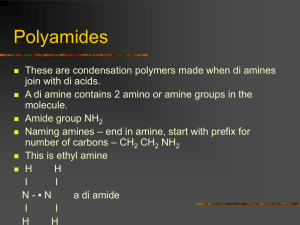
Practice Problems
advertisement

84 Practice Problems for Chapter 21 – Chem 1C 1. Name the following: A) B) C) D) E) 2. Name the following: A) B) C) D) 3. isopropane methylpentane methylbutane n-pentane dodecane n-heptane 2-methyl-2-ethylbutane 3,3-dimethylpentane 2,2-diethylpropane Name the following: A) 2,4-diethylpentane B) 3,5-dimethylheptane C) secondary ethylpentane D) 2,3-dimethyl-2,3-diethylpropane E) none of these 4. In lecture, a professor named a molecule 2-ethyl-4-tert-butylpentane. A student pointed out that the name was incorrect. What is the correct systematic name for the molecule? A) 2-t-butyl-5-methylhexane B) 2-ethyl-4,5,5-trimethylhexane C) 3,5,6,6-tetramethylheptane D) 2,2,3,5-tetramethylheptane E) undecane 5. Structural isomers have A) different molecular formulas and different structures. B) different molecular formulas but the same structure. C) the same molecular formula and the same structure. D) the same molecular formula but different structures. E) none of these 6. How many structural isomers does propane have? A) 3 B) 2 C) 1 D) 5 E) 4 7. The product of ethane undergoing dehydrogenation is called A) propene. B) methene. C) ethene. D) propane. E) none of these 8. Which of the following, upon reacting with oxygen, would form the greatest amount of carbon dioxide? A) n-pentane B) isopentane C) neopentane D) Two of these would form equal amounts. E) All of these would form equal amounts. 9. Which of the following has the lowest boiling point? A) methane B) butane C) ethane D) propane E) All of these have the same boiling point. 10. Which of the following names is a correct one? A) 3,4-dichloropentane B) 1-chloro-2,4-methyl-3-ethylcyclohexane C) 1,1-dimethyl-2,2-diethylpentane D) cis-1,3-dimethylbutane E) 2-bromo-1-chloro-4,4-diethyloctane 11. What is the compound whose carbon skeleton (minus any hydrogen atoms) appears below? A) B) C) D) E) 2,4-diethyl-3,6-dimethylheptane 2,5-dimethyl-4,6-diethylheptane 1,4-diethyl-3,6-dimethyl-tridecane 5-ethyl-3,4,6-trimethyloctane 4-ethyl-2,5,6-trimethyloctane 12. The compound below is the carbon skeleton (minus any hydrogen atoms) of I. a C12H26 II. a substituted octane III. a compound with 3 tertiary carbons IV. a compound with 3 secondary carbons V. a compound with 2 isopropyl groups A) B) C) D) E) 13. I, II, III II, III, IV III, IV, V II, IV, V I, II, III, IV A student gave a molecule the following name: 3-methyl-4-isopropylpentane However, the teacher pointed out that although the molecule could be correctly drawn from this name, the name violates the IUPAC rules. What is the correct (IUPAC) name for the molecule? A) B) C) D) E) 14. 4-isopropyl-3-methylpentane 2-isopropyl-3-methylpentane 1,1,2,3-tetramethylpentane 2,3,4-trimethylhexane 3,4-dimethylheptane A student gave a molecule the following name: 2-ethyl-3-methyl-5-butylhexane However, his TA pointed out that although the molecule could be correctly drawn from this name, the name violates the systematic rules. What is the correct (IUPAC) name for the molecule? A) B) C) D) E) 3,4-dimethyl-6-butylheptane 2-butyl-4,5-dimethylheptane 5,7,8-trimethyldecane 1,2-diethyl-3,6,7-trimethylnonane 3,4,6-trimethyldecane 15. Name the following: A) B) C) D) E) 2,2,3,5-tetramethyl-7-propyl-7-t-butyldecane 6-propyl-2,6-di-t-butylnonane 2,2,5,7,8,8-hexamethyl-3,3-dipropylnonane isonanane none of these 16. How many isomers of C4H10 are there? A) 3 B) 5 C) 4 D) 2 E) 6 17. How many isomers are there with the formula C3H4? Include both structural and geometric isomers. A) 3 B) 2 C) 5 D) 6 E) 4 18. 