Teresa Nguyen and Rachel Tung P.4 Solubility Solubility: The ability
advertisement

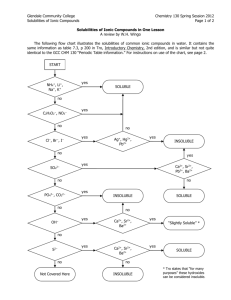
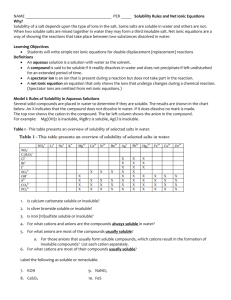
Teresa Nguyen and Rachel Tung P.4 Solubility Solubility: The ability for a substance to dissolve in water. Memorize Solubility Rules: Compounds with the following are ALWAYS soluble Alkali metals (H, Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr) Nitrate (NO3-), Nitrite (NO2-) Ammonium (NH4+), Ammonia (NH3) Chlorate (ClO3-), Chlorite (ClO2-), Perchlorate (ClO4-) Acetate (C2H3O2 ) Acidic Hydrogen (H_) Compounds with the following are always soluble… Chloride (Cl-), Bromide (Br-), Iodide (I-) Chromate (CrO42-) Sulfate (SO42-) Compounds with the following are always insoluble… Hydroxide (OH ) Oxide (O2-) (S2-) Sulfide Phosphate (PO43-) UNLESS with… Silver (Ag+), Dimercury (Hg22+), Lead (Pb2+) Silver (Ag+), Dimercury (Hg22+), Strontium (Sr2+), Barium (Ba2+) Mercury (Hg22+), Lead (Pb2+), Calcium (Ca2+), Strontium (Sr2+), Barium (Ba2+) UNLESS with… Calcium (Ca2+), Strontium (Sr2+), Barium (Ba2+) Strontium (Sr2+), Barium (Ba2+) Compounds with the following are ALWAYS insoluble Sulfite (SO32-) Carbonate (CO32-) Solubility Problems: Name whether these compounds are soluble or insoluble RaOH CaO Ag2CrO4 SrSO4 K3PO4 (NH4)2O HCl PbI2 Al2(CO3)3 Zn(C2H3O2)2 Teresa Nguyen and Rachel Tung P.4 Reactions Chemical Reactions: Chemical reaction – process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances Reactants Products yields Reactants – original substances Products – resulting substances Classifying Types of Reactions: Synthesis o 2 or more substances yields 1 product A + X AX Decomposition o 1 reactant yields 2 products AX A + X o Specific Decomposition Reactions Metallic carbonates yield metallic oxides and carbon dioxide Metallic hydroxides yield metallic oxides and water Metallic chlorates yield metallic chlorides and oxygen Carbonic acid yields carbon dioxide and water Single Displacement o An element exchanges places with an ion of a compound to form a different compound and a element Single element on both sides of reaction A + BX B + AX Check activity series to see if a single displacement reaction will occur A reaction will only occur if the single element (A) is higher in the series than the element in the compound (B). Teresa Nguyen and Rachel Tung P.4 Double-Displacement o The ions from two compounds exchange places to form two different compounds AX + BY AY + BX Combustion o A compound (usually hydrocarbon) reacts with oxygen and yields carbon dioxide and water Predicting Reaction Types – Steps: 1. Identify the type of reaction 2. Predict products in the word equation 3. Write formula equation using symbols 4. Balance equation o Use coefficients to make sure both sides of the reaction have an equal number of atoms for each element 5. Indicate phase of matter o Use solubility rules (s) = solid, (g) = gas, (l) = liquid, (aq) = aqueous o If all of them are aqueous in a double displacement reaction, there is no reaction. *Remember: o Ammonia – NH3 o Sulfur – S8 o Phosphorus – P4 Teresa Nguyen and Rachel Tung P.4 Predicting Reaction Types WS: Indicate the type of reaction (NR for no reaction), complete the word equation, and write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following. Make sure to include phase symbols. ____ 1. Barium and Chlorine gas Activity Series: ____2. Magnesium and Potassium Iodide ____ 3. Hydrochloric Acid and Ammonium Sulfide ____ 4. Lithium Hydroxide ____ 5. ___C6H12O6 + ___O2 Element Li Rb K Ba Ca Na Mg Al Mn Zn Cr Fe Ni Sn Pb ____ 6. Rubidium and Sodium Nitrate ____ 7. Silver + Fluorine ____8. Phosphoric Acid and Calcium Hydroxide ____ 9. Strontium Phosphide ____ 10. Aluminum and Silver Bromide H2 Cu Hg Ag Pt Au F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 Reactivity React with cold water and acids replacing H React with acids or steam, but usually not liquid water, to replace hydrogen All react with acids, but not water, to replace hydrogen All react with oxygen to from oxides Mostly unreactive Listed from most to least reactive Teresa Nguyen and Rachel Tung P.4 Answer Key Solubility Problems: RaOH – insoluble Ag2CrO4 – insoluble K3PO4 - soluble HCl - soluble Al2(CO3)3 – insoluble CaO – insoluble SrSO4 – insoluble (NH4)2O - soluble PbI2 – insoluble Zn(C2H3O2)2 – soluble Predicting Reaction Types WS: S 1. Barium and Chlorine gas Barium Chloride Ba(s) + Cl2(g) BaCl2(aq) NR 2. Magnesium and Potassium Iodide No Reaction Mg(s) + KI(aq) NR NR 3. Hydrochloric Acid and Ammonium Sulfide No Reaction HCl(aq) + (NH4)2S(aq) NR (all aqueous) D 4. Lithium Hydroxide Lithium Oxide and Water 2LiOH(s) Li2O(s) + H2O(l) C 5. ___C6H12O6(g) + _6_O2(g) 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(g) SD 6. Rubidium and Sodium Nitrate Sodium and Rubidium Nitrate Rb(s) + NaNO3(aq) Na(s) + RbNO3(aq) S 7. Silver + Fluorine Silver Fluoride 2Ag(s) + F2(g) 2AgF(s) DD 8. Phosphoric Acid and Calcium Hydroxide Calcium Phosphate and Water 2H3PO4(aq) + 3Ca(OH)2(aq) Ca3(PO4)2(s) + 6H2O(l) D 9. Strontium Phosphide Strontium and Phosphorous 2Sr3P2(s) 6Sr(s) + P4(s) SD 10. Aluminum and Zinc Bromide Zinc and Aluminum Bromide 2Al(s) + 3ZnBr2(aq) 3Zn(s) + 2AlBr3(aq)