Diabetes Complications Risk Profile
advertisement

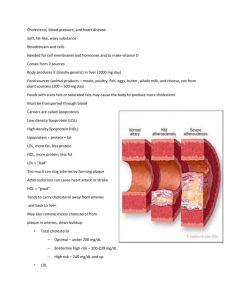
Name Date Diabetes Complications Risk Profile A1C: ______ % UMHS normal range 4-6.5% My goal is:__ % A1C is your average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. When your blood sugar is close to normal, you are likely to have more energy and think more clearly than when your blood sugar is high. This number also tells you about your risk for complications from diabetes. Keeping your A1C closer to normal reduces your risks for long-term damage to your eyes, kidneys and nerves. To help lower your blood sugar you can: eat smaller portions eat smaller portions more often throughout the day eat fewer sweets maintain a reasonable weight exercise more take medicine (diabetes pills or insulin) take a different dose of medicine take a combination of medicines (diabetes pills or insulin) add or adjust insulin dose, timing or shots per day ©University of Michigan 2004. Name: ©University of Michigan 2004. Name: Blood Pressure: mm/Hg Ideal: less than 130/80 My goal is: A blood pressure reading has two numbers. The first number is called systolic blood pressure. This is the amount of pressure against the blood vessel walls when your heart pumps. The second number is called diastolic blood pressure. This is the amount of pressure against the blood vessel walls when your heart relaxes, as it does between heart beats. In general, high blood pressure means that the systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, or both may be too high. For people with diabetes, high blood pressure is 130/80 or higher. High blood pressure increases your risk for strokes, heart attacks, kidney damage and eye disease. To lower your blood pressure you can: eat less salt stop smoking take blood pressure medicine change dose or type of blood pressure medicine exercise more limit alcohol to less than two drinks per day maintain reasonable weight Other ______________________________ ______________________________ ©University of Michigan 2004. Name: Cholesterol: Normal: 199 mg/dl or below My goal is: A waxy, fat-type substance in your blood. Your body makes some cholesterol from saturated fats and it is also present in certain foods. There are different kinds of cholesterol. High cholesterol adds to your risk for heart and blood vessel disease. To lower your cholesterol you can: eat less saturated (hard) and trans fats and cholesterol containing foods like butter, bacon, shortening maintain a reasonable weight eat skinless, lean meats exercise more take medicine to lower cholesterol eat more soluble fiber- like dark, green leafy vegetables and whole grain cereals use margarines and dressings with plant stanols/sterols added Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL): Your level Normal: 99 mg/dl or less LDL is the bad or lousy kind of cholesterol that deposits fat in your blood vessels. High LDL adds to your risk for heart and blood vessel disease. With multiple risk factors that include cardiovascular disease, consistently high blood pressure, obesity, smoking, high triglycerides, or low HDL in addition to diabetes the goal would be 70 mg/dl ©University of Michigan 2004. Name: To lower your LDL you can: eat less saturated (hard) and trans fats and cholesterol use monounsaturated oils instead of saturated (hard) fats ©University of Michigan 2004. Name: High Density Lipoproteins (HDL): Your level Normal: 45 mg/dl or higher for men 55 mg/dl or higher for women HDL is the good or healthy cholesterol that removes fat deposits from your blood vessels. A high HDL helps to protect you against heart and blood vessel disease. Some ways to improve your HDL: exercise more lower triglycerides use monounsaturated (liquid) oils in place of saturated (hard) fats eat more baked or broiled cold-water fish Triglycerides: Your level Normal: 149 mg/dl or less Another kind of fat carried in the blood stream that is linked to high blood sugars. High triglycerides may contribute to heart and blood vessel disease. Some ways to lower your triglycerides: lower your blood sugar eat fewer sweets drink less sweet liquids (including unsweetened fruit juice) drink less alcohol eat more broiled or baked cold-water fish ©University of Michigan 2004. Name: Smoking: Amount you smoke No smoking is ideal. Smoking increases your risk for heart, blood vessel and kidney disease. Some ways to cut back and quit smoking are: attend stop-smoking classes use nicotine patches, lozenges or gum take anti-smoking medicine smoke less often Body Mass Index (BMI): Height: inches Weight: shoes) Your BMI is _________ Target: 18.5-24.9 My goal is: pounds (lightly clothed, without Body Mass Index tells you if your weight is in a healthy range. It is based on your height and weight. Losing even small of amounts of weight can lower your blood sugar and blood pressure, and reduce your risk for joint problems and heart disease. To lose weight you can: eat smaller portions eat smaller portions more often throughout the day eat less fat exercise more drink less alcohol Other ______________________________ ______________________________ ©University of Michigan 2004. Name: ©University of Michigan 2004.