1-Propene undergoes hydrogenation. The product of this is A) methane. B) ethane. C) propane. D) 2-propane. E) none of these 19. Which of the following is not a structural isomer of 1-pentene? A) 2-pentene B) 2-methyl-2-butene C) cyclopentane D) 3-methyl-1-butene E) 1-methyl-cyclobutene 20. Which of the following is an incorrect name? A) trans-1,2-dichloroethene B) butene C) ethyne D) cis-1,1-dichloropropane E) 1,1-dichloropropane 21. H2CCHCH2N(CH3)2 is A) an alkyne and a secondary amine. B) an alkene and a primary amine. C) an alkene and a tertiary amine. D) an alkyne and a tertiary amine. E) none of these 22. Name the following: A) B) C) D) E) 23. Name the following: A) B) C) D) E) 24. 1-hexyne 2-ethynyl butane 2-ethyl-3-butyne 3-methyl-1-pentyne 3-methyl-4-pentyne 2-chloro-3-chloro-cis-2-butene 2,3-dichloro-cis-2-butene 2,3-dichloro-trans-2-butene 1-chloro-1-methyl-2-chloro-propene 2,3-dichloro-1-methyl-propene Name the following: A) 1,1,1-trichloro-5-bromo-3-pentene B) 5,5,5-trichloro-1-bromo-2-pentene C) 1,1,1-trichloro-5-bromo-2-pentene D) 1,1,1-trichloro-5-bromo-3-pentyne E) none of these 25. How many structural and geometric isomers are there of chloropropene? A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5 E) more than 5 26. Consider the molecule trans-2-butene. Which statement is true? A) The molecule has two bonds. B) There is free rotation around every bond in the molecule. C) Cis-2-butene is its structural isomer. D) Carbon #2 exhibits sp2 hybridization. E) None of these 27. Which of the following compounds can exhibit geometric isomerism? A) B) C) D) E) 28. Consider the following four compounds: Which of these compounds would have the same physical properties (melting point, boiling point, density, and so on)? 29. A) B) C) D) I and II I and III II and III III and IV E) I and IV Which of the following types of compounds lacks an sp2-hybridized carbon center? A) aldehydes B) ketones C) alcohols D) alkenes 30. For which of the following compound(s) are cis and trans isomers possible? A) 3,4-diethyl-3-hexene B) 2,3-dichloro-2-butene C) 2,2-dimethylcyclohexanol D) ortho-chloroanaline E) dibromoethyne 31. How many different possible tetramethylbenzenes exist? A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5 E) 6 32. Which of the following have a -C-O-C- functional group? A) esters B) ethers C) amines D) aldehydes E) alcohols 33. The common name for 2-propanol is A) n-propyl alcohol. B) ethanol. C) methanol. D) isopropyl alcohol. E) none of these 34. The oxidation of secondary alcohols results in A) ketones. B) secondary alcohols. C) aldehydes. D) esters. E) ethers. 35. In which of the following lists do all members have a C=O bond? A) ester, aldehyde, secondary alcohol, ketone B) any alcohol, ether, ester C) secondary alcohol, ketone, aldehyde D) ester, aldehyde, ketone E) carboxylic acid, ether, tertiary alcohol 36. Identify the type of organic compound shown: (CH3)2CHNH2 A) B) C) D) E) 37. primary alcohol primary amine tertiary amine carboxylic acid ether Name the following: A) B) C) D) E) 38. Name the following: A) B) C) D) E) 39. acetone butyraldehyde diethylketone diethyl ether none of these Name the following: A) B) C) D) E) 41. methyl alcohol ethyl alcohol propyl alcohol isopropyl alcohol butanol Name the following: A) B) C) D) E) 40. n-propyl acetate isopropyl formate isopropyl acetate ethyl propanoate none of these 2-chloro-3-ethyl-1-isopropylbutanone isopropyl-chloro,methylbutyl ketone 2-butyl,chloro,isobutanoyl methane 4-chloro-2,5-dimethyl-3-heptanone 3-methyl-4-chloro-1-isopropylpentanone Identify the type of organic compound shown: A) B) C) D) E) aldehyde ester amine ketone none of these 42. Identify the type of organic compound shown: A) B) C) D) E) 43. Classify the following molecule: A) B) C) D) E) 44. NH2OH (CH3)2NCH2CH3 Classify the following molecule: A) B) C) D) E) 46. primary alcohol secondary alcohol tertiary alcohol ether phenol Identify the secondary amine. A) CH3CH2NH2 B) CH3NHCH2CH3 C) D) E) 45. aldehyde ester amine ketone none of these primary amine secondary amine tertiary amine amino acid peptide Classify the following molecule: A) B) C) D) E) acid aldehyde amine ketone carbonyl 47. Which of the following will yield a carboxylic acid upon oxidation? A) a secondary alcohol B) an aldehyde C) a cycloalkane D) a ketone E) tertiary alcohol 48. If you were to heat pentanoic acid and 2-butanol with an acid catalyst, which of the following would you be most likely discover in your flask? A) a ketone B) an ester C) an amine D) an alkane E) an aldehyde 49. Classify the following molecule: A) B) C) D) E) 50. 