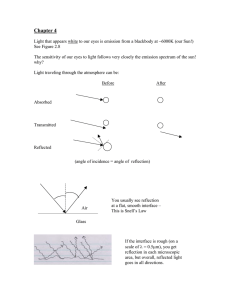
Optical Phenomena in Nature
advertisement

Optical Phenomena in Nature How do Rainbows form? Rainbows explained • Refraction of sun light through water dropplets. • The centre of the rainbow is directly opposite the sun • The order of colours is always the same due to the different angles of refraction. (red refracts the least and violet refracts the most. Notice anything special about double rainbows? A Secondary rainbow has the colours reversed!!! • Because the angle of sun light is “shallower” it refracts differently in the water droplets Why is the sky blue and clouds white? • This is actually a hard one… • Very small particles disperse light well (smaller than the wavelengths of light (390-750 nm). • These are gas particles of oxygen and nitrogen in the atmosphere. Blue to violet are the dominant colours which are dispersed but human eyes are more sensitive to the blue wavelengths. • Larger particles do not disperse light well (the larger cloud water droplets are in this range) and therefore reflect all wavelengths in the spectrum and light retains its white appearance. Apparent depth, an illusion… • The refraction of light from water to air makes an object appear shallower than it really is. Shimmering… Shimmering… • Hot air and cold air have different optical densities (index of refraction). • When air is very hot (hot pavement, campfire, above a bbq or desert) it moves around and mixes with colder air constantly changing the direction of light giving the ``wavy`` appearance of objects. Why do mirrages happen? A Mirrage • Works on the same principle as shimmering. • hot air is less dense than cold air and has a lower index of refraction (light travels faster). • When the air directly above the ground is much hotter than the air above. Light is bent upwards (away from the normal). • This causes you to interpret light coming from the sky or a distant object as something on the ground. Sun/moon rise and set • When the sun or moon is on the horizon the light must pass through much more atmosphere before it reaches you. Remember the blues and violets are being diffracted by atmospheric gases and buy the time the light reaches you all that is left are the red, yellow, and orange wave lengths. Sun/moon rise and set