Midterm Study Guide (word)

Midterm Study Guide – Thursday (12/17) @ 12:30pm in Room F-2
Chapter 2 (p. 30-34; 38-43)
1.
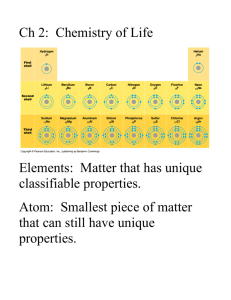
Define/understand isotopes, valence electrons, & ions
2.
Know difference between 4 bond/interaction types; which are strongest a.
Covalent – sharing of electrons i.
Non-polar covalent – sharing of electrons is equal (e.g. carbon dioxide) ii.
Polar covalent – unequal sharing due to one atom being more electronegative (e.g. water) b.
Ionic – bond formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another (e.g. NaCl) i.
Define electronegativity; which elements have greatest electronegativity c.
Know what a hydrogen bond is, why it forms, who it forms between
3.
Define chemical reactions, reactants, products, & chemical equilibrium
Chapter 3 (p. 46-56)
4.
Know the 4 emergent properties of water & why they occur, define hydrophilic/hydrophobic
5.
Define acid & base (how H + affected), pH scale; predict pH changes w/ & w/o buffers (carbonic acid)
Chapter 4 (p. 58-66)
6.
Define/recognize organic molecules, hydrocarbons, & 7 functional groups (p. 64-65)
7.
Know characteristics of ATP; how it stores energy
8.
Be able to read structure diagrams of molecules
Chapter 5 (p. 68-85)
9.
Define polymer/monomer; which classes form polymers; describe dehydration & hydrolysis reactions
10.
Lipids: a.
Discuss functions/characteristics of lipids (fat, phospholipid, steroid, ester linkage) b.
Describe structure of fats; why hydrophobic; difference b/w saturated & unsaturated fatty acids c.
Describe structure of phospholipids (amphipathic)
11.
Carbohydrates a.
Discuss functions/characteristics of carbs b.
Define mono-, di-, polysaccharide, glycosidic linkage c.
Discuss characteristics of starch, glycogen, cellulose, glucose
12.
Proteins a.
Discuss functions/characteristics of proteins b.
Describe general amino acid structure c.
Define polypeptide, peptide bond, denaturation, chaperonin; know 4 levels of protein folding
13.
Nucleic Acids a.
Discuss characteristics of DNA & RNA (know differences) b.
Know 3 parts of a nucleotide & 5 bases (A,G,T,C,U); complementary pairs
Chapter 8 (p. 152-160)
14.
Describe general characteristics of an enzyme (structure, function, cofactors, conenzymes)
15.
Discuss factors that affect enzyme activity (substrate/enzyme concentration, temp/pH, competitive/noncompetitive inhibitors, allosteric regulation/cooperativity, feedback inhibition)
Chapter 6 (p. 94-124)
16.
Differentiate b/w prokaryotic/eukaryotic cells (kingdoms/domains/structures on p. 100-101)
17.
Know description/functions of nucleus, nuclear envelope, nuclear lamina, chromosomes, chromatin, nucleolus
18.
Know how ribosome is formed, what it’s made of; where located; define transcription & translation
19.
Name structures of endomembrane system & how system works a.
Know difference b/w two types of ER & what their functions are b.
Know structure of Golgi (two faces), its functions c.
Discuss lysosome function (autophagy & phagocytosis) d.
Know the three vacuoles & what each does
20.
Describe structure & function of mitochondrion, chloroplast, & peroxisomes
21.
Discuss what cytoskeleton is; distinguish b/w three fibers of cytoskeleton; roles of each a.
Describe general interaction b/w dynein & microtubules b.
Describe general interaction b/w myosin & microfilaments
22.
Know what a cell wall is, composition of plants/fungi, function
23.
Discuss structure/function of ECM & four intercellular junctions (who has them)
Chapter 7 (p 125-140; 768-771 on water potential)
24.
Know different molecules that make up cell membrane (functions/characteristics); characteristics of molecules that pass freely across membrane & which need help
25.
Understand fluidity of membrane (movement of PLs, temp effect, cholesterol’s role, fatty acid’s role)
26.
Define & give functions of integral & peripheral proteins, glycoprotein & glycolipid
27.
Know two types of transport proteins (carrier & channel) & how each works
28.
Define/understand diffusion, concentration gradient, & passive transport
29.
Define water potential & understand how to calculate it (from lab & lecture)
30.
Know isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic & what happens to cell (w/ & w/o cell walls) when placed in diff. solutions; know lyse (lysis), turgid, flaccid, plasmolyze
31.
Understand facilitated diffusion & active transport
32.
Describe 2 electrogenic pumps work & purpose (Na + -K + & Proton pumps); how cotransport works
33.
Describe functions of exocytosis, endocytosis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosis
Chapter 12 (p. 228-243)
34.
