Teacher: Eugene Kobielnik Year: 2011
advertisement

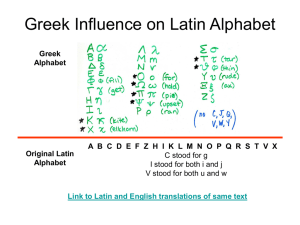
Teacher: Eugene Kobielnik Year: 2011-12 Course: Latin Month: All Months S The e Greek p World ~ t e m b e r The first marking period: The Greek World Conversational Latin: greetings, politeness, permission, Latin names, functional directives/responses, Happy Birthday, basic questions/answers, spelling and pronunciation Vocabulary: cardinal numbers and Roman numerals, 1-100, classroom/school objects, geographical nouns & place names, subject pronouns, adjectives describing oneself and others, linking verbs, names of people. Grammar: linking verbs (present tense), nominative and accusative case nouns, predicate nominatives and predicate adjectives, noun/adjective agreement, noun and adjective gender, conjugation chart, person & number, endings, vocative case nouns. Culture: definition and overview of Western civilization, Greek geography (including southern Italy), Greek alphabet, Greek mythology, Greek art, architecture, & literature, Greek history, culture, philosophy Skill sets: basic pronunciation, maintenance of Latin binder, paper headings for this class, spelling practice, definition and etymology from dictionary, verb conjugation, labeling sentences, talk-to-the-text, answering reading comprehension questions, summarizing and paraphrasing Standards Essential Questions WL-CS1.12.2.AKnow the basic sound system and spelling patterns of classical Latin or Greek. WL-CS1.12.2.BRecognize What Latin expressions do I need to understand (read, write, speak, hear, and respond to) in order to succeed in Latin class this year? What are the basic spelling Assessment Skills s Hear and be able to appropriately respond to greetings in the Latin language. Use expressions of politeness and ask for permission within the Latin classroom. Follow functional Content Letters of the Greek alphabet Four major stages of Western civilization Latin vowels, consonants, and diphthongs. Geography of the Mediterranean world. Lesson Resource s s common and vocabulary pronunciation terms patterns of through classical reading and Latin? listening. How do I WL-CScount from 1.12.2.Cone to oneKnow hundred in common Latin, and vocabulary what English forms and words are structures derived from used in basic these speaking and vocabulary writing. items? WL-CSWhat 1.12.2.Dgeographical Know simple terms and sentence and place names question do I need to structures in know to order to read meaningfully and translate discuss the classical Greek world in Latin or the Latin Greek. language? WL-CSWhat 1.12.2.Eadjectives do I Identify need to know words from in order to the classical describe languages myself and that are other commonly classmates in used in the Latin English. language? WL-CSWhat are the 1.12.2.F18 presentKnow how tense linking the classical verbs I need to languages know in order have to create basic influenced Latin other school sentences curriculum describing classroom Latin directives in the expressions of Latin language, politeness and responding greetings. appropriately in Latin verb Latin when commands. required. Latin numbers, Respond to basic one to oneLatin questions hundred. in complete, nouns of appropriate Latin classroom sentences. objects. Pronounce Latin Linking verbs in vowels, the imperfect, consonants, and present, and diphthongs with future tenses. correct accepted Latin adjectives classical Latin of selfvalues. description. Spell Latin English phrases and vocabulary words correctly, words derived using the sound from Latin. system and Noun macrons. case: nominativ Count from one e and to one-hundred accusative. in the Latin The major language aloud Greek deities and in writing, and some including the use primary Greek of Roman myths. numerals. Foreign Identify language study classroom techniques. objects upon request in the Latin language. Conjugate three different linking verbs: sum (I am), absum (I am absent), adsum (I am present). Describe oneself areas. myself and WL-CSothers in the 1.12.4.Cclass? Describe What are the similarities ten subject and pronouns I differences will need to of daily life know in order and social to create basic structures sentences between describing modern and myself and Grecoothers in the Roman class? culture. What are the WL-CSbasic forms of 2.12.2.Enouns and Identify adjectives I words in will need to English that know in order have origins to understand in the basic classical sentences in languages. the Latin WL-CSlanguage? 