File - Respiratory Therapy Files
advertisement

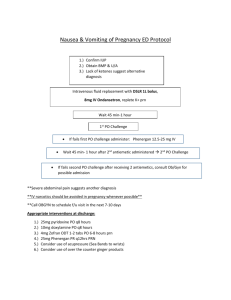
Disease Treatments (consider multiple diseases when considering treatment recommendations) Asthma: For an acute asthmatic attack: Fast acting Adrenergic; either Albuterol (2.5 mg) or Xopenex (0.31,0.63 or 1.25mg); may give multiple doses or continuously through a HEART neb. May also give via MDI/holding chamber; typically this is given with oxygen, assess SpO2, patient response and LOC. May use Bipap for severe asthma attacks. May also use Heliox Anti-cholinergic; given along with an adrenergic, Atrovent 0.5mg Systemic Steroid may be warranted, Solumederol or Prednisone. Assess breath sounds, cough, vital signs, Peak flow measurements o Once stabilized: Conduct asthma education including severity of symptoms, allergies and spirometry For status asthmaticus; patient will require intubation and mechanical ventilation Once admitted, deliver round the clock frequencies of an adrenergic; either Q4-6, wean from this as the patient improves. Check Peak flow measurements BID, give an ICS/LABA BID. Check Esionphil level Recommend follow up spirometry testing after discharge and allergy testing if not done previously Patient will receive a systemic steroid upon discharge for 3-5 days; avoid triggers and allergens, check air quality daily Treatment for NON attacks Mild Intermittent: Albuterol or Xopenex MDI PRN with holding chamber Take 1 hour before exertion for sports induced asthma Avoid known allergens, perform peak flow meter to determine severity of symptoms Mild persistent: Albuterol or Xopenex MDI PRN with holding chamber Take 1 hour before exertion for sports induced asthma Avoid known allergens, perform peak flow meter to determine severity of symptoms Anti-allergen such as a mast cell inhibitor like Intal or Tilade OR a Leukotriene inhibitor such as Singular or Accolate If patient has seasonal allergens recommend nasal sprays, may also require monthly allergy shot Xolair Patient may replace allergen medication with a mild ICS/LABA such as Advair or symbicort Moderate persistent Albuterol or Xopenex MDI PRN with holding chamber Take 1 hour before exertion for sports induced asthma Avoid known allergens, perform peak flow meter to determine severity of symptoms Anti-allergen such as a mast cell inhibitor like Intal or Tilade OR a Leukotriene inhibitor such as Singular or Accolate If patient has seasonal allergens recommend nasal sprays, may also require monthly allergy shot Xolair Patient should take a moderate dose of ICS/LABA such as Advair, Symbicort, Asmanex, Qvar… Along with a LABA such as Serevent, Foradil or Brovona Severe Persistent Albuterol or Xopenex MDI PRN with holding chamber Take 1 hour before exertion for sports induced asthma Avoid known allergens, perform peak flow meter to determine severity of symptoms If patient has seasonal allergens recommend nasal sprays, may also require monthly allergy shot Xolair Patient should take a high dose of ICS/LABA such as Advair, Symbicort, Asmanex, Qvar… Along with a LABA such as Serevent, Foradil or Brovona Chronic Bronchitis Smoking cessation Daily/continuous use of low concentration oxygen; an Adrenergic and Anti-cholinergic; such as Combivent or DuoNeb. Frequency depends on severity. For exacerbations may be given Q4. For home use BID, TID, QID May give multiple treatments during an exacerbation. You will assess CXR, ABG, Labs and history to help assess cause of exacerbation Treat all underlying or contributing problems; such as infection May use BiPAP for exacerbation May use Spiriva in place of Atrovent. If using Spiriva they should not also use Atrovent. Mucolytics for episodes of congestion. May