Fossils and Adaptations - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
advertisement

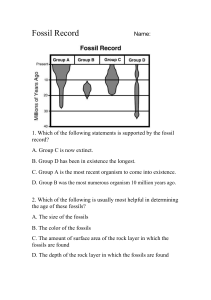
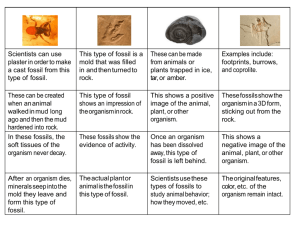
Essential Questions: Fossils and Adaptations 1. What qualifies an organism as extinct? All members of a species are no longer living. Endangered? Only a few members of a species are still living and are likely going to become extinct. 2. List natural vs. man-made causes of extinction. Natural CausesLack of sunlight/ Kills off producers (food source) Changes in climate Lowering of sea-level/Habitat destruction for Marine life Natural Disasters Flooding Plate Tectonics Predation Natural Selection/Lack of adaptation Disease Man-made CausesPollution Deforestation Habitat destruction Oil Spills Hunting Fishing Littering 3. Describe how each of the 6 types of fossils are formed. Mold Fossil- A cavity in the rock when the hard part decayed or dissolved. Cast Fossil– When sediment fills the cavity and produces a copy of the original object. Petrified/ Permineralized Fossil- Fossils in which the spaces inside are filled with minerals from groundwater. Preserved Fossil/ Original Remains – When original soft parts of organisms are preserved. Carbonized Fossil– A thin film of carbon residue if left, forming a silhouette of the original organism. Trace Fossil– Fossilized tracks and other evidence of activity of organisms. 4. What is the law of superposition? In undisturbed layers of rock, the oldest layers are found on the bottom and the youngest on the top. 5. Compare/Contrast relative and absolute ages of fossils. How do scientists determine each (methods of each)? Relative Age Absolute Age Age in comparison to Both used for dating The number of years the age of other rock and fossils. since the rock or things. organism formed. METHOD: Uses METHOD: Uses principle of amount of Carbon (in superposition. once-living things). 6. What defines a species? Groups of organisms that are similar and are able to reproduce. 7. Describe the process of natural selection v. Lamarck’s theory of evolution. Natural Selection (Accepted by scientists today): Darwin believed in variations among a species occurring naturally due to mutations. Organisms with variations best suited for their environment have a better chance of surviving and reproducing. The variation best suited (genetic trait) is passed on to the offspring. Lamarcks Theory of Acquired Traits (Abandoned Theory): Lamarck believed frequent and vigorous use of a body part led to a slight increase in its size (acquired trait). Ex: Muscles, wings, tails, necks, etc. That acquired trait is passed on to the offspring. 8. Compare/Contrast behavioral and structural adaptations. Explain the examples for each. Behavioral Structural Adaptations Adaptations Inherited, instinctive Both are traits which Affects the way an traits an organism help an organism organism looks (body does to survive. meet its basic needs parts) or the way it is and survive in its colored. environment. Ex: Migration, Ex: Camouflage, Carrying Young, Night Pouch, Sturdy beak, Vision, etc. etc.