Describe binary fission of prokaryotes
35.
Discuss what happens in interphase (G
1
, S, & G
2
phases), know what G
0
phase is
36.
Understand chromosomal structure after S phase
37.
Describe structures of mitotic spindle
38.
Discuss each stage of mitosis (prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) & cytokinesis
39.
Describe mechanism of each cell cycle checkpoint (G
1
, G
2
, & M)
40.
Discuss how external factors can affect cell cycle
41.
Describe characteristics of cancer cells
Chapter 13 (p. 248-260 & section 15.4: p. 297-300)
42.
Define all terms under ‘Cell Terminology’ in notes
43.
Give general description of each reproductive life cycle
44.
Describe stages of meiosis & how genetic variation can arise
Chapter 14 (p. 262-279, stop at genetic testing)
45.
Discuss the findings of Mendel’s pea experiments from both mono- & dihybrid cross
46.
Recognize/understand genetics terminology & generation names (P, F
1
, F
2
)
47.
Understand/solve genetics problems using monohybrid/dihybrid/test crosses/law of probabilities
48.
Describe/understand traits that are…sex-linked, incompletely dominant, codominant, multiple allelic, pleiotropic, epistatic, polygenic
49.
Be able to read pedigrees & predict the cause of a disorder from a pedigree
Chapter 15 (p. 286-302)
50.
Describe the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
51.
Understand sex determination in humans, sex linked traits, & X inactivation
52.
Understand Morgan’s fruit fly experiments (sex linkage & gene linkage)
53.
Be able to read/use common nomenclature of fruit fly alleles (b + is wild type/gray body, b is mutant/black body)
54.
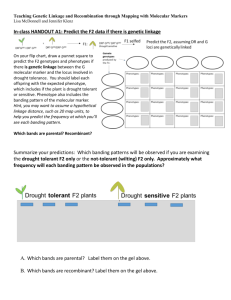
Calculate percent recombination in fly crosses & use data to create a linkage map (order of genes)
55.
Understand genomic imprinting & extranuclear DNA
56.
Be able to calculate chi-squared
Chapter 22 (p. 452-467)
57.
Know/understand Darwin’s 4 observations & 2 inferences; Discuss steps to evolution (mutate, natural selection, evolution); Read/ understand Natural Selection: A Summary (pg 460)
58.
Explain evidence of evolution: artificial selection, fossil record, structural homology, comparative embryology, molecular homology
59.
Describe what homologous/vestigial/analogous structures are & convergent evolution
60.
Be able to read a phylogenetic tree (chapter 26)
Chapter 23 (p. 469-485)
61.
Define genetic variation, population, gene pool, & gene frequency
62.
Explain Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (know 5 assumptions) & be able to use the equation
63.
Explain process & effects of genetic drift, founder effect, bottleneck effect, gene flow
64.
Discuss how only natural selection leads to adaptive evolution (relative fitness)
65.
Explain three selection types (directional, disruptive, stabilizing)
66.
Understand sexual selection, sexual dimorphism, intrasexual & intersexual selection
67.
Discuss significance of & modes for preservation of genetic variation
Chapter 24 (p. 488-504)
68.
Understand microevolution, macroevolution, speciation, & Biological Species Concept
69.
Describe two modes of speciation (allopatric & sympatric) w/ examples
70.
Explain 8 reproductive isolating mechanisms (p. 490-91)
71.
Describe concept of Punctuated Equilibrium (vs. Gradualism)
Chapter 53 (p. 1170 – 1191)
72.
Define/recognize organism, population, community, ecosystem, biosphere, biotic/abiotic factors (ch 52)
73.
Define population density & dispersion; understand how to calculate population size
74.
Know three types of dispersion & possible reasons for each
75.
Describe exponential growth (J-curve), logistic growth (S-curve), carrying capacity
76.
Discuss limiting factors on a population, density dependent & density independent factors
77.
Describe survivorship curves & 3 types
78.
Define life history (3 factors it involves) & discuss K-selection & r-selection
79.
Calculate population change rates & percentages
80.
Read an age structure pyramid & predict future growth/social issues
81.
Discuss steps/reasons for demographic transition
Chapter 54 (p. 1194-1215)
82.
Describe/recognize what ecological niche is (fundamental & realized); generalist & specialist species
83.
Discuss/recognize types of intraspecific & interspecific interactions (competition, predation, herbivory, parasitism, mutualism, commensalism)
84.
Describe competitive exclusion theory & resource partitioning
85.
Recognize/understand the different mechanisms of prey defense (coloration & mimicry) & predator adaptations; define coevolution
86.
Define/understand species richness, relative abundance, & theory of island biogeography
87.
Define/understand dominant, invasive, keystone, foundation species in a community
88.
Recognize what a disturbance is & describe process of primary & secondary terrestrial succession (characteristics of pioneer species, early, mid, & late successional/climax plants)