GEOL 101 2015
advertisement
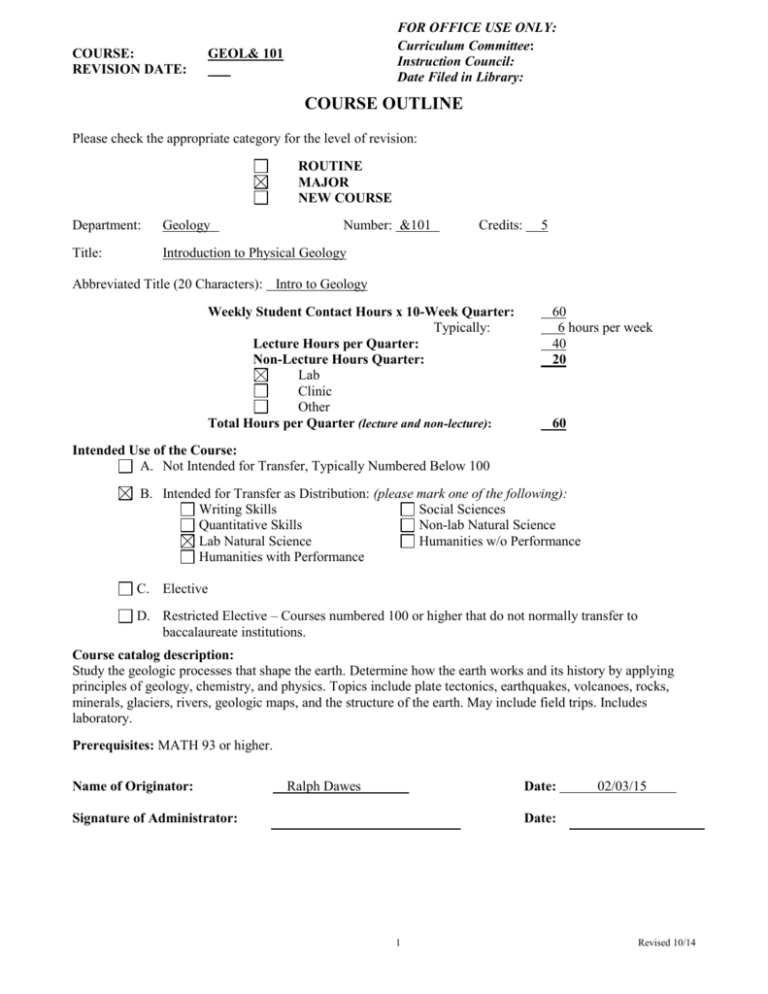
COURSE: REVISION DATE: FOR OFFICE USE ONLY: Curriculum Committee: Instruction Council: Date Filed in Library: GEOL& 101 COURSE OUTLINE Please check the appropriate category for the level of revision: ROUTINE MAJOR NEW COURSE Department: Geology Number: &101 Title: Introduction to Physical Geology Credits: 5 Abbreviated Title (20 Characters): Intro to Geology Weekly Student Contact Hours x 10-Week Quarter: Typically: Lecture Hours per Quarter: Non-Lecture Hours Quarter: Lab Clinic Other Total Hours per Quarter (lecture and non-lecture): 60 6 hours per week 40 20 60 Intended Use of the Course: A. Not Intended for Transfer, Typically Numbered Below 100 B. Intended for Transfer as Distribution: (please mark one of the following): Writing Skills Social Sciences Quantitative Skills Non-lab Natural Science Lab Natural Science Humanities w/o Performance Humanities with Performance C. Elective D. Restricted Elective – Courses numbered 100 or higher that do not normally transfer to baccalaureate institutions. Course catalog description: Study the geologic processes that shape the earth. Determine how the earth works and its history by applying principles of geology, chemistry, and physics. Topics include plate tectonics, earthquakes, volcanoes, rocks, minerals, glaciers, rivers, geologic maps, and the structure of the earth. May include field trips. Includes laboratory. Prerequisites: MATH 93 or higher. Name of Originator: Ralph Dawes Date: Signature of Administrator: 02/03/15 Date: 1 Revised 10/14 COURSE OBJECTIVES I. Student Learning Outcomes STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES 1. Problem Solving: A. B. C. D. Critical Thinking Creative Thinking Quantitative Reasoning Qualitative Reasoning 2. Communication: A. Oral Expression B. Written Expression C. Artistic Expression 3. Social Interaction: A. B. C. D. Collaboration Ethical Conduct Professional Conduct Cultural Diversity 4. Inquiry: A. Information Literacy B. Research C. Documentation List your principal course objectives and then match them with the Student Learning Outcomes (SLO’s) above. It is important to note you DO NOT need to provide a course objective to match each of the above categories. No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Upon completion of this course, successful students will (be able to): Describe (orally or in writing) the major topics studied in geology. Distinguish a scientific theory from a hypothesis, and distinguish the colloquial meaning of theory from the scientific meaning. Describe practical and economic benefits of geology to human society. Describe how geology is unique among sciences in its emphasis on history. Explain observations of geologic phenomena in terms of geologic theory, as demonstrated in lab reports and field trip reports. Describe how the theory of plate tectonics accounts for earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain ranges, and the creation of the earth’s crust. Determine the physical properties of minerals and identify several common types of minerals. Describe the earth as a system of interaction and feedback between life, rock, atmosphere, and hydrosphere. Work through diagrams and concept formulations involving cycles involving a system and exchanges between systems. For example, describe and model processes involved throughout Earth’s hydrologic cycle. Diagram the rock cycle, show how it connects to all other earth systems at various points, and name and describe the main categories of rocks. Identify several common types of rock and explain how each rock formed in terms of geologic processes. Read elevations, directions, and distances on topographic maps, and draw a topographic profile along a designated line. Identify rock types, rock ages, faults, and folds on geologic maps and geologic crosssections. From geologic maps and cross-sections, write a geologic history of the area depicted. Make systematic observations of minerals, rocks, and geologic sites in the real world, and identify some basic geologic aspects of what they see using appropriate geological terminology. List rock formations and geologic structures in correct relative age sequence, based on evidence in maps, cross-sections, or the actual world, using geologic principles Describe how the