VLE Dead Week Review - Iowa State University
advertisement

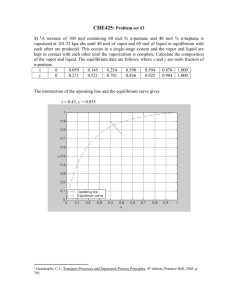
Dead Week Review: Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: German Parada ChE 210 Lamm/Scheider 12/04/2012 Conceptual Questions: 1) In which situations would you use Raoult’s Law, and in which ones would you use Henry’s Law? When would you use an equilibrium plot? 2) Raoult’s Law relates certain variables in an equilibrium situation. What are those variables? Short Problem: 1) In a pilot plant, a polymer is manufactured from an organic solvent solution. The finished product (8 mol polymer, 2 mol solvent) is dried before further processing. The solvent is removed by a stream of hot air, which enters the drying unit at P= 3atm and T = 75C and exits the unit at a P=1atm and T=55C, in equilibrium with the polymer product. The vapor pressure of the solvent at 55C is 630 mmHg. If 95% of the solvent is to be removed, what is the volumetric flow rate of air required? Engineering Problems: 1) Two streams containing mixtures of carbon disulfide (CDS) and benzene (B) are to be blended and heated, and then the resulting stream will be separated by distillation. One mixture is a liquid stream (15 mol/s) at 40C that is 80% B; the other mixture is a partially vaporized equilibrium stream at 55C (25 mol/s). This stream contains both CDS and B as a liquid and as a vapor. This stream has equal liquid and vapor molar flows. The blended streams are heated to 65C, the temperature of the exit equilibrium stream (which has both liquid and vapor molar flows, and CDS and B in both phases). A Txy diagram with the CDS fraction on the x-axis has been provided. Calculate the molar rates of liquid and vapor in the exit stream to be fed to the distillation column. Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu