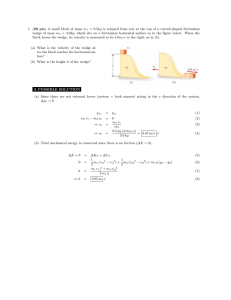
77777 J. Ipser PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2004
advertisement
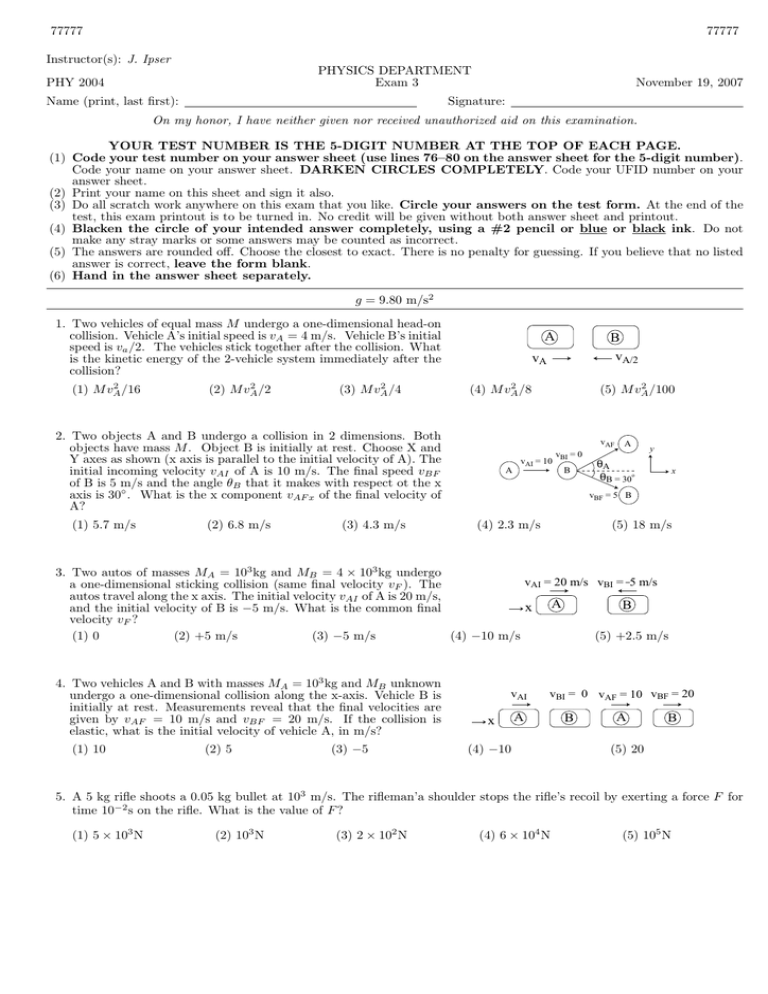
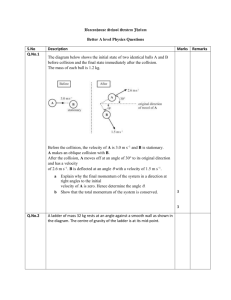
77777 77777 Instructor(s): J. Ipser PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Exam 3 PHY 2004 Name (print, last first): November 19, 2007 Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination. YOUR TEST NUMBER IS THE 5-DIGIT NUMBER AT THE TOP OF EACH PAGE. (1) Code your test number on your answer sheet (use lines 76–80 on the answer sheet for the 5-digit number). Code your name on your answer sheet. DARKEN CIRCLES COMPLETELY. Code your UFID number on your answer sheet. (2) Print your name on this sheet and sign it also. (3) Do all scratch work anywhere on this exam that you like. Circle your answers on the test form. At the end of the test, this exam printout is to be turned in. No credit will be given without both answer sheet and printout. (4) Blacken the circle of your intended answer completely, using a #2 pencil or blue or black ink. Do not make any stray marks or some answers may be counted as incorrect. (5) The answers are rounded off. Choose the closest to exact. There is no penalty for guessing. If you believe that no listed answer is correct, leave the form blank. (6) Hand in the answer sheet separately. g = 9.80 m/s2 1. Two vehicles of equal mass M undergo a one-dimensional head-on collision. Vehicle A’s initial speed is vA = 4 m/s. Vehicle B’s initial speed is va /2. The vehicles stick together after the collision. What is the kinetic energy of the 2-vehicle system immediately after the collision? 2 (1) M vA /16 2 (2) M vA /2 2 (3) M vA /4 A vA 2 (4) M vA /8 2. Two objects A and B undergo a collision in 2 dimensions. Both objects have mass M . Object B is initially at rest. Choose X and Y axes as shown (x axis is parallel to the initial velocity of A). The initial incoming velocity vAI of A is 10 m/s. The final speed vBF of B is 5 m/s and the angle θB that it makes with respect ot the x axis is 30◦ . What is the x component vAF x of the final velocity of A? (1) 5.7 m/s (2) 6.8 m/s (3) 4.3 m/s B vA/2 2 (5) M vA /100 vAF vAI = 10 A A vBI = 0 B y θA θB = 30o x vBF = 5 B (4) 2.3 