A Level Physics - The Beaconhouse Times
advertisement

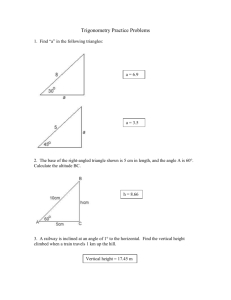
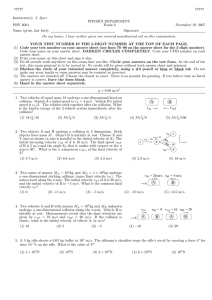
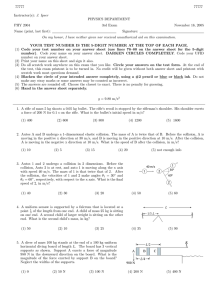
Beaconhouse School System Jhelum Better A level Physics Questions S.No Q.No.1 Description Marks Remarks The diagram below shows the initial state of two identical balls A and B before collision and the final state immediately after the collision. The mass of each ball is 1.2 kg. Before the collision, the velocity of A is 3.0 m s−1 and B is stationary. A makes an oblique collision with B. After the collision, A moves off at an angle of 30° to its original direction and has a velocity of 2.6 m s−1. B is deflected at an angle with a velocity of 1.5 m s−1. a Explain why the final momentum of the system in a direction at right angles to the initial velocity of A is zero. Hence determine the angle . b Show that the total momentum of the system is conserved. 3 3 Q.No.2 A ladder of mass 32 kg rests at an angle against a smooth wall as shown in the diagram. The centre of gravity of the ladder is at its mid-point. [3] [3] a Determine the force R exerted by the wall on the ladder by taking moments about the base of the ladder. b Explain why the force at the base of the ladder was not included when doing the calculation in a. Q.No.3 3 1 The diagram shows two springs X and Y connected in series and supporting a weight of 8.0 N. The force constants of the springs are shown on the diagram. a Calculate the extension of each spring. b Determine the force (spring) constant for the combination. c According to a student, the force constant for the springs in series is the sum of the force constants of the individual springs. Is the student correct? 2 2 1 Q.No. 4 The intensity of a wave may be defined as the power transmitted per unit cross-sectional area at right angles to the direction of travel. a 3 For a point source of light, explain why the intensity I at a distance r away from the source obeys an inverse square law with distance, that is: I 1 . r2 b The intensity of visible light from the Sun reaching the upper parts of our atmosphere is about 1.4 kW m−2. The Sun has a radius of 7.0 108 m and is 1.5 1011 m from the Earth. Calculate: i the intensity of visible light emitted from the Sun’s surface ii the total power radiated by the Sun in the visible region of the electromagnetic [3] 3 2 3 [3] spectrum iii the intensity of light from the Sun at the planet Neptune. (Neptune is 4.5 1012 m from the Sun.) Q.No.5 [2] The circuit shows a non-inverting amplifier with an output voltage of 8.0 V. a State two differences between an op-amp used as an inverting amplifier and as a non-inverting amplifier. b Calculate the gain of the amplifier shown in the circuit. c Calculate the value of the input voltage Vin. d Calculate the value of the current in the 40 k resistor. e Determine the voltage across the 20 k resistor. 2 2 1 2 1 [2] [2] [1] [2]