Biology 12 * Enzyme Test * Written Responses
advertisement

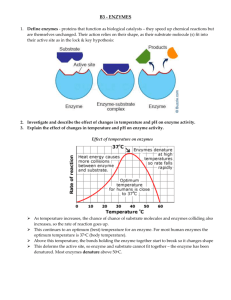
Biology 12: ENZYMES Written Response – Key 1) An experiment investigating enzyme activity was carried out. A test tube was prepared containing substrate solution W and enzymes solution 1 and 2. The reactions that occur in the test tube are summarized below: 1 2 W ----------- > X ---------------- > Y The letters represent substrates and the produces and the numbers represent the enzymes. a) State two ways to increase the rate of production of product Y. (2 marks) Increase the temperature to the optimal temperature Increase the concentration of enzymes 1 and 2 Increase the substrate W concentration b) A substance is added to the test tube containing substrate W. As a result, product X still formed but no product Y formed. Suggest what this substance may be and explain how it achieves these results. (2 marks) The substance is most likely an inhibitor that impacts Enzyme 2 As it only impacts enzyme 2 it must be a specific inhibitor that binds to the active site of Enzyme 2 Binding to Enzyme 2’s active site, prevents substrate X from binding to enzyme 2’s active site, thus preventing the formation of product 2. a) Graphs should have a reasonable scale, both axis labeled and show an increasing reaction rate with a sudden drop off at 43°C b) Use the graph above to describe the effect of temperature on an enzyme catalyzed reaction. (4 marks) As temperature increases the number of collisions between substrates and enzymes increases, thus increasing the rate of product formation At 43 °C the rate of product formation decreases This decrease is due to the denaturing of enzymes by the high temperature 3) Explain the change in the reaction rate for the graph below. Your answer should include labelled diagrams of enzymes, substrates and active sites. (4 marks) Reaction Rate versus Substrate Concentration (for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction) Reaction Rate Substrate Concentration REID Document1 - Page 1 of 2 The reaction rate first increases as more substrate is added because the available enzymes are not all working at their maximum capacity. It levels off because after a certain concentration of subtrate because after that level, all the enzymes are working at their maximum capacity and can't bind substrate any more quickly. Enzyme concentration is what ultimately limits the rate of the reaction.] Diagram should show enzyme saturation of active site. See below. NOT SATURATED SATURATED: can’t work faster 4) Two digestive enzymes produced by two different glands act on the same substrate. Both enzymes function optimally at a pH of 7.1 to 8.4 and a temperature of 37C. a) Describe the similarity of the enzymes’ structures and explain why this affects their ability to act on the same substrate. (2 marks) • The tertiary structure is the same. • The active sites will both be the same shape. • The substrate can lock into either active site due to similar shapes. • The substrate and enzyme are complementary. b) What would happen to the rate of the reaction above if the pH was changed to 3.0? Explain your answer. (2 marks) • The reaction would stop / slow down. (1 mark) AND • The enzyme would be denatured. • The substrate would no longer be able to fit into the active site. • The bonds between the R-groups would be disrupted. • The shape of the enzyme is changed. ROBERTS via Raycroft Document1 - Page 2 of 2