m/s (5) 18 m/s 3. Two autos of masses MA = 103 kg and MB = 4 × 103 kg undergo vAI = 20 m/s vBI = 5 m/s a one-dimensional sticking collision (same final velocity vF ). The autos travel along the x axis. The initial velocity vAI of A is 20 m/s, B x A and the initial velocity of B is −5 m/s. What is the common final velocity vF ? (1) 0 (2) +5 m/s (3) −5 m/s (4) −10 m/s (5) +2.5 m/s 4. Two vehicles A and B with masses MA = 103 kg and MB unknown undergo a one-dimensional collision along the x-axis. Vehicle B is initially at rest. Measurements reveal that the final velocities are given by vAF = 10 m/s and vBF = 20 m/s. If the collision is elastic, what is the initial velocity of vehicle A, in m/s? (1) 10 (2) 5 (3) −5 vAI x vBI = 0 vAF = 10 vBF = 20 A (4) −10 B A B (5) 20 5. A 5 kg rifle shoots a 0.05 kg bullet at 103 m/s. The rifleman’a shoulder stops the rifle’s recoil by exerting a force F for time 10−2 s on the rifle. What is the value of F ? (1) 5 × 103 N (2) 103 N (3) 2 × 102 N (4) 6 × 104 N (5) 105 N 77777 77777 6. Two autos of the same mass undergo a two-dimensional perpendicular T-bone sticking collision as shown. The autos move together after the collision with common final velocity vF that makes an angle θ with respect to the x-axis. What is the value of θ? vF |vAI| = 20 m/s A y x θ |vBI| = 40 m/s MA = MB B (1) 65◦ (2) 5◦ (3) 15◦ 7. Three children of equal weight sit on a uniform seesaw of length 4 m. One child sits at each end, and the third child sits 1 m from the left end as shown. What is the value of D, the distance of the fulcrum (the support point about which the seesaw rotates) from the left end of the seesaw? Neglect the weight of the seesaw itself. (1) 5/3 m (2) 1/3 m (3) 2 m (4) 20◦ L=4m D 1m Ms (2) 50 N (3) 25 N Ms Ms (4) 4 m 8. A uniform ladder leans against a vertical wall at an angle of θ = 60◦ with respect to the horizontal as shown. A climber stands at the middle of the ladder, and the combined weight of the ladder and climber is 2000 N. The length of the ladder is 4 m. The force FW of the wall on the ladder is hroizontal and has magnitude 100 N. What is the magnitude of the horizontal force (force of friction) of the floor on the ladder? (1) 100 N (5) 25◦ (5) 3 m FW = 100 N θ (4) 150 N (5) 250 N