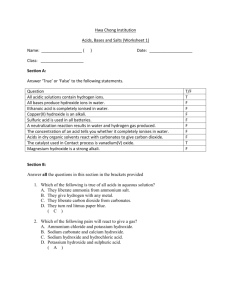
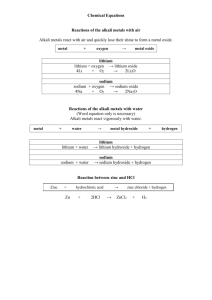
Revision Questions – Stoic
advertisement

Revision Questions – Stoic Q1. When alchemists gently heated mercury(II) oxide, a “mirror” of mercury condensed on the walls of the vessel. The equation for this is: 2HgO(s) 2Hg(l) + O2(g) What mass of mercury(II) oxide must have reacted if a mirror containing 10.0g of mercury was produced? Q2. In the sealed environment of a space shuttle, canisters of the strong base lithium hydroxide are used to absorb carbon dioxide so that toxic levels do not build up. The reaction is shown in the following equation: 2LiOH(s) + CO2(g) Li2CO3(s) + H2O(l) What mass of carbon dioxide can be absorbed by 200g of lithium hydroxide? Q3. A piece of copper wire of mass 2.25g completely dissolves on a solution of silver nitrate. The balanced equation for the metal displacement reaction is: Cu(s) + 2AgNO3 (aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s) (a) What mass of copper(II) nitrate will be produced? (b) What mass of crystals of pure silver crystals will be produced in this process? Q4. When a cake mixture containing bicarb soda, NaHCO3, is baked, the sodium hydrogen carbonate decomposes according to the following equation: 2NaHCO3(s) Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) The CO2 gas produced rises through the mixture, causing the cake to rise. However, if too much bicarb soda is used, the cake will be spoilt because the sodium carbonate has a bitter, foul taste. If 0.60g of bicarb soda is used: (a) What mass of carbon dioxide gas will be produced? (b) What mass of sodium carbonate will be produced? (c) From your answers to parts a and b, deduce the mass of water vapour that will produced, state your reasoning. Q5. When concentrated nitric acid is poured onto copper, a vigorous reaction occurs and a pungent brown gas is evolved. This is nitrogen dioxide gas, NO2. When the reaction has ceased, the remaining solution is blue. The balanced equation is: Cu(s) + 4HNO3(l) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO2(g) + 2H2O(l) (a) What mass of copper(II) nitrate will be produced when excess concentrated nitric acid is poured on to 3.85g of copper? (b) What mass of nitrogen dioxide gas will be produced in the process? Q6. The combination of limestone country and a steady rainfall can lead to the formation of stunning underground caves. This is because even pure rain has a pH of 6, since carbon dioxide dissolves in it and produces carbonic acid, H2CO3, a weak acid. This acid acts on the limestone, CaCO3, and dissolves it in the form of soluble calcium hydrogen carbonate. The simplified equation for the solution process that creates a cave is: CaCO3(s) + H2CO3(aq) Ca(HCO3)2(aq) As the solution drips down from the ceiling of the cave, it decomposes: Ca(HCO3)2(aq) CaCO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(g) Thus solid limestone forms again, producing stalactites suspended from the ceiling and stalagmites that rise from the floor where the drips have landed. (a) What mass of solid limestone is formed when 1.00kg of calcium hydrogen carbonate completely decomposes? (b) What mass of carbon dioxide is returned to the air during this decomposition process? Q7. What must be the concentration of a solution of ammonium hydroxide, if a 20.00mL sample of the solution requires precisely 19.04 mL of hydrochloric acid of concentration 0.1058 mol/L to completely reaction with it? The full equation for the reaction is: HCl(aq) + NH4OH(aq) NH4Cl(aq) + H2O(l) Q8. What must be the concentration of a hydrochloric acid solution is a 20.00mL sample of the solution requires precisely 21.46mL of sodium carbonate solution of concentration 0.05129M to completely react with it? 2HCl(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) 2NaCl(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) Q9. Lactic acid HC3H5O3, is a weak, monoprotic acid that accumulates as a waste product in muscle tissue during exertion, leading to pain and a feeling of fatigue. What must be the concentration of a sample of lactic acid 20.00mL of sodium hydroxide of concentration 0.1426M requires 24.58mL of the acid for a complete reaction? HC3H5O3 (aq) + NaOH(aq) NaC3H5O3(aq) + H2O(l) Q10. (a) Write the balanced full equation for the neutralisation reaction of potassium hydroxide solution by nitric acid (b) What mass of potassium nitrate would be produced by the addition of 19.50mL 0.1249M nitric acid to 20.00mL of 0.09878M potassium hydroxide solution. Q11. (a) Write the balanced full equation for the neutralisation of sodium hydroxide by sulphuric acid (b) What mass of water would be produced when 25.00mL of sulphuric acid of concentration 0.1510M is added to exactly 20.00mL of sodium hydroxide of concentration 0.2485M? Q12. A pair of students were determining the concentration of some hydrochloric aid by titrating it against a sodium carbonate solution, using methyl orange indicator to detect the end point. The full equation is: 2HCl(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) 2NaCl(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) First they weighed out 1.315g of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3. They added it to a 250.00mL volumetric flask and made up the solution to the etched mark with distilled water. They then titrated 25.00mL aliquots of this solution against hydrochloric acid. The table below shows their results. Initial Burette Reading(mL) 0.10 0.25 0.00 0.12 Final Burette Reading(mL) 19.24 19.23 18.94 19.09 Titre (mL) 19.14 18.98 18.94 18.97 (a) Calculate the concentration of the sodium carbonate solution in the 250.00mL flask (b) State the number of mole of the sodium carbonate in the 250.00mL flask (c) Calculate the number of mole in the 25.00mL aliquots (d) Which titres would be classified as concordant? Justify your answer (e) Calculate the mean titre, using only the concordant titres. (f) Calculate the concentration of the acid Q13. Sulfur dioxide gas escaping from a natural gas well may react with water to produce an acid which damages the environment when it falls to the ground as acid rain. If 32g of sulfur dioxide reacts with 18g of water: (a) How much H2SO3 is produced? (b) Which reactant is in excess and by what mass Q14. Hydrazine is used in rocket fuel. It reacts with oxygen as follows: N2H4(l) + O2(g) N2(g) + 2H2O(l) In a particular rocket engine 2.29g of hydrazine and 3.14g of oxygen are available for reaction (a) Find the limiting reactant (b) Determine which reactant is in excess and by how much (in g) (c) Calculate the mass of water produced Q15. Magnesium Oxide is produced by the following reaction: 2Mg(s) + O2(g) 2MgO(s) 2 mol of magnesium and 2 mol of oxygen are reacted (a) Determine the amount (in mol) of unused reactant remaining after the reaction (b) Calculate the maximum mass of MgO produced Q16. Calcium Hydroxide dissociates in water according to the following equation: Ca(OH)2 (aq) Ca2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) If 4g of calcium hydroxide is placed in 120.00mL of water find: (a) the concentration of hydroxide ions (b) the pH of the solution