File
advertisement
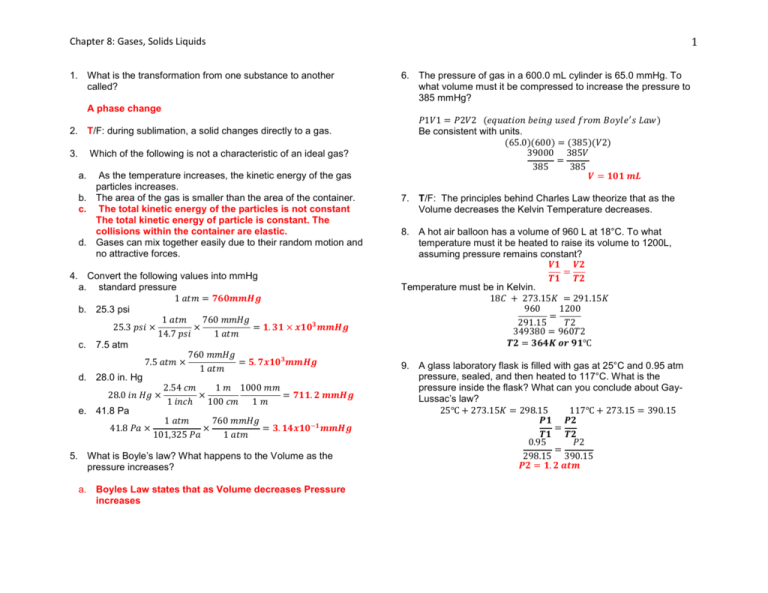
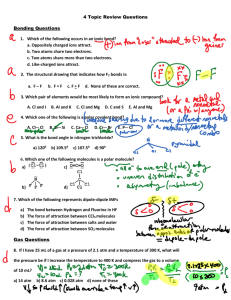
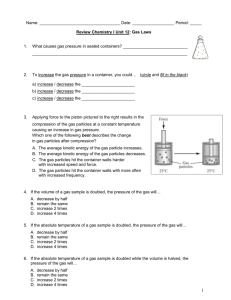
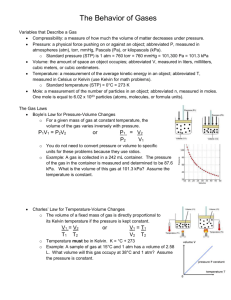
1 Chapter 8: Gases, Solids Liquids 1. What is the transformation from one substance to another called? 6. The pressure of gas in a 600.0 mL cylinder is 65.0 mmHg. To what volume must it be compressed to increase the pressure to 385 mmHg? A phase change 2. T/F: during sublimation, a solid changes directly to a gas. 3. Which of the following is not a characteristic of an ideal gas? a. As the temperature increases, the kinetic energy of the gas particles increases. b. The area of the gas is smaller than the area of the container. c. The total kinetic energy of the particles is not constant The total kinetic energy of particle is constant. The collisions within the container are elastic. d. Gases can mix together easily due to their random motion and no attractive forces. 4. Convert the following values into mmHg a. standard pressure 1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 = 𝟕𝟔𝟎𝒎𝒎𝑯𝒈 b. 25.3 psi 1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 760 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 25.3 𝑝𝑠𝑖 × × = 𝟏. 𝟑𝟏 × 𝒙𝟏𝟎𝟑 𝒎𝒎𝑯𝒈 14.7 𝑝𝑠𝑖 1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 c. 7.5 atm 760 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 7.5 𝑎𝑡𝑚 × = 𝟓. 𝟕𝒙𝟏𝟎𝟑 𝒎𝒎𝑯𝒈 1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 d. 28.0 in. Hg 2.54 𝑐𝑚 1 𝑚 1000 𝑚𝑚 28.0 𝑖𝑛 𝐻𝑔 × × = 𝟕𝟏𝟏. 𝟐 𝒎𝒎𝑯𝒈 1 𝑖𝑛𝑐ℎ 100 𝑐𝑚 1 𝑚 e. 41.8 Pa 1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 760 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 41.8 𝑃𝑎 × × = 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒𝒙𝟏𝟎−𝟏 𝒎𝒎𝑯𝒈 101,325 𝑃𝑎 1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 5. What is Boyle’s law? What happens to the Volume as the pressure increases? a. Boyles Law states that as Volume decreases Pressure increases 𝑃1𝑉1 = 𝑃2𝑉2 (𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑏𝑒𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑢𝑠𝑒𝑑 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝐵𝑜𝑦𝑙𝑒 ′ 𝑠 𝐿𝑎𝑤) Be consistent with units. (65.0)(600) = (385)(𝑉2) 39000 385𝑉 = 385 385 𝑽 = 𝟏𝟎𝟏 𝒎𝑳 7. T/F: The principles behind Charles Law theorize that as the Volume decreases the Kelvin Temperature decreases. 8. A hot air balloon has a volume of 960 L at 18°C. To what temperature must it be heated to raise its volume to 1200L, assuming pressure remains constant? 𝑽𝟏 𝑽𝟐 = 𝑻𝟏 𝑻𝟐 Temperature must be in Kelvin. 18𝐶 + 273.15𝐾 = 291.15𝐾 960 1200 = 291.15 𝑇2 349380 = 960𝑇2 𝑻𝟐 = 𝟑𝟔𝟒𝑲 𝒐𝒓 𝟗𝟏℃ 9. A glass laboratory flask is filled with gas at 25°C and 0.95 atm pressure, sealed, and then heated to 117°C. What is the pressure inside the flask? What can you conclude about GayLussac’s law? 25℃ + 273.15𝐾 = 298.15 117℃ + 273.15 = 390.15 𝑷𝟏 𝑷𝟐 = 𝑻𝟏 𝑻𝟐 0.95 𝑃2 = 298.15 390.15 𝑷𝟐 = 𝟏. 𝟐 𝒂𝒕𝒎 2 Chapter 8: Gases, Solids Liquids 10. When H2 gas was released by the reaction of HCl with Zn, the volume of H2 collected was 75.4 ml at 23°C and 748 mmHg. What is the volume of the H2 at 0°C and 1.00 atm pressure (STP)? 𝑷𝟏𝑽𝟏 𝑷𝟐𝑽𝟐 = 𝑻𝟏 𝑻𝟐 Step 1: Convert to correct units: 0℃ + 273.15𝐾 = 273.15𝐾 23℃ + 273.15𝐾 = 296.15𝐾 1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 748𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 × = 0.98 𝑎𝑡𝑚 760 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 Step 2: Place in known values and cross multiple to solve for unknown V2: (0.98)(75.4) (1 .0)(𝑉2) = (296.15) 273.15 𝑉 0.2495 = 273.15 𝑽 = 𝟔𝟖 𝒎𝒍 11. How many liters does 1 mol of gas occupy at STP? 