Human Geography-Thinking Geographically Name____________
advertisement

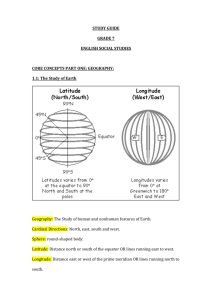
Human Geography-Thinking Geographically Name____________ Hour ________ Ch. 1.1 Welcome to Geography (pages 4-5) Vocabulary terms: define each of the following and draw a simple picture/symbol to represent it. -geography -place -region -scale -space -connection 1) What 3 specific things do geographers explain? 2) Which Greek scholar invented the word “geography’? 3) What do human geographers specifically study? 4) What do physical geographers specifically study? 5) Think of a place you have lived or visited and give one example of each of the following for it (similar to “Geography at Ipanema” on page 5): -Physical Geography: -Place: -Scale: -Region: -Space: -Connection: Ch. 1.2 Ancient and Medeval Geography (pages 6-7) 1) This early geographer was first to demonstrate the Earth was spherical. 2) Eratosthenes was the first geographer to divide the Earth up into 5 what? 3) The oldest known map dates back to approximately when? 4) The oldest known map is a drawing of what? 5) Describe two differences you notice between the 3 maps shown on page 7. 1- 2- 6) Give two similarities you notice amongst the 3 maps shown on page 7. 1- 2- Human Geography-Thinking Geographically Name____________ Hour ________ Ch. 1.3 Reading Maps (pages 8-9) Vocabulary terms: define each of the following and draw a simple picture/symbol to represent it. -map -cartography -map scale -ratio/fraction -written scale -graphic scale -projection 1) Maps serve what two purposes? 1- 2- 2) What two decisions does a cartographer need in order to make a map? 1- 2- 3) Although a globe accurately represents the Earth, explain two ways in which a globe is a limited tool to communicate info about the Earth’s surface. 1- 2- 4) List and explain each of the 4 types of map distortion. 1- 2- 3- 4- Human Geography-Thinking Geographically Ch. 1.4 The Geographic Grid (pages 10-11) Name____________ Hour ________ Vocabulary terms: define each of the following and draw a simple picture/symbol to represent it. -geographic grid -meridian -longitude -prime meridian -parallel -latitude -International Date Line 1) The equator has how many hours of sun each day? 2) Which line is scientifically derived-Latitude or Longitude? 3) Why was England chosen for having the 0 degree line of longitude to run through it? 4) How many time zones are there in the world? 5) Each time zone is equal to how many degrees of longitude? 6) Name the 4 time zones Canada and the U.S. share. 7) Look at the 1.4.4 Time Zones map-why did Kiribati move the International Date Line nearer its eastern boundary in 1997? Ch. 1.5 Geography’s Contemporary Analytic Tools (pages 12-13) 1) What is Geographic Information Science? 2) Define Remote Sensing: 3) What is GPS? 4) What is GPS commonly used for? 5) Define GIS: 6) How might you use GPS in your daily life today or in the future? Explain- 7) Explain what a mash-up is? Human Geography-Thinking Geographically Ch. 1.4 The Geographic Grid (pages 10-11) Name____________ Hour ________ Vocabulary terms: define each of the following and draw a simple picture/symbol to represent it. -geographic grid -meridian -longitude -prime meridian -parallel -latitude -International Date Line 1) The equator has how many hours of sun each day? 2) Which line is scientifically derived-Latitude or Longitude? 3) Why was England chosen for having the 0 degree line of longitude to run through it? 4) How many time zones are there in the world? 5) Each time zone is equal to how many degrees of longitude? 6) Name the 4 time zones Canada and the U.S. share. 7) Look at the 1.4.4 Time Zones map-why did Kiribati move the International Date Line nearer its eastern boundary in 1997? Ch. 1.5 Geography’s Contemporary Analytic Tools (pages 12-13) 1) What is Geographic Information Science? 2) Define Remote Sensing: 3) What is GPS? 4) What is GPS commonly used for? 5) Define GIS: 6) How might you use GPS in your daily life today or in the future? Explain- 7) Explain what a mash-up is? Human Geography-Thinking Geographically Ch. 1.6 Place: A Unique Location (pages 14-15) Name____________ Hour ________ 1) Location is the position that something occupies on _______________. 2) In what 3 ways can location be described? 3) Define toponym: 4) True or False-All inhabited places on Earth have been named. 5) The longest place name in the U.S. is located in Massachusetts, which was agreed upon by three groups of Native Americans living on what? 6) Define situation: 7) How does Singapore’s situation make it important (figure 1.6.2)? 8) Define site: 9) What are 5 important site characteristics? 10) Manhatten Island’s site has been altered by building on top of what? CH. 1.7 Region: A Unique Area (pg’s.16-17) 11) Define region: 12) Define functional region: 13) What are 3 examples of a functional region? 14) What are the names of the 2 major newspapers here in the Twin Cities metropolitan area? 15) Which newspaper would have a larger functional region-The Villager (Highland Park) or Pioneer Press? Explain why- 16) What is breaking down traditional functional regions? 17) Define formal region: 18) Why is Montana a good example of a formal region? 19) Define vernacular region: 20) Which of the 6 characteristics for the South map do you find most convincing? Explain why you feel this way please.