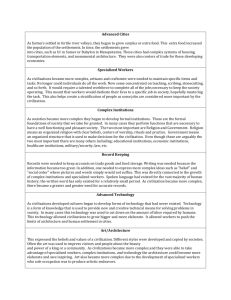
Social Studies Grade 5 Civilizations part 1
advertisement
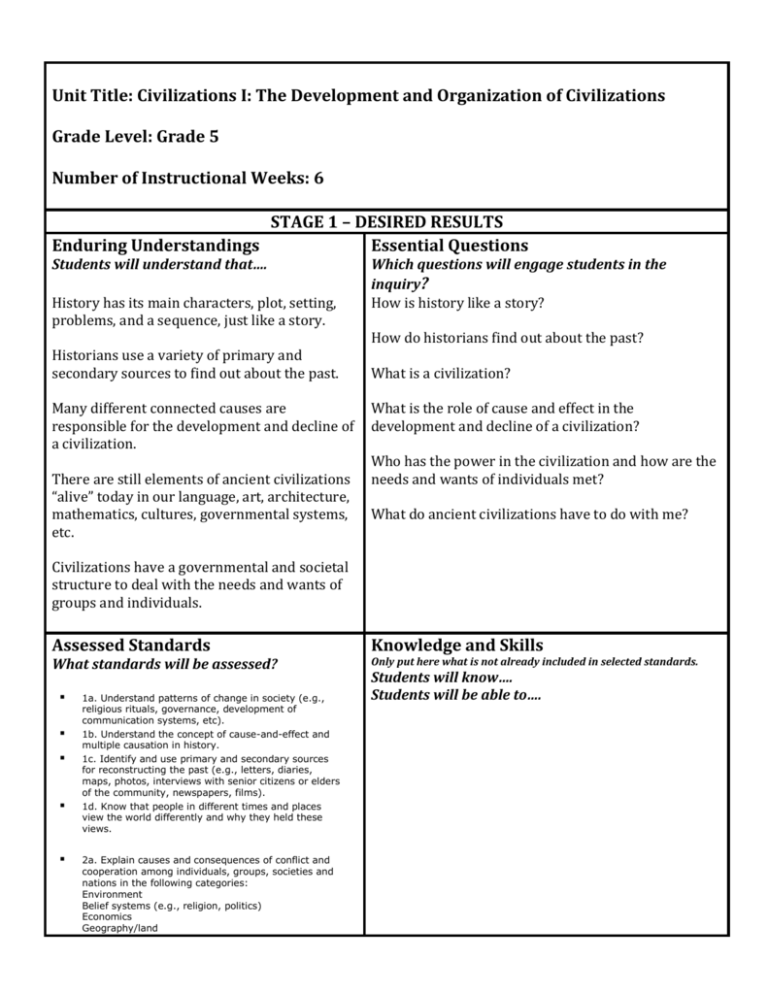
Unit Title: Civilizations I: The Development and Organization of Civilizations Grade Level: Grade 5 Number of Instructional Weeks: 6 STAGE 1 – DESIRED RESULTS Enduring Understandings Essential Questions Students will understand that…. History has its main characters, plot, setting, problems, and a sequence, just like a story. Historians use a variety of primary and secondary sources to find out about the past. Many different connected causes are responsible for the development and decline of a civilization. There are still elements of ancient civilizations “alive” today in our language, art, architecture, mathematics, cultures, governmental systems, etc. Which questions will engage students in the inquiry? How is history like a story? How do historians find out about the past? What is a civilization? What is the role of cause and effect in the development and decline of a civilization? Who has the power in the civilization and how are the needs and wants of individuals met? What do ancient civilizations have to do with me? Civilizations have a governmental and societal structure to deal with the needs and wants of groups and individuals. Assessed Standards What standards will be assessed? 1a. Understand patterns of change in society (e.g., religious rituals, governance, development of communication systems, etc). 1b. Understand the concept of cause-and-effect and multiple causation in history. 1c. Identify and use primary and secondary sources for reconstructing the past (e.g., letters, diaries, maps, photos, interviews with senior citizens or elders of the community, newspapers, films). 1d. Know that people in different times and places view the world differently and why they held these views. 2a. Explain causes and consequences of conflict and cooperation among individuals, groups, societies and nations in the following categories: Environment Belief systems (e.g., religion, politics) Economics Geography/land Knowledge and Skills Only put here what is not already included in selected standards. Students will know…. Students will be able to…. Ethnicity/race/gender Culture 2c. Explain the major ways groups, societies, and nations interact with one another (e.g., trade, cultural exchanges, international organizations). 3e. Describe geographic factors that influence human migration. 3f. Describe and explain various types and patterns of settlement and land use and reasons why particular locations are used for certain human activities. 4b. Understand the components of a belief system (creed, code of behavior, rituals, community). 4c. Identify and compare various belief systems and their principle tenets. 4h. Understand cultural differences regarding what is public and private. 4j. Describe the influence of arts, crafts, music, and language on various cultures. 5c. Describe the various forms of institutions (e.g., family, school, church, clubs) and how they influence the individual. 5e. Understand how social systems (e.g., schools, media, religions, families) prescribe gendered identities. 6b. Describe how governments meet needs and wants of individuals and society. 7b. Explain relationships between the locations of resources and patterns of population distribution. 7e. Explain and compare ways in which people satisfy their basic needs and wants through the production of goods and services. 7h. Describe economic causes of human migration. 8b. Examine ways in which tools and techniques make certain tasks easier. 8d. Describe instances in which changes in values, beliefs, and attitudes have resulted from new scientific knowledge and from technological knowledge Technology Integration



![world history - New Page 1 [je074.k12.sd.us]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009977422_1-26b439736c031db692fcb89a191e6c98-300x300.png)