51. acid aldehyde amine ketone carbonyl Oxidation of 2-methyl-1-butanol could yield I. 2-methyl-1-butanone II. 2-methylbutanal III. 2-methylbutanoic acid A) B) C) D) E) I only II only III only II and III I and III Refer to the following structures. Which of the statements below is true of them? A) B) C) D) E) 52. I and II have different molecular formulas. I and III are structural isomers of each other. II and III are stereoisomers of each other. II and III are different conformations of the same compound. I and III are the same compound. Which structure represents an optically active aldehyde? A) B) C) D) E) 53. Pick the optically active molecule among the following: A) B) C) D) E) none of these 54. Which of the following molecules exhibits chirality? A) CH4 B) CH3OH C) CH3CH2OH D) E) CH3CClFOH 55. Which of the following is optically active (that is, chiral)? A) diethylamine B) difluoromethane C) 2-bromopropane D) 2-chloropentane E) 1-chlorohexane 56. Which of the following yields a primary alcohol upon reduction? A) a ketone B) an alkene C) an amine D) an aldehyde E) an ether 57. When C4H8 is treated with water and H2SO4, a tertiary alcohol is produced. Which of the following structures could represent C4H8 in this reaction? A) CH3CH = CHCH3 B) CH3CH2CH = CH2 C) D) E) CH3CH2CH2CH3 none of these 58. Oxidation of a primary alcohol results in a(n) __________, and oxidation of a secondary alcohol results in a(n) _________. A) carboxylic acid, amine B) aldehyde, ketone C) ester, ether D) ketone, aldehyde E) amine, carboxylic acid 59. The boiling point of methanol is much higher than that of ethane. This is primarily due to A) the difference between the molar mass of methanol and that of ethane. B) the hydrogen bonding in methanol. C) the significant molecular size difference between methanol and ethane. D) the carbon-oxygen double bond in the methanol. E) none of these 60. Teflon is an example of a A) copolymer. B) homopolymer. C) dimer. D) two of these E) none of these 61. No atoms are lost from starting material in making which kind of polymer? A) condensation polymer B) polyester polymer C) addition polymer D) vulcanized polymer E) branched polymer 62. The structures of proteins are partially determined by the order of various amino acids in the macromolecule. This level of structural determination is known as A) primary structure. B) secondary structure. C) tertiary structure. D) quaternary structure. E) the order of bases. 63. A polypeptide is A) an addition polymer of amino acids. B) a condensation polymer of amino acids. C) a polymer of sugar molecules. D) a part of nucleic acids. E) none of these 64. Which of the following is the best description of a protein? A) an alternating chain of amino acids and nucleic acids B) a chain of amino acids connected by ester bonds C) two antiparallel chains of nucleic acids connected by hydrogen bonding D) a chain of amino acids formed by condensation polymerization E) a chain of nucleotides connected by phosphodiester bonds 65. A protein is A) a polysaccharide. B) a saturated ester of glycerol. C) one of the units composing a nucleic acid. D) a polymer of amino acid units. E) an aromatic hydrocarbon with a fused ring structure. 66. The condensation product of two amino acids is a(n) A) peptide. B) ketone. C) ether. D) ester. E) alcohol. 