Chapter 10 key ideas
advertisement

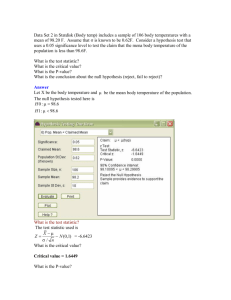
Chapter 10 Key Ideas and Words Section 10.1 o Null hypothesis o Alternative hypothesis o Two-tailed test, left-tailed test, right-tailed test o Four possible outcomes from hypothesis testing (draw two-by-two table) o Type 1 error o Type 2 error o Alpha = level of significance and it’s relationship to a type 1 error o Stating the conclusion to a hypothesis tests General steps o Determine your question ; e.g., coin is fair vs. coin is not fair o Rephrase your question in terms of a probability distribution and a parameter o Combine the question and parameter into null and alternative hypotheses o Determine your level of significance; e.g., alpha=0.05 o Collect the data o Calculate the test statistic under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true o Treating the test statistic as a random variable created with the null hypothesis being true, determine the probability distribution of the test statistic o Calculate if your observed test statistic is unusual Classical method determine critical value(s) using alpha Reject if test statistic is in reject region P-value method Assuming null is true, calculate probability of getting test statistic as extreme or more extreme than what you got from your data Reject null hypothesis if p-value less than or equal to alpha o State conclusion Section 10.2 o Hypothesis testing for a population proportion o Z-statistic o Classical approach o P-value approach o Definition and interpretation of a p-value o Specifics of working with a one-tailed vs. two-tailed test Section 10.3 o Hypothesis tests for a population mean o 1-sample t-statistic o T distribution T-table Degrees-of-freedom o Statistical vs. practical significance o Section 10.6 : Power What is it? How do effect size and sample size affect power?