Chapter 32: Electrostatics
advertisement

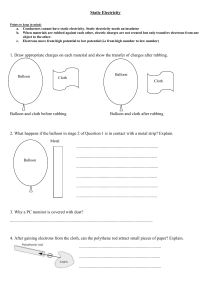
Examples of Electrostatics in the world are: A doorknob shock Static in the dryer Your hair standing up when combed Electricity at rest Involves electrical charges, the forces between them, and their behavior in materials Mutual attractions or repulsions between electrons or protons is called charge. Charges can be negative (-) or positive (+) Protons= positively charged Neutrons= no charge, not repelled or attracted to other particles Electrons= negatively charged Draw a picture to represent the saying above. Law of conservation: the principle that electric charge can neither be created nor destroyed. The net quantity of electric charge, the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge in the universe, is always conserved. The first written statement of the principle was by American scientist and statesman Benjamin Franklin in 1747. Material in which an electrical charge can flow Examples: copper, metal, your body, water Poor conductor for electricity Examples: rubber, glass, cotton Friction- rub hands together Contact- touch another person or an object Charging of an object without direct contact When we allow charges to move off (or onto) a conductor by touching it Why and how do we ground the electricity in our house? One side of the atom or molecule is induced to be slightly more positive (or negative) than the opposite side Example: Balloon and hair--- rub a balloon on hair for static Neg (-) pos (+)