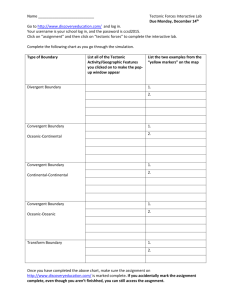
2015 Plate and Structure Study Guide Key
advertisement
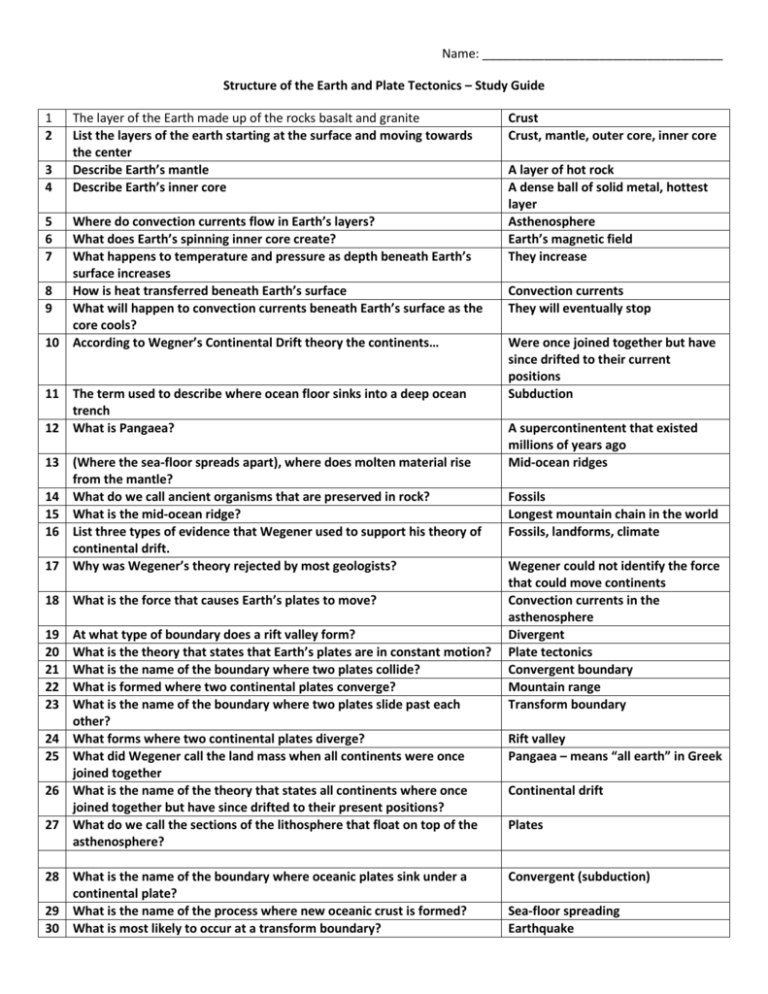
Name: ___________________________________ Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics – Study Guide 1 2 3 4 The layer of the Earth made up of the rocks basalt and granite List the layers of the earth starting at the surface and moving towards the center Describe Earth’s mantle Describe Earth’s inner core 5 6 7 Where do convection currents flow in Earth’s layers? What does Earth’s spinning inner core create? What happens to temperature and pressure as depth beneath Earth’s surface increases 8 How is heat transferred beneath Earth’s surface 9 What will happen to convection currents beneath Earth’s surface as the core cools? 10 According to Wegner’s Continental Drift theory the continents… 11 The term used to describe where ocean floor sinks into a deep ocean trench 12 What is Pangaea? 13 (Where the sea-floor spreads apart), where does molten material rise from the mantle? 14 What do we call ancient organisms that are preserved in rock? 15 What is the mid-ocean ridge? 16 List three types of evidence that Wegener used to support his theory of continental drift. 17 Why was Wegener’s theory rejected by most geologists? 18 What is the force that causes Earth’s plates to move? 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 At what type of boundary does a rift valley form? What is the theory that states that Earth’s plates are in constant motion? What is the name of the boundary where two plates collide? What is formed where two continental plates converge? What is the name of the boundary where two plates slide past each other? What forms where two continental plates diverge? What did Wegener call the land mass when all continents were once joined together What is the name of the theory that states all continents where once joined together but have since drifted to their present positions? What do we call the sections of the lithosphere that float on top of the asthenosphere? 28 What is the name of the boundary where oceanic plates sink under a continental plate? 29 What is the name of the process where new oceanic crust is formed? 30 What is most likely to occur at a transform boundary? Crust Crust, mantle, outer core, inner core A layer of hot rock A dense ball of solid metal, hottest layer Asthenosphere Earth’s magnetic field They increase Convection currents They will eventually stop Were once joined together but have since drifted to their current positions Subduction A supercontinentent that existed millions of years ago Mid-ocean ridges Fossils Longest mountain chain in the world Fossils, landforms, climate Wegener could not identify the force that could move continents Convection currents in the asthenosphere Divergent Plate tectonics Convergent boundary Mountain range Transform boundary Rift valley Pangaea – means “all earth” in Greek Continental drift Plates Convergent (subduction) Sea-floor spreading Earthquake 31 Why does oceanic crust subduct under continental crust? 32 What is most likely to form at an oceanic-continental convergent boundary? 33 At which type of boundary do Island Arches form? 34 What is most likely to form at a continental-continental convergent boundary? 35 Earth’s inner core is found inside which of the Earth’s layers? 36 In which of Earth’s layers would the pressure be the greatest? 37 The asthenosphere is part of which of Earth’s layers? 38 Which of Earth’s layers is the thickest? Oceanic crust is more dense Volcano (or folded mountains) Oceanic-oceanic convergent boundaries Mountains Outer core Inner core Mantle Mantle 39. What type of plate boundary is occurring in diagram A? a. convergent b. divergent c. transform 40. What type of plate boundary is occurring in diagram B? a. convergent b. divergent A B C c. transform 41. What type of plate boundary is occurring in diagram A? a. convergent b. transform c. divergent 42. What type of plate boundary is occurring in diagram C? a. convergent b. transform c. divergent