This table - Healthcare Professionals Blog | Clot Connect
advertisement

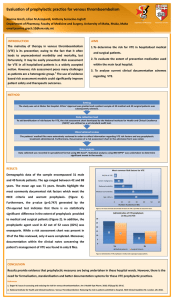
The new oral anticoagulants for VTE – Comparison (Advantages, Disadvantages) Dabiagatran (Pradaxa) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Apixaban (Eliquis) Edoxaban (Savaysa) no yes yes no twice daily once daily twice daily once daily Renal clearance 80 % 33 % 25 % 35 % Efficacy compared to warfarin (recurrent VTE) Safety compared to warfarin in respect to relevant bleeding Reversal agent / antidote available for major bleeding 4 FDA approved for VTE treatment same same same same same same/better1 better 2 better 3 none none none none yes yes yes yes Started immediately upon diagnosis of VTE Dosing “Major bleeding” same as with warfarin in DVT trial, but less in PE trial Less “major bleeding” with apixaban 3 Less “clinically relevant bleeding” with edoxaban, same “major bleeding” 4 reversal agents are in early clinical development for all 4 anticoagulants 1 2 References 1. HOKUSAI-Investigators. Edoxaban versus warfarin for the treatment of symptomatic venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 2013;Sept 1. 2. Agnelli G et al. Oral Apixaban for the Treatment of Acute Venous Thromboembolism. N Engl J Med, 369:799-808. 3. The Einstein Investigators: Oral Rivaroxaban for symptomatic venous thromboembolism. New Engl J Med 2010;363:2499-510. 4. The Einstein Investigators: Oral Rivaroxaban for the treatment of symptomatic pulmonary embolism. New Engl J Med 2012;366:1287-97. 5. Schulman s et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in the treatment of acute venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2009 Dec 10;361(24):2342-52.