67. An example of a secondary structure of a protein is A) an alpha amino acid. B) a peptide linkage. C) a pleated sheet. D) serine. E) none of these 68. Hydrogen bonding between –C=O groups and NH– groups in the backbone of a protein determines the A) primary structure. B) secondary structure. C) tertiary structure. D) quaternary structure. E) all of these 69. The overall shape of a protein is maintained by A) hydrogen bonding. B) ionic bonds. C) dipole-dipole bonding. D) covalent bonds. E) all of these 70. The analysis of a protein for its amino acid content is valuable in determining the protein's A) tertiary structure. B) secondary structure. C) quaternary structure. D) primary structure. 71. The alpha helix of a protein is held in a coiled conformation partly because of A) hydrogen bonding. B) optical activity. C) active sites. D) double bonding. 72. What are the building blocks of proteins? A) nucleotides B) glucose and sucrose C) lipids D) amino acids 73. Which of the following is not a carbohydrate? A) ribose B) asparagine C) glycogen D) starch E) fructose 74. Which of the following is a carbohydrate reservoir for animals? A) starch B) cellulose C) glycogen D) two of these E) none of these 75. What is the complementary nucleic acid sequence for the DNA sequence GAC TAC GTT AGC? A) GAC TAC GTT AGC B) TCA GCA TGG CTA C) CGA ATG CAT CAG D) CTG ATG CAA TCG E) GCG AAA GGG TTA 76. Which one of the following statements about the structure of proteins is incorrect? A) Disulfide bonds provide strong intrachain interactions. B) Hydrogen bonding stabilizes the -helix proteins. C) Nonpolar groups tend to face the outside of a protein in an aqueous solution. D) Ionized amino acid side chains can form salt bridges within a protein. E) Heat can disrupt tertiary structure. 77. Which of the following pairs of substances could form a polyester? A) H2C=CHCH3 + CH3CH2CH2COOH B) HOOC(CH2)2COOH + H2NCH2CH=CHCH3 C) H2C=CH2 + H2C=CHCH3 D) HOCH2CH2OH + HOOCCOOH E) H2NCH2COOH + H2NCOCH2CH2COOH 78. Consider the polymer drawn below: What monomer(s) is (are) needed to produce the above polymer? A) B) C) D) E) 79. CH2 = CH2 and CH3CH = CH2 CH2 = C(CH3)2 CH3CH = CHCH3 CO and CH2 = CH2 none of the above What is added to form the polymer below? n A) B) C) D) E) CH2 = CH – CH3 CH3CH2CH3 CH3 – CH = CH – CH3 H2C = CH – CH – CH2 CH3CH = C(CH3)2 80. Which of the following pairs of substances could form an addition copolymer? A) HOOCCH2OCH2COOH + HOCH2CH2OH B) HO(CH2)4COOH + HOCH2CH2CH2NH2 C) H2C=CHCH=CH2 + H2CCH=CHCH3 D) HOCH2CH2OH + HOOCCH2COOH E) H2NCH2COOH + H2NCOCH2CH2COOH 81. The structure of the polymer used in a freezer wrap can be described mainly as follows: [CCl2 CH2 CCl2 CH2 CCl2 CH2 CCl2 CH2]n The chief monomer of this wrap would have which structure? A) B) C) D) E) 82. Indicate which of the following monomers is(are) used to produce the polymer A) B) C) D) E) 83. CCl2 = CH2 Cl2C – CH2 Cl2C = CH2 = CCl2 CCl2 none of these I only II only III only I and III II and III The formula below is the repeating unit of a A) B) C) D) E) homo-polymer formed by an addition reaction. homo-polymer formed by a condensation reaction. co-polymer formed by an addition reaction. co-polymer formed by a condensation reaction. polyester formed by an addition reaction. 84. What monomer(s) is(are) needed to make the polymer shown here? I. HOCH2CH2OH II. HOOCCH2CH2COOH III. HOCH2CH2COOH IV. HOCH = CHOH V. HOOCCH = CHCOOH A) B) C) D) E) II only III only I and II IV and V II and III Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. C C B D D C C E A E 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. E A D E A D A C E D 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. C D C E E D B C C B 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. B B D A D B C D D D 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. B A C B A B B B D D 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. E B C E D D C B B B 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. C A B D D A C B E D 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. A D B C D C D B C C 81. 82. 83. 84. A B D C