File - Elizabeth Krastev
advertisement

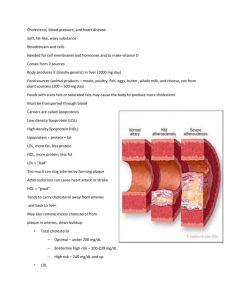
Discharge Planning Project Elizabeth Krastev University of South Florida 1 The patient is a 54-year-old female diagnosed with Coronary artery disease, she has had Percutaneous Coronary Intervention of the left anterior descending artery and stents were placed on 08/15/2014. She returned on the 08/29/14 with chest pain and underwent catheterization where there were two patent stents in the proximal and mid LAD with diffuse spasm that improved with nitroglycerin. She was at baseline until 02/06/15 when she noticed that her blood sugars have elevated to 300-400 and she started having chest pressure that went on to become left arm heaviness and left arm numbness she immediately went to the emergency department and received nitroglycerin. The patient understand how being severely overweight affects the body’s overall health and creates a lot of stress on the heart. She stated that if she doesn’t start exercising she could die. When I asked if she understood why she was hospitalized she told me if was the combination of hypertension, elevated blood sugar, and her coronary artery disease. A person with diabetes makes them two to four times more likely to have heart disease. A major risk for her is uncontrolled diabetes; this is specific to her teaching and is very important to have tight control of glucose. High blood sugars can make artery walls rough. Plaque can then build up, making it harder for blood to flow through the arteries. When blood pressure is high all the time, artery walls become damaged which also increases the risk for plaque to build up. Another topic for teaching is lowing lipid levels because this another risk that can damage the artery walls. Lipids include cholesterol and triglycerides. There are two kinds of cholesterol. LDL cholesterol is the damaging cholesterol. HDL helps clear LDL 2 cholesterol from the blood. After look at the most recent labs her triglycerides are 206, which are above the borderline high. LDL is 84, and HDL is 36, which is below the borderline low, which should be 39. She states she follows a strict healthy diet but it doesn’t seem like that is enough to get her into a healthy state of living. She is trying to quit smoking and hopefully she stays away from smoking because this too damages the arteries and allows plaque to build up in the arteries. Additionally, smoking constricts the arteries causing her blood pressure to rise on top of the hypertension she already is diagnosed with. Cigarette smoking also increases the production of stomach acid and will create more exacerbations of her GERD symptoms. A core measure that is associated with chest pain is administration of aspirin and beta-blocker along with an ordered prescription for both medications for discharge. Another important core measure is Surgical Infection Prevention and proper catheterization technique and appropriate use of sterile equipment will decrease the wound infection rate. Its very important during post catheterization for the nurse to be assessing the puncture wound, dressing and making sure the patient is laying down still to prevent development of a hematoma. The patient’s new medication list includes: Acetaminophen-HYDROcodone 325mg-5mg oral tablet. It should be taken as needed for breakthrough pain, every 4 hours for 3 days. She was aware that it is used for pain and can cause sedation and dizziness. She also knew it could causes nausea and vomiting but was unaware of constipation. She was 3 taught that narcotics cause this common side effect and are usually taken with a stool softener in combination. Cyclobenzaprine (10 mg oral tablet) 5mg =0.5 tablet by mouth 3 times a day as needed for muscle spasms for 5 days. Common side effects are dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, arrhythmias, dyspepsia (she is also taking pantoprazole to counteract), nausea, and urinary retention. Docusate (docusate sodium 100 mg oral capsule). 1 capsule by mouth every 12 hours as needed for constipation for 7 days. Prevention of constipation in patients who should avoid straining, such as after MI or rectal surgery. May cause mild cramps or diarrhea. Patients with cardiac disease should avoid straining because of valsalva maneuver. Pantoprazole (40 mg oral delayed release tablet). 1 tablet by mouth daily for heartburn, take for 30 days. This will decrease relapse rates of daytime and nighttime symptoms on patients with GERD. This drug also may cause hyperglycemia, but also hypomagnesaemia if treatment is longer than 3 months. Important to monitor serum magnesium and may cause abnormal liver function tests. A life-threatening issue is pseudomembranous colitis bloody stools should be reported to health care professional immediately. GI irritation may occur when taking aspirin or NSAIDs. Metoprolol (Metoprolol Tartrate 25 mg oral tablet). 1 tablet by mouth 2 times a day for 30 days. This is a beta-blocker that helps decrease blood pressure and heart rate, frequency of attacks of angina pectoris, and rate of cardiovascular mortality and hospitalization in patients with heart failure. 