geologic timescale was constructed by relative age determination methods. Explain the methods of absolute age measurement, including more than one of the sources of data that are used to measure the age of the earth. Identify, classify and describe types of mass movement. Identify and interpret driving and resisting forces on various slopes composed of various geologic materials. Investigate the formation glacial ice, compare and contrast glacier types and past and 2 Categories 2 A, 2B 1A, 1D 2.A, 2B 2A, 2B 2B, 4B, 4C 2.A, 2B, 4B, 4C 1A, 1D, 4A, 4B, 4C 1A, 1D, 2B 1A, 2A, 2B, 4A, 4B 1A, 2A, 2B, 4A, 4B 1A, 1D, 4A, 4C 1A, 1C, 1D, 4B 4A, B, C, 1A, C, D, 2B 1A, 1D, 2A, 2C, 3A, 3B, 4B 1A, 1C, 1D 1A, 4B 1C, 4B 1A, 1D, 4A, 4C 1A, 1D, 4A, 4C Revised 10/14 20 present locations of glacial ice, and explain how glaciers and ice ages have impacted Earth and local regions. Recognize geologic topics in news reports and explain the geologic topics in a broader or more detailed geologic context than presented in the news reports. 1A, 1D, 4A, 4C Footnotes: (1) A typical course addresses two or three of the four principal SLO areas, though one or all four may be acceptable for a given course (2) It is the AAS-DTA in total which covers all of the SLO’s. 3 Revised 10/14 II. List core topics of this course. 1. absolute and relative geologic time 2. principles of relative geologic age 3. origin of earth in the solar system 4. radioactive isotopes in minerals and rocks (used for measuring ages) 5. minerals 6. rocks 7. the rock cycle 8. weathering 9. erosion and mass wasting 10. sediment deposition, sedimentary structures, and stratigraphic sequences 11. streams 12. floods (optional) 13. groundwater (optional) 14. glaciers 15. climate change in earth history 16. earthquakes 17. volcanoes 18. plate tectonics 19. earth’s interior 20. (optional) earth resources III. Text and Reference Materials: a) The text and lab manual are the GEOL& 101 open course library, which was created by WVC and is available online from the Washington State Community and Technical Colleges, currently available at http://ocl.azurewebsites.net/geol-101-introduction-to-physical-geology/ . The text covers the above outcomes and topics with the aim of achieving the appropriate level of up-to-date science knowledge, affordability, and online and hard copy versatility. IV. Special Equipment, Supplies and/or Materials Required Instructor equipment: Multimedia teaching station, including document camera with strong zoom/magnification capability, computer with Internet connection, and video camera with adapter for showing microscope images projected to large screen. Student Equipment: Computer stations with Internet connectivity. Rocks, minerals, maps (topographic and geologic), rulers, protractors, standard testing tools for determining the physical properties of minerals (glass plates, bottles of 5% HCl solution, streak plates, hand lenses, pieces of steel for scratching), low-power binocular microscopes for viewing rocks, minerals, sediments, or fossils in detail. Other: Access to vans or bus for field trips. V. Transferability: Least transferable RESTRICTED CREDIT (as defined by DTA and ICRC) Most transferable GER (General Education Requirement) with our degree; Generally does not transfer unless with DTA completed) GTC (General Transfer Credit) Transfers w/ or w/o the degree; Generally transfers as credit without completing DTA but only as XX or no specific equivalent course COURSE EQUIVALENT (please list equivalent course descriptor/ number) Transfers w/or w/o degree because it has specific course equivalent GEOL 100 GEOL 101 GEOL 101 GEOL 101 ESS 101 Eastern WU Central WU WSU Western WU UW 4 Revised 10/14 VI. Lab Fees: Course already has an existing Lab Fee: YES This is a NEW course and needs to establish a Lab Fee: YES Existing Lab Fee: $ 20.00 Suggested NEW Lab Fee: $ VII. Course Development Stipend Authorization. For course development stipends the appropriate Dean must COMPLETE this section: NEW Course development Conversion of an existing course for Online or Hybrid or NO NO Other (check one) Major online revision (check one) VIII. Changes: For your Routine or Major Revision, please list or briefly describe all changes made to this course outline compared to the previous outline. Updating Student Learning Outcomes 5 Revised 10/14