𝟐𝟐. 𝟒 𝑳𝒊𝒕𝒆𝒓𝒔 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 12. If 15.0 g of CO2 has a volume of 0.30 L at 310K, what is its pressure in mmHg? PV=nRT R=0.0821 (constant) 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝐶𝑂2 15.0 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑚𝑠 × = 0.34 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝐶𝑂2 44.01 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑚𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝐶𝑂2 = # 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑛 (𝑝)(0.30) = (0.34)(0.0821)(310) 760 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 𝑃 = 28.84 𝑎𝑡𝑚 × = 𝟐. 𝟐 × 𝟏𝟎𝟒 𝒎𝒎𝑯𝒈 1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 13. If the partial pressure of oxygen in the air at 1.0 atm is 160mmHg, what is the partial pressure on the summit of Mt. Whitney, where the atmospheric pressure is 440 mmHg? Assume that the percent oxygen is the same. 1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 160 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 (𝑃𝑃) = = 𝟗𝟑 𝒎𝒎𝑯𝒈 0.58 𝑎𝑡𝑚 (𝑃𝑃 𝑜𝑛 𝑀𝑡. 𝑊ℎ𝑖𝑡𝑛𝑒𝑦) 440 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 𝑥 1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 = 0.58 𝑎𝑡𝑚 (𝑝𝑙𝑢𝑔 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑜 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛) 760 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 14. If I place 3 moles of N2 and 4 moles of O2 in a 35 L container at a temperature of 250 C, what will the pressure of the resulting mixture of gases be? pv = nrt Using the ideal gas law, you can determine that the partial pressure of nitrogen in this mixture will be 2.09 atm (211.8 kPa) and the partial pressure of oxygen will be 2.79 atm (282.7 kPa). When you add these together, the total pressure in the container is 4.88 atm (494.5 kPa). 15. What are the only atoms that can bond with hydrogen to form a hydrogen bond? What type of charge is present within the molecule? Hydrogen atoms will bond with F,N,O. 16. List the intermolecular forces in order of increasing strength Hydrogen Bonds > Dipole-dipole> London Dispersion 17. Draw the following structures (A-C). Identify what type of intermolecular force is present. a. b. c. d. N2 dispersion HCN dispersion, Dipole-dipole CH3CO2H dispersion, Dipole-dipole, Hydrogen Bonds MgBr2 London Dispersion 18. Dimethyl ether (CH3OCH3) and ethanol (C2H5OH) have the same formula (C2H6O), but the boiling point of dimethyl ether is -25°C while ethanol is 78°C. Explain. Dimethyl Ether does not have a hydrogen bond it has an CH3-OCH3 structure. Ethanol is an alcohol and has an O-H bond, which is a hydrogen bond. Hydrogen Bonds have high melting point and high boiling points because the bond will require higher temperatures to break or phase change. Chapter 8: Gases, Solids Liquids 19. What is the difference between amorphous and crystalline solid? An amorphous solid is a solid whose particles do not have an orderly arrangement whereas a crystalline solid is a solid whose atoms, ions, and molecules are held together in an orderly fashion. Crystalline solids can be further characterized as ionic, molecular, covalent, or metallic 3