4 Common side effects are fatigue, weakness, anxiety, mental status changes, hypotension, heartburn, hyper or hypo glycemia. Adverse effects are bradycardia, heart failure, and pulmonary edema. Patient should check pulse daily and blood pressure biweekly. Important to take medication as directed, at the same time each day even if feeling well. Insulin glargine (Lantus) 40 units subcutaneous at bedtime for the control of hyperglycemia in patients with type 1 and 2. Lowers blood glucose by stimulating glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and fat. Also inhibits hepatic glucose production. Adverse reaction is hypoglycemia and allergic reaction like anaphylaxis. Insulin lispro (HumaLOG) 12 units subcutaneous three times a day before meals if fasting blood glucose is above 155. Nicotine (14 mg/24hr transdermal film, extended release) 1 patch daily for tobacco cessation. Could cause headache, insomnia, tachycardia, chest pain, hypertension, burning at patch site, erythema. No more than 1 patch should be worn at a time. Wash hands with soap and water after handling patches. Dispose of used patches by folding adhesive sides together. The patient’s continued medications: ALPRAZolam (Xanax 2mg oral tablet) 3 times a day as needed for anxiety. This is not a new medication for the patient. Common side effects are dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, constipation, and physical dependence. Atorvastatin 40 mg at bedtime. Lowers total and LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. Slightly increases HDL cholesterol. This drug can cause 5 abdominal cramps, constipation, heartburn, and an important side effect for this patient to pay attention to is hyperglycemia. A life-threatening adverse affect is rhabdomyolysis patient needs to be aware of unexplained muscle pain. Grapefruit juice should be avoided because it increases the risk of toxicity. Aspirin 81mg, oral, at bedtime used as prophylaxis of transient ischemic attacks and MI. Atorvastatin 40 mg at bedtime. Lowers total and LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. Slightly increases HDL cholesterol. Nitroglycerin (0.4 mg sublingual tablet). Increases coronary blood flow by dialating coronary arteries and improving flow to ischemic area. Can cause a severe headache, dizziness, hypotension, tachycardia, and syncope. Patient needs to change positions slowly. If patient is having an acute angina attack they should sit and use medication at first sign of attack. Relief usually occurs within 5 minutes. Dose may be repeated; if anginal pain is not relieved by 3 tablets in 15 minutes must call health care professional or go to the nearest ER. Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3 1000 oral capsule) by mouth at bedtime. Treatment or prevention of vitamin D deficiency. Must be cautious of hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, and hpyerphosphatemia may present with nausea, vomiting, anorexia, weakness, constipation, headache, bone pain, and a metallic taste. Later symptoms could include polyuria, polydipsia, photophobia, and cardiac arrhythmias. 6 Clopidogrel (Plavix) 75 mg by mouth at bedtime. Decreases occurrence of atherosclerotic events in patients at risk. Side effects are depression, dizziness, chest pain, hypertension, and pruritus. Adverse effects are GI bleeding, and neutropenia. Fenofibrate 160 mg oral tablet at bedtime. Lowering of cholesterol and triglycerides with subsequent decreased risk of pancreatitis. Side effects that could occur are arrthymias, DVT, fatigue, headache, rash, and decreased HDL levels. A life-threatening reaction could be pulmonary embolism. This medication should be in conjunction with diet restriction (fat, cholesterol, carbohydrates, alcohol), exercise, and cessation of smoking. Lisinopril 10 mg 1 tablet by mouth at bedtime. Lowers BP, increases survival and decreases symptoms in patients with heart failure. Watch for hypotension and hyperkalemia. Patient should avoid salt substitutes containing potassium. Patient has a healthy and supportive living situation. She and her husband have recently moved in with their adult son, his wife and kids. She is retired and has means of transportation by her family. Her son is a personal trainer and is very aware of healthy nutrition. She states he buys all the groceries and is very strict with her and has changed her eating habits. She has two types of insurance, United Health Care and Medicare. No occupational therapy, physical therapy, or speech therapy is needed. She had been instructed to avoid heavy lifting, follow a diabetic, low calorie, low cholesterol diet. She needs to follow up with her primary care provider within 1 week. 7 There is a lot of teaching for a patient with diseases like diabetes, CAD, hypertension because all the factors of these diseases work together increasing the morbidity and mortality. I think it would be helpful for her to talk to a professional nutritionist and personal trainer that can start her at a lower level and help her progress at her pace. It crucial to follow the medication regimen, follow dietary restrictions, keep tight control on blood glucose levels, eliminate any tobacco use, avoid alcohol consumption, and increase daily exercise. If she takes everything into consideration each day she could be healthier than the day before and prevent re hospitalization.