Mosaic Origin of the Heme Biosynthesis
Pathway in Photosynthetic Eukaryotes
The evolution of metabolic pathways is a subject of much current interest, with a number of
different hypotheses to explain the origin of new enzymes (Nara, Hshimoto, and
Aoki 2000; Illingworth et al. 2003; Schmidt et al. 2003). In this work, we address the next level
of evolution: gene acquisition/replacement related to the endosymbiotic origins of organelles.
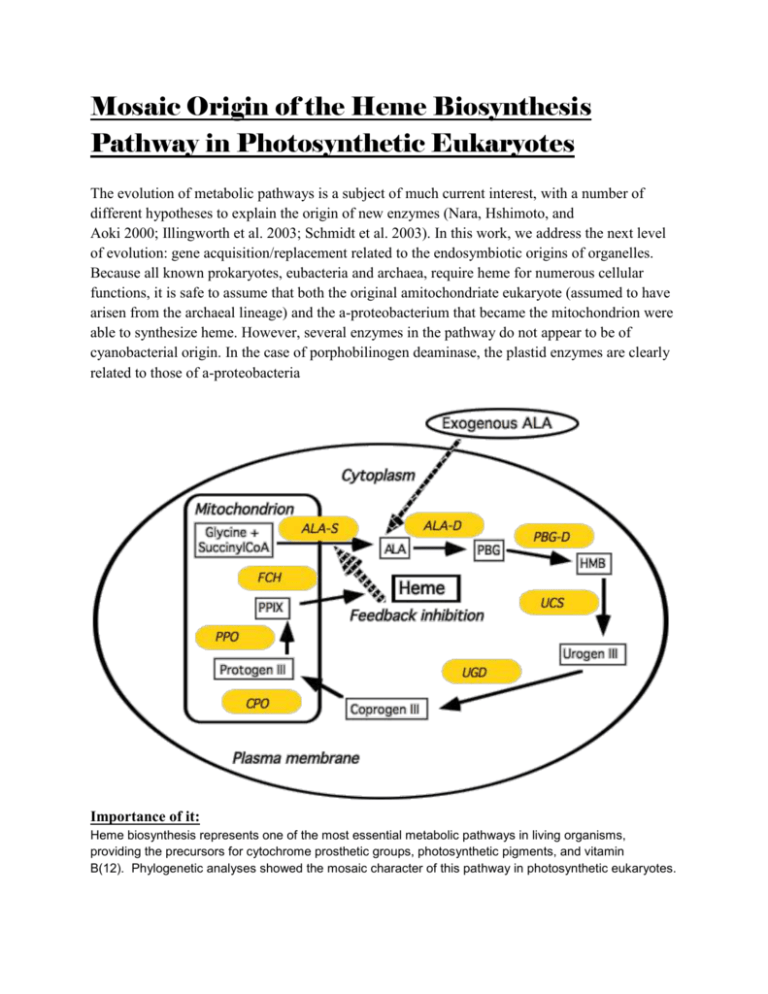
Because all known prokaryotes, eubacteria and archaea, require heme for numerous cellular
functions, it is safe to assume that both the original amitochondriate eukaryote (assumed to have
arisen from the archaeal lineage) and the a-proteobacterium that became the mitochondrion were
able to synthesize heme. However, several enzymes in the pathway do not appear to be of
cyanobacterial origin. In the case of porphobilinogen deaminase, the plastid enzymes are clearly
related to those of a-proteobacteria
Importance of it:
Heme biosynthesis represents one of the most essential metabolic pathways in living organisms,
providing the precursors for cytochrome prosthetic groups, photosynthetic pigments, and vitamin
B(12). Phylogenetic analyses showed the mosaic character of this pathway in photosynthetic eukaryotes.
Nyllaine Ann M. Rodriguez
Grade 9- Maaasahan
Take Home UT – Biology. Metabolic Pathway.
2. Nonphotosynthetic Heterokonts
Phytophthora species are plant pathogens classified asoomycetes, the sister group to the
photosynthetic heterokonts(e.g., diatoms). It is still unclear whether the oomycetes once had a
chloroplast and lost it or whether the photosynthetic heterokonts acquired plastids after the
two branches of the family separated.
3. How would this Heme Biosynthesis will really affect the body if these synthesis act as
enzymes?
4. Heme contained in the food is taken up from the intestines, but this is only relevant because of
the iron it contains. The organic porphyrin ring is mostly synthesized from scratch. The synthetic
pathway is split across two compartments; the initial and final steps occur in the mitochondria,
while the intervening ones occur in the cytosol. Heme exercises feedback inhibition on the first
step in the pathway.
Mosaic Origin of the Heme Biosynthesis Pathway in Photosynthetic Eukaryotes
Mol. Biol. Evol. 22(12):2343–2353. 2005
doi:10.1093/molbev/msi230
Advance Access publication August 10, 2005
The Author 2005. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of
the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution. All rights reserved.
For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oupjournals.org
Accepted July 18, 2005
References:
http://mbe.oxfordjournals.org/content/22/12/2343.full.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16093570
http://www.gopixpic.com/485/hemebiosynthesis/http:%7C%7Cwww*sivabio*50webs*com%7Cplas026*jpg/
http://watcut.uwaterloo.ca/webnotes/Metabolism/ironHemeBiosynthesis.html




![Major Change to a Course or Pathway [DOCX 31.06KB]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006879957_1-7d46b1f6b93d0bf5c854352080131369-300x300.png)