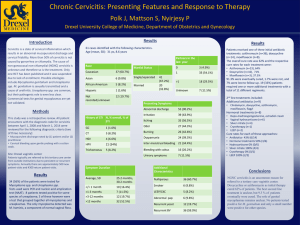
Pathogen Disease Treatment Notes Borrelia B.burgdorferi,B.afzelii
advertisement
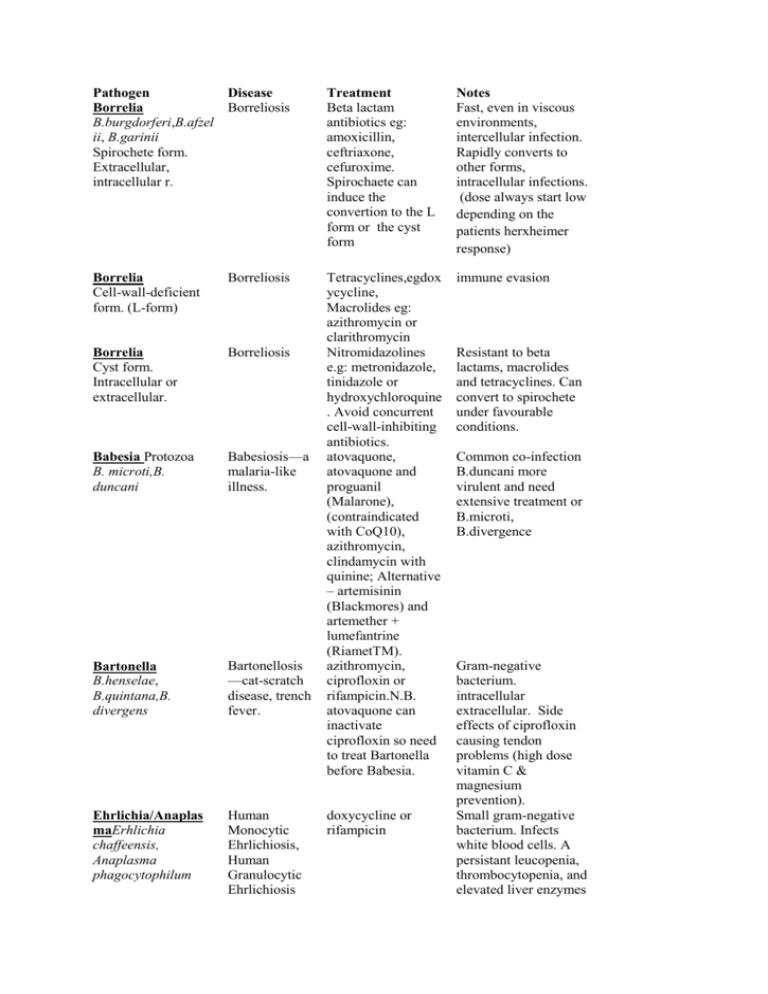
Pathogen Disease Borreliosis Borrelia B.burgdorferi,B.afzel ii, B.garinii Spirochete form. Extracellular, intracellular r. Borrelia Cell-wall-deficient form. (L-form) Borreliosis Borrelia Cyst form. Intracellular or extracellular. Borreliosis Babesia Protozoa B. microti,B. duncani Babesiosis—a malaria-like illness. Bartonella B.henselae, B.quintana,B. divergens Bartonellosis —cat-scratch disease, trench fever. Ehrlichia/Anaplas maErhlichia chaffeensis, Anaplasma phagocytophilum Human Monocytic Ehrlichiosis, Human Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis Treatment Beta lactam antibiotics eg: amoxicillin, ceftriaxone, cefuroxime. Spirochaete can induce the convertion to the L form or the cyst form Notes Fast, even in viscous environments, intercellular infection. Rapidly converts to other forms, intracellular infections. (dose always start low depending on the patients herxheimer response) Tetracyclines,egdox ycycline, Macrolides eg: azithromycin or clarithromycin Nitromidazolines e.g: metronidazole, tinidazole or hydroxychloroquine . Avoid concurrent cell-wall-inhibiting antibiotics. atovaquone, atovaquone and proguanil (Malarone), (contraindicated with CoQ10), azithromycin, clindamycin with quinine; Alternative – artemisinin (Blackmores) and artemether + lumefantrine (RiametTM). azithromycin, ciprofloxin or rifampicin.N.B. atovaquone can inactivate ciprofloxin so need to treat Bartonella before Babesia. immune evasion doxycycline or rifampicin Resistant to beta lactams, macrolides and tetracyclines. Can convert to spirochete under favourable conditions. Common co-infection B.duncani more virulent and need extensive treatment or B.microti, B.divergence Gram-negative bacterium. intracellular extracellular. Side effects of ciprofloxin causing tendon problems (high dose vitamin C & magnesium prevention). Small gram-negative bacterium. Infects white blood cells. A persistant leucopenia, thrombocytopenia, and elevated liver enzymes RickettsiaeR.honei, R.australis,R.typhi, Orientia tsutsugamushi Mycoplasma M.fermentans,M.pne umoniae Flinders Island spotted fever, Queensland tick typhus, Murine Typhus, Scrub typhus Mycoplasmosi s DNA Viruses HHV-6 ( Human herpes virus), EBV (Epstein Barr virus), CMV (cytomegalovirus), RNA VirusesTick Borne encephalitis Virus (TBE) common with tick bites as co-infection and can present with serious symptomology of paralysis if not detected early. In Australia Murray Valley encephalitis virus, other flavi viruses should be explored in chronic L Lyme like illness with very serious paralytic nature in Australia may occur in acute infection. Maculopapular skin rash, severe headache(especially behind eyes). doxycycline doxycycline, azithromycin or clarithromycin and hydroxychloroquine . famciclovir, valaciclovir, ganciclovir or anti-retrovirals eg. zidovudine, ritonavir Over 100 species. Smallest bacteria known. Intracellular. Difficult to eliminate and slow growing. Utilise host cholesterol.. depression,SOB, problems and gastrointestinal problems. Low bacterial load and minimal symptomology, usually no treatment. If serious symptomology and big viral load antiviral are utilised. Vaccine available for TBE vaccination should be encouraged in people travelling to Europe and Asia, including Japanese encephalitis virus (Banzhoff et al 2008). Two vaccines area available, the vaccine for the K23/Neudorfl show subtye provide cross protection against other subtypes Far Eastern and Siberian subtypes). .