Algebra 2
advertisement
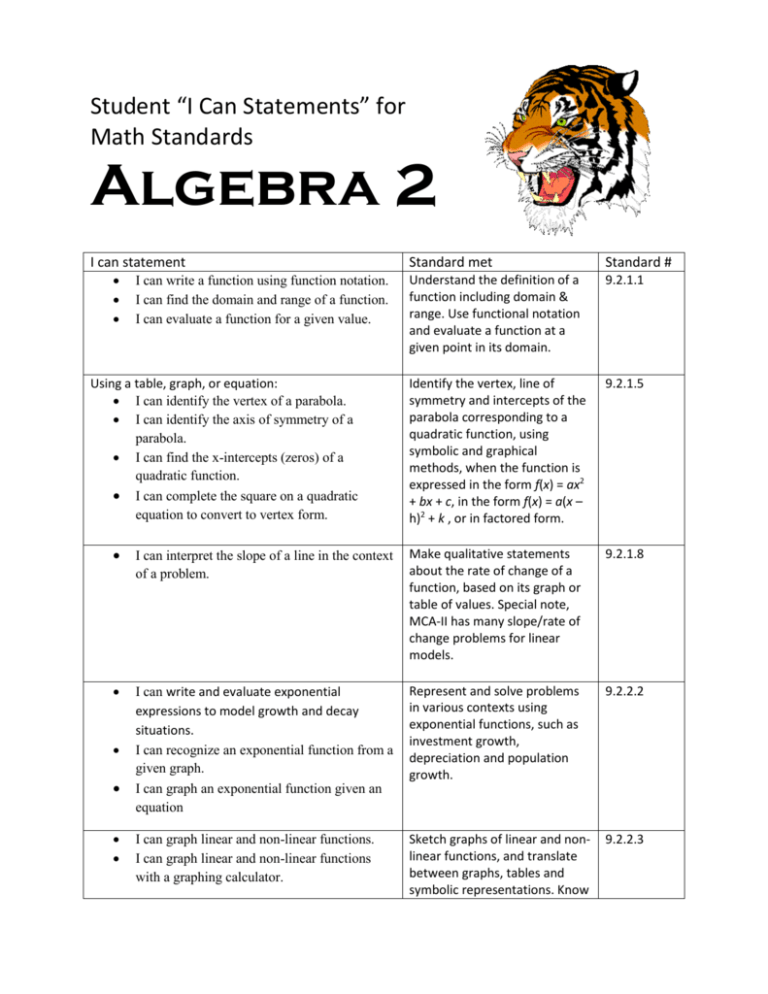
Student “I Can Statements” for Math Standards Algebra 2 I can statement I can write a function using function notation. I can find the domain and range of a function. I can evaluate a function for a given value. Using a table, graph, or equation: I can identify the vertex of a parabola. I can identify the axis of symmetry of a parabola. I can find the x-intercepts (zeros) of a quadratic function. I can complete the square on a quadratic equation to convert to vertex form. Standard met Standard # Understand the definition of a function including domain & range. Use functional notation and evaluate a function at a given point in its domain. 9.2.1.1 Identify the vertex, line of symmetry and intercepts of the parabola corresponding to a quadratic function, using symbolic and graphical methods, when the function is expressed in the form f(x) = ax2 + bx + c, in the form f(x) = a(x – h)2 + k , or in factored form. 9.2.1.5 I can interpret the slope of a line in the context of a problem. Make qualitative statements about the rate of change of a function, based on its graph or table of values. Special note, MCA-II has many slope/rate of change problems for linear models. 9.2.1.8 I can write and evaluate exponential expressions to model growth and decay situations. I can recognize an exponential function from a given graph. I can graph an exponential function given an equation Represent and solve problems in various contexts using exponential functions, such as investment growth, depreciation and population growth. 9.2.2.2 I can graph linear and non-linear functions. I can graph linear and non-linear functions with a graphing calculator. Sketch graphs of linear and nonlinear functions, and translate between graphs, tables and symbolic representations. Know 9.2.2.3 I can translate between graphs, tables, and symbolic representations of linear and nonlinear functions. how to use graphing technology to graph these functions. I can solve quadratic equations by factoring, completing the square, graphing, and the quadratic formula. I can solve quadratic inequalities by using tables, graphs, and analytic techniques. I can find non-real complex zeros when they exist in a quadratic function. I can recognize that a particular solution may not be applicable in the original context of the problem. Represent relationships in various contexts using quadratic equations and inequalities. Solve quadratic equations and inequalities by appropriate methods including factoring, completing the square, graphing and the quadratic formula. Find non-real complex roots when they exist. Recognize that a particular solution may not be applicable in the original context. Know how to use calculators, graphing utilities or other technology to solve quadratic equations and inequalities. 9.2.4.1 I can graph a system of linear inequalities. I can identify the set of solutions in a system of linear inequalities. Represent relationships in various contexts using systems of linear inequalities; solve them graphically. Indicate which parts of the boundary are included in and excluded from the solution set using solid and dotted lines. 9.2.4.4 I can calculate the mean for a data set. I can find the five-number summary in a numeric data set. I can use the five-number summary to create a box-and-whisker plot. I can describe the effect of changes to the data set (mean, median, range) if an outlier is included or excluded from the data set Describe a data set using data displays, such as box-andwhisker plots; describe and compare data sets using summary statistics, including measures of center, location and spread. Measures of center and location include mean, median, quartile and percentile. Measures of spread include standard deviation, range and inter-quartile range. Know how to use calculators, spreadsheets or other technology to display data and calculate summary 9.4.1.1 statistics.