3.12.1.BHow do I Know conjugate a advanced verb? vocabulary Why is it and idiomatic beneficial for expressions Americans to used in learn Latin? speaking and What are two writing. basic sentence WL-CSpatterns in any 3.12.4.Alanguage that Explain a employ linking variety of verbs? historical Why is the events, Greek world products and important to customs of Western Grecocivilization, Roman and most culture. importantly, to WL-CSmodern in complete Latin sentences using correctly declined adjectives. Identify and label the geography of the Greek world (including Italy). Find the origin of English words derived from Latin vocabulary words in the English dictionary. Agree nouns and adjectives according to gender and noun case. Create the accusative form for any nominative case noun. Identify and label the subject, linking verb, and subject complements for basic Latin sentences with linking verbs. Recite and write the classical Greek alphabet. Explain what is meant by "Western" civilization, and list its four major phases, in correct order. 3.12.4.CAmerican Compare and culture? contrast the What does the similarities ancient Greek and world look differences like between geographically modern and , articstically, Grecophilosophicall Roman y, historically, culture. and literarily? WL-PSWhat 1.12.2.Aorganizational, Recite the reading, and classical practice Latin or mindset and Greek skills will be alphabet and helpful for associated success in sounds and Latin class? words with proper accentuation. WL-PS1.12.2.BComprehend written sentences and spoken conversation s using simple vocabulary and verbs of being, saying, seeing. Description of dress and color; Talk between friends or family members; Talk between persons of Explain what a "myth" originally was and has now become. Recount a few of the most important Greek myths. Name the major gods from the Greek pantheon, and define them by their spheres of control (i.e. Poseidon is the god of the sea), Explain why Latin is studied by Americans today. Respond to reading comprehension questions about Greek history and culture in complete English sentence s, using the questions to help form the answers. Talk-to-the-text for full reading engagement. Organize the binder and journal for Latin class, as well as head papers with Latin name, date, and period. Practice and review for assessments for different social classes WL-PS1.12.2.D-Use simple sentence and question structures to comprehend simple written sentences and conversation s. Parts of speech in Latin or Greek and English; Conjugation of simple verbs in present tense; Basic patterns of noun, adjective and article changes; Nounadjective agreement; Basic interrogative words; Basic case uses WL-PS3.12.4.CRead, interpret, discuss and write about cultural similarities and differences in foreign language vocabulary and translations. Greco Roman culture and another culture. Gender roles; Social status WL-PS4.12.2.EDiscuss a Greek or Roman event or cultural phenomenon that has influenced English. “Achilles' heel―; Delphic Oracle, Sibyl; Socratic method WL-PS1.12.4.ADiscuss the fundamental products and customs of GrecoRoman culture. Basic classical mythology; Famous people and cities; Roman marketplace N The o Roman v Republic ~ e m The Second marking period: The Roman World Conversational Latin: most and least favorites, expressions of time, the calendar (years, months, weeks, days), major roman festivals, fasti & nefasti, location of people and objects (i.e. "where is..."), the pledge of allegiance, idiomatic vs. b e r literal expressions, Vocabulary: family and household nouns, action verbs (infinitives and verb commands), prepositions, adverbs, ordinal numbers (first, second, third, etc.), English derivations from Latin (legal terms). Grammar: verb infinitives, negative verb commands, pronouns (nominative and accusative), prepositional phrases, Miss Kelly's Rule, ablative case nouns, how to pluralize nominative and accusative case nouns. Culture: Roman interaction with Greek world, Roman gods, Roman foundation legends, Revolution against the Etruscans and foundation of the Republic, Italian Geography, Roman myths (poetry), the history of the alphabets, Latin alphabet, refined Latin pronunciation rules, Roman history from the Etruscans to Julius Caesar's dictatorship. Skill Sets: how to create and effectively use foreign language flashcards; sentence translation, regular syntax. Standards J The a Roman n Empire ~ u a r y Essential Questions Assessments Skills Content Lessons Resources The Third marking period: The Roman Empire Conversational Latin: sports and other leisure activities, clothing and dress, daily routines (dressing, washing, school, etc.), love. Vocabulary: animals, more action verbs, prepositions, and adverbs, some interjections, some conjunctions, Roman gods and heroes, nouns of love Grammar: genitive/possession, present tense action verbs; how to translate sentences with flexible syntax. Culture: Julius Caesar's revolution and the Empire, history to 420's AD, Shakespeare's Julius Caesar, Catullus' poetry, Was Caesar justified? What is more important -- fixing problems with a dictator, or having Skill sets: help kids determine what language they'd like to take in high school, how to conjugate action verbs in the present tense, Standards Essential Questions Assessments Skills Content Lessons Resources