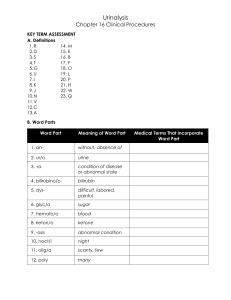
Urinalysis Chapter 16 Clinical Procedures Key Term Assessment A
advertisement
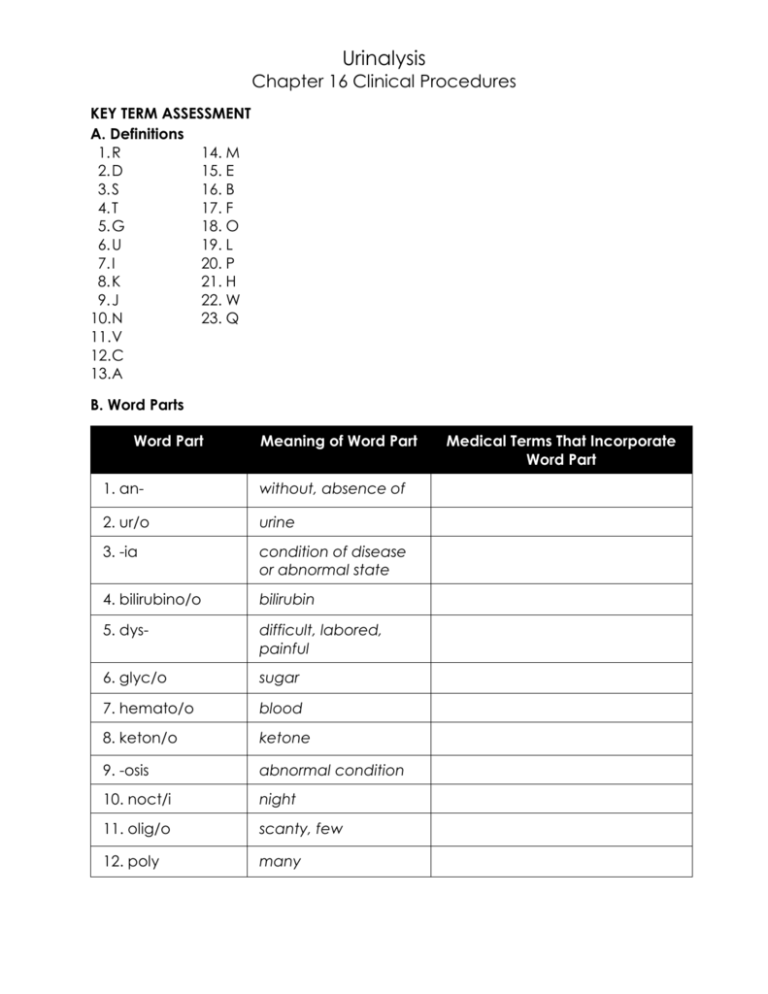
Urinalysis Chapter 16 Clinical Procedures KEY TERM ASSESSMENT A. Definitions 1. R 14. M 2. D 15. E 3. S 16. B 4. T 17. F 5. G 18. O 6. U 19. L 7. I 20. P 8. K 21. H 9. J 22. W 10. N 23. Q 11. V 12. C 13. A B. Word Parts Word Part Meaning of Word Part 1. an- without, absence of 2. ur/o urine 3. -ia condition of disease or abnormal state 4. bilirubino/o bilirubin 5. dys- difficult, labored, painful 6. glyc/o sugar 7. hemato/o blood 8. keton/o ketone 9. -osis abnormal condition 10. noct/i night 11. olig/o scanty, few 12. poly many Medical Terms That Incorporate Word Part Word Part Meaning of Word Part 13. py/o pus 14. supra above 15. pub/o pubis 16. -ic pertaining to Medical Terms That Incorporate Word Part EVALUATION OF LEARNING 1. To regulate the fluid and electrolyte balance of the body and to remove waste products. 2. What is the function of the urinary bladder?To store and expel urine. 3. In males, the urethra functions in transporting urine and reproductive secretions. In females, the urethra functions in urination only. 4. The external opening of the urethra. 5. Water. 6. The excessive intake of fluids; the intake of fluids that contain caffeine and diuretics; diabetes mellitus; diabetes insipidus; and renal disease. 7. Decreased fluid intake, dehydration, profuse perspiration, vomiting, diarrhea, or kidney disease. 8. A clean-catch midstream specimen. 9. It contains the greatest concentration of dissolved substances. 10.Kidney stone formation. 11.The preservative could splash onto the patient’s skin, resulting in a chemical burn. 12.An acidic urine becomes more alkaline, increasing the pH, which also may cause a false-positive result on the protein test; bacteria multiply, resulting in a cloudy specimen and an increase in the nitrite concentration; if glucose is present in the specimen, it decreases in amount; any red or white blood cells present may break down; casts decompose. 13. Concentrated urine contains more dissolved substances, making it darker in color. 14.The presence of bacteria, pus, blood, fat, yeast, sperm, mucous threads, or fecal material. 15. Ammonia. 16. It provides information on the ability of the kidneys to dilute or concentrate the urine. 17.1.003 to 1.030. 18.Qualitative test results provide an approximate indication of whether a substance is present in abnormal quantities. Quantitative test results indicate the exact amount of a chemical substance that is present. 19. A bacterial infection of the urinary tract. 20. Urea (acidic) is converted to ammonia (alkaline) by bacterial action. 21. Diabetes mellitus, alimentary glycosuria. 22. Glomerular filtration problems, renal diseases, and bacterial infections of the urinary tract. 23. Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, starvation, a diet composed almost entirely of fat. 24. Gallstones, hepatitis, and cirrhosis. 