FormalModels
advertisement

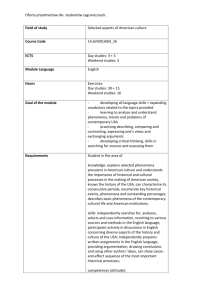
Oferta przedmiotów dla studentów zagranicznych. Field of study Formal models of natural languages Course Code ECTS Module Language English Hours 45 Goal of the module To introduce students to some of the more important theoretical concepts and empirical findings of modern theory of languages diversity. 2. To equip students with some tools and techniques for structure of languages analysis. 3. To oblige students to consider and evaluate different opinions on issues discussed. Requirements Attendance and active participation in classes. Oral presentations. Course content 1. Diversity of languages (6hrs). 2. Classification of languages (8hrs). 3. The Indo-European family of languages (6hrs). 4. Different theories of IndoEuropeans’ origin (6hrs). 5. Analytic vs. inflectional languages (6hrs). 6. Comparative vs. contrastive linguistics and their methods (6hrs). 7. The origin of language (7hrs). Reading and written assignments. Tests. End-ofsemester credit with a grade. Form and terms of examination Education methods Literature Atkinson, M., Kilby, D., Roca, I. (1988), Foundations of General Linguistics. London: Unwin Hyman. Fromkin, V. & Rodman, R. (1998), An Introduction to Language. Harcourt Brace College Publishers. 6th edition. Lexicography and the OED. Pioneers in the Untroden Forest. Ed. By Linda Mugglestone (2000), Oxford: OUP. Lyons, J. (1987), An Introduction to Language and Linguistics. London & New York: CUP. Quirk, R., Greenbaum, S., Leech, G. and Svartvik, J. (1972), A Grammar of Contemporary English. Longman. 2nd edition. Trask, R. (1997), A Student’s Dictionary of Language and Linguistics. London & New York: Arnold. Oferta przedmiotów dla studentów zagranicznych. Wardhaugh, R. (1994), Investigating Language. Central Problems in Linguistics. Oxford UK & Cambridge USA: Blackwell. Module coordinator Prof. dr hab. O.Molchanova Field of study Seminarium przedmiotowe (MA II) Oferta przedmiotów dla studentów zagranicznych. Course Code ECTS Module Language English Hours 60 Goal of the module 1.To introduce students to some of the more important theoretical concepts and empirical findings of modern cognitive linguistics theory. 2. To equip students with some tools and techniques for language analysis and give them a lot of practice in using them (exercises). 3. To oblige students to consider and evaluate different opinions on issues discussed. Requirements Attendance and active participation in classes. Oral presentations. Course content 1. Introductory survey (3hrs). 2. Revision of tenses (4hrs). 3. The traditional class of prepositions (4hrs). 4. Basic concepts (4hrs). 5. Space (4hrs). 6. Spatial relations and meaning; spatial senses; perceptual analysis and the embodiment of meaning (4hrs). 7. The nature of lexical representation; experimental correlation; perceptual resemblance (4hrs). 8. The proto-scene; atemporality; on-line meaning construction; pragmatic strengthening (4hrs). 9. Extensions from spatial meanings (4hrs). 10. Further category contrasts (4hrs). 11. Grammaticised uses of prepositions (4hrs). 12. Preposition stranding (4hrs). 13. The structure of PPs (4hrs). 14. PP complements in clause structure (3hrs). 15. Prepositional idioms and fossilisation (6hrs). Reading and written assignments. Tests. End-ofsemester credit with a grade. Form and terms of examination Education methods Literature Cruse, A. (2007), A Glossary of Semantics and Pragmatics. Edinburg University Press. Huddleston, R. & Pullum, G. K. (2002), The Cambridge Grammar of the English language. Cambridge University Press. Huddleston, R. & Pullum, G. K. (2005), A Student’s Introduction to English Grammar. Cambridge University Press. Evans, V. (2007), A Glossary of Cognitive Linguistics. Edinburg University Press. Oferta przedmiotów dla studentów zagranicznych. Evans, V. & Green, M. (2006), Cognitive Linguistics. An Introduction. Edinburg University Press. Hurford, J., Heasley, B. & Smith M. B. (2007), Semantics: a coursebook. Cambridge: CUP. Langacker, R. W. (2000), Grammar and Conceptualization. Berlin. New York: Mouton de Gruyter. Lee, D. (2005), Cognitive Linguistics. Introduction. Oxford: OUP. The Linguistics Encyclopedia. (1995) Edited by Kirsten Malmkjaer. London & New York: Routledge. Tyler, A., Evans V. (2003), The Semantics of English Prepositions. Oxford: OUP. Module coordinator Prof. dr hab. O.Molchanova Oferta przedmiotów dla studentów zagranicznych. Field of study Seminarium przedmiotowe (MA I) Course Code ECTS Module Language English Hours 30 Goal of the module 1.To introduce students to some of the more important theoretical concepts and empirical findings of modern cognitive linguistics theory. 2. To equip students with some tools and techniques for language analysis and give them a lot of practice in using them (exercises). 3. To oblige students to consider and evaluate different opinions on issues discussed. Requirements Attendance and active participation in classes. Oral presentations. Course content 1. Introductory survey (3hrs). 2. Number and countability (5hrs). 3. Categories of definiteness and indefiniteness (4hrs). 4. Determiners and determinatives (5hrs). 5. Genitive case (3hrs). 6. Denotation vs. reference (5hrs). 7. Pronouns (5hrs). Reading and written assignments. Tests. End-ofsemester credit with a grade. Form and terms of examination Education methods Literature Cruse, A. (2007), A Glossary of Semantics and Pragmatics. Edinburg University Press. Huddleston, R. & Pullum, G. K. (2002), The Cambridge Grammar of the English language. Cambridge University Press. Huddleston, R. & Pullum, G. K. (2005), A Student’s Introduction to English Grammar. Cambridge University Press. Evans, V. (2007), A Glossary of Cognitive Linguistics. Edinburg University Press. Evans, V. & Green, M. (2006), Cognitive Linguistics. An Introduction. Edinburg University Press. Hurford, J., Heasley, B. & Smith M. B. (2007), Semantics: a coursebook. Cambridge: CUP. Langacker, R. W. (2000), Grammar and Conceptualization. Berlin. New York: Mouton de Oferta przedmiotów dla studentów zagranicznych. Gruyter. Lee, D. (2005), Cognitive Linguistics. Introduction. Oxford: OUP. The Linguistics Encyclopedia. (1995) Edited by Kirsten Malmkjaer. London & New York: Routledge. Module coordinator Prof. dr hab. O.Molchanova