use Mucomyst 10-20% 3-5ml along with adrenergic. Anti-biotic, used during acute infections, but may be recommended on a daily basis for prevention of infection May use PEP devices to deliver medications, Use breathing techniques such as pursed lip breathing, diaphragmatic breathing and Huff cough; give bronchial hygiene to manage secretions Daily ICS/LABA such as Advair or Symbicort Recommend pulmonary rehabilitation, exercise and proper nutrition Emphysema Smoking cessation Daily/continuous use of low concentration oxygen; Adrenergic and Anti-cholinergic; such as Combivent or DuoNeb. Frequency depends on severity. For exacerbations may be given Q4. For home use BID, TID, QID May give multiple treatments during an exacerbation. You will assess CXR, ABG, Labs and history to help assess cause of exacerbation May use BiPAP for exacerbation May use Spiriva in place of Atrovent. If using Spiriva they should not also use Atrovent. Anti-biotic, used during acute infections, but may be recommended on a daily basis for prevention of infection May use PEP devices to deliver medications, Use breathing techniques such as pursed lip breathing, diaphragmatic breathing and Huff cough; give bronchial hygiene to manage secretions Daily ICS/LABA such as Advair or Symbicort Recommend pulmonary rehabilitation, exercise and proper nutrition Surgery available but not common For Alpha 1-Antitrypsin, avoid inhaling toxic particles, avoid air pollution o May use drugs such as Prolastin Cystic Fibrosis Daily/continuous use of low concentration oxygen; Adrenergic and Anti-cholinergic; such as Combivent or DuoNeb. Frequency depends on severity. For exacerbations may be given Q4. For home use BID, TID, QID May give multiple treatments during an exacerbation. You will assess CXR, ABG, Labs and history to help assess cause of exacerbation May use BiPAP for exacerbation May use Spiriva in place of Atrovent. If using Spiriva they should not also use Atrovent. Anti-biotic, used during acute infections, but may be recommended on a daily basis for prevention of infection May use PEP devices to deliver medications, Use breathing techniques such as pursed lip breathing, diaphragmatic breathing and Huff cough; give bronchial hygiene to manage secretions; IPV/IPPB/Flutter/CPT with Vest… Daily ICS/LABA such as Advair or Symbicort Recommend pulmonary rehabilitation, exercise and proper nutrition Surgery available but not common Pulmozyne (Dornase Alfa) BID Dietary supplements. Vitamins Pneumonia If patient has no underlying pulmonary disease, treat judiciously based on symptoms and patients ability to cough and maintain their airway If patient has increased pulmonary congestion, give bronchial hygiene, such as a CPT, Flutter, IPV, IPPB, Suctioning… Recommend bronchoscopy (therapeutic) if patient has tenacious impissiated secretions Anti-biotics, may be broad initially but once the bacteria is identified will become specific Treat fever with cooling measures and Tylenol Treat congestion with Mucolytics such as Mucomyst 10-20% and a Adrenergic via HHN or PEP device or hyperinflation therapy such as IPPB or an IS Administer continuous heated aerosol or humidity Ensure proper IV Hydration Treat any underlying condition or precipitating conditions such as pleural effusions/thorencentesis. May require positive pressure for shunts Patient may get steroids systemically Assess Labs (WBC, lactic acid), Cultures, vitals… Suspect ARDS development with increasing O2 demand and worsening compliance and shunting; watch for developing Sepsis Croup Treat cold like symptoms Isolate from other children May give Racemic Epi (0.25 ml or 0.5ml) for upper airway constriction May give a systemic