25. Injury, cystitis, tumors of the bladder, urethritis, kidney stones, and certain kidney disorders. 26. A false-positive result may occur because of bacterial contamination from the atmosphere. 27. In a cool, dry area away from direct sunlight with the cap tightly closed. 28. To help clarify the results of the physical and chemical examination of urine. 29. It is more concentrated and contains more dissolved substances; small amounts of abnormal substances are more likely to be detected. 30. It causes them to become shrunken or crenated. 31. A cylindrical structure formed in the lumen of the tubules that make up a nephron. 32. Candidiasis. 33. To assist in diagnosing a UTI; to assess the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy for a patient with a UTI. 34. For the early detection of pregnancy and before certain medications are ordered and before procedures are performed that may cause injury to a fetus. 35. Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). 36. Use clean urine containers. Use a first-voided morning specimen. Determine the specific gravity of the urine specimen before performing the test. A specific gravity reading less than 1.010 may lead to false-negative test results. The urine specimen should be at room temperature. The urine pregnancy testing kit should be stored according to information in the product insert. Test reagents past their expiration date should not be used. If more than one patient is being tested at a time, label each testing device to prevent mix-up of specimens. If the internal control does not perform as expected, the test result is invalid and must be retested. A positive and negative external control should be performed with each new lot of pregnancy testing kits and then monthly thereafter. CRITICAL THINKING ACTIVITIES A. First-Voided Specimen 1. It contains many dissolved substances, and if something is abnormal in your urine it will be easier to detect it. 2. So there are no changes to the urine that could cause inaccurate test results. B. Clean-Catch Specimen 1. To remove microorganisms that are normally present on the meatus. 2. So that contaminants are not brought from the anal area into the area that is being cleansed. These contaminants could get into the urine specimen and cause inaccurate test results. 3. To flush out microorganisms. 4. Touching the inside would contaminate it, and the test results may then be inaccurate. APPLY YOUR KNOWLEDGE 1. B. 2. C. 3. A 4. D. 5. D. 6. B. 7. B 8. C. 9. B. 10. A. VIDEO EVALUATION FOR CHAPTER 16: URINALYSIS Video: Procedure 16-1: Clean-Catch Midstream Specimen Collection Instructions ____T___1. ____T___2. ____F___3. ____T___4. ____T___5. ____F___6. ____T___7. ____F___8. Video: Procedure 16-3: Chemical Testing of Urine with the Multistix 10 SG Reagent Strip ____T___1. ____F___2. ____T___3. ____F___4. ____T___5. ____T___6. ____F___7. ____T___8. . ____F___9. ____T___10. ____T___11. Video: Procedure 16-6: Performing a Urine Pregnancy Test ____T___1. ____F___2. ____T___3. ____T___4. . ____T___5. ____T___6.