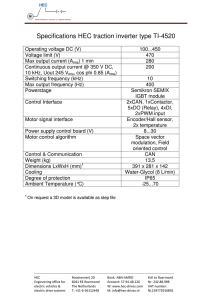
EE302 Problem Set 1
advertisement

EC312 Homework 12
Name: ____________________________
Read: (1) Lecture 12 Notes
(2) Frenzel, Principles of Electronic Communications Systems, 3rd Ed, Ch. 1-4 (p. 8),
Ch. 3-1 to 3-2 2 (p. 93-99)
1. (a) Calculate the wavelength of signals with frequencies of 1.5 kHz, 18 MHz, and 22 GHz.
λ=c/f
λ1.5k = (3x108)/1500 = 200000m
λ18M = (3x108)/(1.8x107) = 16.7m
λ22G = (3x108)/(2.2x1010) = 0.0136m
(b) Understanding that an antenna needed to transmit these frequencies must be at least a tenth of the
wavelength, which frequency would not be suitable to transmit?
1.5kHz
(c) Name and define the technique used to transmit the frequency in part (b).
Modulation: To overcome limitations of the communications channel and permit multiple access,
information signals are impressed upon a higher-frequency carrier signal for transmission.
(d) What is the name associated with the frequency of part (b).
Baseband
2. An AM signal is comprised of the following two signals:
vinfo(t) = 80 cos(2π 500 t) [V]
vcarrier(t) = 100 cos(2π 800,000 t) [V]
(a) Find the carrier frequency, the upper-sideband and lower-sideband frequencies, and the percent
fC 800 kHz
modulation (m).
f USB f c fi 800.5 kHz
f LSB f c fi 799.5 kHz
V
80 V
m i
0.8 80%
Vc 100 V
vinfo(t) changes to 120 cos(2π 500 t) [V].
(b) Find the percent modulation (m). Give the technical term for this condition and explain the effects
V 120 V
m i
1.2 120%
of this condition occurring.
Vc 100 V
This is overmodulation. For an overmodulated signal, the carrier signal's amplitude is too small to
support modulating the information signal. Thus, clipping occurs, and the signal is distorted.
3. A radio station, 1280AM, is conducting a monthly test of the Emergency Alert System. The test begins
with an annoying sound comprised of two pure tones at 853Hz and 960Hz. The signal being broadcast
has exactly five frequency components, i.e., the signal could be written as follows:
vAM(t) = v1 sin(2π f1 t) + v2 sin(2π f2 t) + v3 sin(2π f3 t) + v4 sin(2π f4 t) + v5 sin(2π f5 t) [V]
(a) Find the five frequencies that comprise the AM signal being broadcast. The carrier frequency and the
two sidebands for each of the two tones will be involved.
{1280 kHz, [1280 kHz ± 853 Hz], and [1280 kHz ± 960 Hz]}, or {1279040 Hz, 1279147 Hz, 1280000
Hz, 1280853 Hz, and 1280960 Hz}
1
(b) Find the bandwidth for this particular broadcast.
The bandwidth is the frequency range spanned by the AM tones with the highest and lowest frequencies:
BW = 1280960 Hz – 1279040 Hz
= (1280 kHz + 960 Hz) – (1280 kHz – 960 Hz) = 2(960 Hz)
= 1920 Hz = 1.92 kHz
(c) Determine which of these two tones determines the bandwidth.
The tone that is higher in frequency determines BW (i.e., the 960 Hz tonal) because it causes sideband
frequencies further from the carrier frequency.
(d) What is the bandwidth assigned to an AM radio station in the United States?
10 kHz
4. An AM signal is shown below in the frequency domain, answer the following questions:
(a)What is the frequency of the carrier,fc?
fc = 700MHz
(b) What is the frequency of the modulating
signal, fm?
670
700
fm= 30MHz
730
(c) What is the Bandwidth of the AM signal?
Frequency (Mhz)
BW= 60MHz
5. An AM transmitter has a carrier power of 30 W. The percentage modulation is 85%. Calculate (a) the
total power, and (b) the power in one sideband.
a) Pt=30(1+(.85^2)/2)=40.8375W
b) Plsb+Pusb=Pt-Pc=40.8375-30= 10.8375W
Pssb=10.8375/2 = 5.4188W
2