STUDY GUIDE FOR ALGEBRA II MIDTERM Identify a property
advertisement

STUDY GUIDE FOR ALGEBRA II MIDTERM
A) Identify a property demonstrated by an equation. (1-2 Example 2, pg. 15)
Example: (3+6)-(-6)=3+⌈6 + (−6)⌉
Associative Property of Addition
B) Adding and Subtracting Square Roots (1-3 Example 4, pg. 23)
Example: 5√3 − √12 = 3√𝟑
C) Simplifying Expressions (1-4 Example 3, pg. 28)
Example: b(5a2 – 2a) – 11a2b + 2ab = -6a2b
D) Using Properties of Exponents to Simplify Expressions (1-5 Example 3, Pg. 36)
𝑎𝑏 4
𝒂𝟐
Example: ( 𝑏7 )2 = 𝒃𝟔
E) Determining Whether a Relation is a Function (1-6 Example 2, Pg. 45)
Example: {(7,1), (7,2), (7,3), (7,4), (7,6)}
Not a Function
F) Evaluating Functions (1-7 Example 1, pg. 51)
Example: Evaluate f(0). f(x)=7-2x; f(0)=7-2(0)=7-0=7
G) Translating Points (1-8 Example 1, pg. 59)
Example: Translate the point (2,-1) 2 units right and 3 units up
(4,2)
H) Identifying Parent Functions to Model Data Sets (1-9 Example 2, pg. 68)
I) Solving Inequalities (2-1, Example 5, Pg. 93)
Example: Solve 9x+4 < 12x – 11
x>5
J) Solving Proportions (2-2, Example 1, pg. 97)
Example:
22
9
𝑥
= 13.5
x=33
K) Find the intercepts of a line (2-3 Example 3, pg. 106)
Example: Find the intercepts of 2x-3y = 12
x-intercept= 6, y-intercept=-4
L) Writing Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines (2-4, Example 5, pg. 119)
Example: Write the equation of the line parallel to y=1.5x + 6 and through (4,5)
M) Graphing Linear Inequalities (2-5 Example 1, pg. 124)
y=1.5x-1
1
Example: Graph the inequality y<2 𝑥 + 1 See pg. 124 for graph
N) Transforming Linear Functions (2-6 Examples 1,2,and3, pg. 135-136)
Example: Let g(x) be a horizontal compression of f(x)=2x-1 by a factor of 1/3. Write the rule for g(x).
g(x)=6x-1
O) Find the equation that best fits a data set (2-7 Example 1, pg. 142)
P) Solving Absolute Value Inequalities and Equations (2-8 Examples 1, 2, 3, 4, pg. 151-153)
Example: Solve the inequality
|3𝑥−9|
2
≤ 12
x≤11 and x≥ −5 so the solution set is {𝒙|−𝟓 ≤ 𝒙 ≤ 𝟏𝟏}
Q) Translating Absolute Value Functions (2-9 Examples 1 and 3, pg. 158,159)
Example: Write the rule for the transformation of f(x)= -|𝑥 − 4| + 3 across the y-axis.
g(x)= -|−𝒙 − 𝟒| + 𝟑
R) Solving Linear Systems (3-2 Examples 1, 2, and 3, pg. 190-192)
Example: Solve the system y=x+2; x+y=8
(3,5)
S) Solving a system of linear inequalities (3-3 Examples 1 and 3, pg. 199-201)
Example: Graph the system of inequalities and classify the figure created by the solution region.
y≤5, y≥2, y≤3x+1, y≥3x-4
The solution region is a parallelogram.
T) Solving a Linear System in 3 Variables (3-6 Example 1, pg. 221)
Solve the system: x+2y-3x=-2, 2x-2y + z = 7, x+y+2z = -4
(1,-3,-1)
U) Translating Quadratic Functions (5-1, Example 2, pg. 316)
Using the graph of f(x)=x2 as a guide, describe the transformation. g(x)=(x+3)2+1
g is f translated 3 units left and 1 unit up
V) Graphing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form (Find the axis of symmetry, vertex, y-intercept) (5-2
Example 2, pg. 324-325)
W) Find the zeros of a quadratic equation (5-3 Examples 1 and 2, pg. 333-334)
Example: Find the zeros of f(x)=x2 +2x – 3
-3 and 1
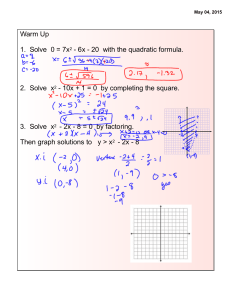
X) Solving a Quadratic Equation by Completing the Square (5-4 Example 3, pg. 343)
Example: Solve x2=27-6x
x=3 or x=-9
Y) Write a quadratic function in Vertex Form (5-4 Example 4, pg. 344)
Example: f(x)=x2 + 10x – 13
f(x)=(x+5)2-38
Z) Solving a Quadratic Equation with Imaginary Solutions (5-5 Example 2, pg. 351)
Examples: Solve 3x2 + 75 = 0
x=±5i
AA) Solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula (5-6 Examples 1 and 2, pg 357)
Example: Find the zeros of f(x)=x2+10x+2
x=-5±√𝟐𝟑
BB) Solve quadratic inequalities (5-7 Example 3, pg. 368)
Example: Solve x2-4x+1>6
x<-1 or x>5, or (-∞, -1) U (5,∞)
CC) Multiplying Complex Numbers (5-9 Example 4, pg. 385)
Example:Multiply (5-6i)(4-3i) = 2-39i
DD)
Adding and Subtracting Polynomials (6-1, Example 3, pg. 407)
Example: (3x2 + 7 + x) + (14x3 + 2 + x2 – x) = 14x3 + 4x2 + 9
EE) Expanding the Power of a Binomial (6-2 Example 4, pg. 416)
Example: (x+y)3 = x3 + 3x2 + 3xy2 + y3
FF) Divide Polynomials (6-3 Examples 1 and 2, pg. 422 and 423)
𝟓𝟎
Example: Divide (4x2 +3x3+10) ÷ (x+2) = 3x2+10x+20+𝐱+𝟐
GG)
Factoring Polynomials (6-4, Examples 2 and 3, pg. 431)
Example: Factor 5x4 + 40x = 5x(x+2)(x2-2x+4)
HH)
Determining Maxima and Minima with a Graphing Calculator (6-7 Example 4, pg. 456)
Example: Graph g(x)=2x3 – 12 x + 6 and estimate the local maxima and minima. Local max: 17.3137
Local min: -5.3137
II) Tranforming a Polynomial Function (6-8 Example 1,2,3,4, pg. 460-462)
Example: Let f(x)=x3-7x2+6x-5. Write a function g that reflects f(x) across the x-axis.
g(x)=-x3+7x2-6x+5