or aerosolized steroid such as Decadron Cool humidity or aerosol continuously May obtain neck x-ray If patient has underlying pneumonia or asthma, treat appropriately Severe Croup may require intubation Epiglottitis An emergent situation, sedate and intubate Deliver systemic steroids once intubated and assess level of swelling by checking neck x-rays and check cuff pressures of ETT if cuff is present (baby ETT have no cuffs), check leak around airway Neuromuscular diseases If no underlying pulmonary disease, assess patients muscle strength by assessing VC, MEP and MIP BID or more frequent as condition worsens Assess ABG to assess ventilation May use night CPAP or BIPAP, eventually leading to continuous use then intubation and tracheotomy Give bronchial hygeiene using PEP, IPV, IPPB, CPT, suctioning, mucolytics and heated aerosol/humidity as the patients cough will be limited Treat underlying and developing conditions such as pneumonia Depending on type of neuromuscular disease may treat with plasmophoresis, immunoglobulins, cholinergics (don’t use if patient has lung disease), steroids… Renal problems Treat with diruretics, hemodialysis/continous dialysis, blood transfusions BiPAP or mechanical ventilation for pulmonary edema Oxygen to support low CaO2 Assess GFR, BUN, Creatnine, Electrolytes, blood pressure, metabolic acidosis, lactic levels, inputs and outputs, renal ultrasounds Steroids, Albumin, proteins, electrolytes, blood pressure medications… Treat underlying conditions, pleural effusions, anemia, lethargy, electrolyte imbalances and cardiac arrhythmias Ensure patent airway if patient develops metabolic encephalopathy CHF Treat with inotropics, BiPAP/CPAP for pulmonary edema, diuretics Treat underlying problems Assess CXR, BNP, Echocardiogram, Ejection fraction, Cardiac output, renal output… EKG Treat Pleural effusion, diet control/obesity, low salt diets, fluid restriction Treat possible hypertension Pulmonary Hypertension Treat with vasodilators such as Nitric Oxide Inhaled iloprost, Prostacyclin Treat underlying disease if one exists Orders for RT medications should include: Medication Dose Frequency; with a PRN frequency and reason for PRN Modality of delivery Examples: Albuterol 2.5 mg with 3ml NS QID & Q4 PRN for wheezing via SVN o OR Xopenex 1.25 mg, TID & Q2 PRN for wheezing via EZPAP o OR Albuterol 90 mcg MDI x 2 puffs BID & Q4 PRN for wheezing. Additional therapies are also listed, such as CPT, Suctioning, Pulse Oximeter checks, ABG, other RT medications, OXYGEN amount and modality, ranges to keep SpO2… GIVE THE APPROPIATE RT MEDICATION, MODALITY AND FREQUENCY TO YOUR PATIENTS. IF THERE IS NO INDICATION FOR A PARTICULAR DRUG, THEN DO NOT RECOMMEND ITS USE. ALWAYS SELECT THE APPROPIATE MODALITY PER THE PATIENTS ABILITY. IF THEY CAN NOT PERFORM A MDI OR DPI FOR EXAMPLE GET IT CHANGED TO A SVN! RECOMMEND MEDICATION AND FREQUENCY CHANGES WHEN APPROPIATE ALWAYS ASSESS YOUR PATIENTS BEFORE, DURING AND AFTER THERAPY; THIS INCLUDES BREATH SOUNDS, HEART RATE, RESPIRATORY RATE, COUGH, PEAK FLOWS, CHEST EXURSION, GENERAL APPEARANCE… IDENTIFY RISKS AND STOP THERAPY IF THE PATIENT’S HR OR OTHER FACTORS BECOME DANGEROUSLY OUT OF RANGE. HR IS TYPICALLY MONITORED SO THAT IF IT INCREASES MORE THAN 20, TREATMENT IS HELD. ALWAYS EDUCATE YOU PATIENTS. LEAVE THEM KNOWING WHY THEY RECEIVED THEIR MEDS AND WHAT SIDE EFFECTS MAY OCCUR. EDUCATE THEM ON THE PROPER USE OF THEIR MEDS AND DEVICES AND THEIR DISEASE. IF THE PATIENT REQUIRES MORE OR LESS THERAPY THAN THEY ARE CURRENTLY RECIEVEING CHANGE THE THERAPY! USE PROPER CLINICAL JUDGMENT AND ISOLATION PERCAUTIONS. USE CRITICAL THINKING TO PROPERLY ASSESS YOUR PATIENTS. NEVER STACK TREATMENTS.