Sykes CH3 problems Lewis Structures, Acid
advertisement
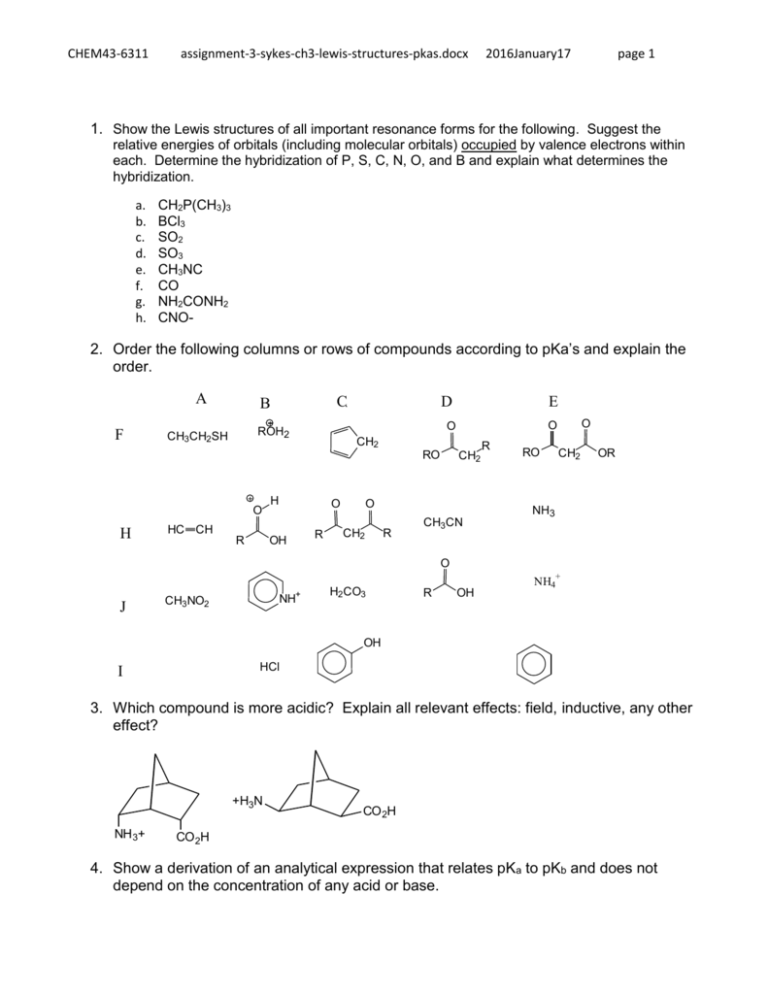
CHEM43-6311 assignment-3-sykes-ch3-lewis-structures-pkas.docx 2016January17 page 1 1. Show the Lewis structures of all important resonance forms for the following. Suggest the relative energies of orbitals (including molecular orbitals) occupied by valence electrons within each. Determine the hybridization of P, S, C, N, O, and B and explain what determines the hybridization. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. CH2P(CH3)3 BCl3 SO2 SO3 CH3NC CO NH2CONH2 CNO- 2. Order the following columns or rows of compounds according to pKa’s and explain the order. A F C B H HC CH R H O OH R CH2 O CH2 R O O CH2 RO O E O ROH2 CH3CH2SH D CH3CN R RO CH2 OR NH3 O + J NH+ CH3NO2 H2CO3 R OH NH4 OH HCl I 3. Which compound is more acidic? Explain all relevant effects: field, inductive, any other effect? +H3N NH 3+ CO 2H CO 2H 4. Show a derivation of an analytical expression that relates pKa to pKb and does not depend on the concentration of any acid or base. CHEM43-6311 assignment-3-sykes-ch3-lewis-structures-pkas.docx 2016January17 page 2 5. Estimate the pKa’s of the most acidic proton on following compounds and explain your reasoning. 6. Show all resonance structures for the intermediate cation that is formed when benzene is protonated. 7. Three isomeric cations are formed when furan is protonated. A) Show the three isomers and all of their resonance structures. B) Which isomer is most stable and explain. CHEM43-6311 assignment-3-sykes-ch3-lewis-structures-pkas.docx 2016January17 page 3 8. Explain why A is a stronger acid. 9. A) Show all tautomers (isomers where only the position of protons change) of the following ketone. As for the ketone, no atom should have a formal charge. (Hint: this ketone has two inequivalent isomers). B) Of the three isomers which is most stable and explain.